
The globalization and rapid industrialization of any country is a function of availability of electricity in desired quality and quantity. Nigeria and Egypt are the most populated countries in West and North Africa respectively with incredible energy resources both renewable and non-renewable. Yet, the former is highly energy deficient when compared to the later. In recent time, the appropriate authorities have tried earnestly to reform the sector with the intent to improve the unpalatable situation through the liberalization of the vertically integrated structure of the power industries. In
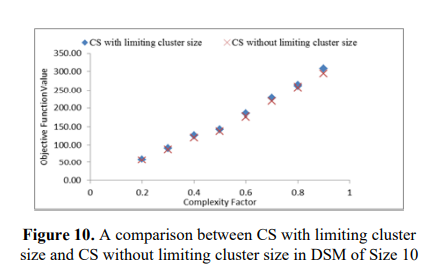
Modularity concepts play an important role in the process of developing new complex products. Modularization involves dividing a product into a set of modules - each of which consisting of a set of components - that are interdependent in the same cluster and independent between clusters. During this process, a product can be represented using a Design Structure Matrix (DSM). A DSM acts as a tool for system analysis to provide clear visualization of product elements. In addition, DSM, shows the interactions between these product elements. This paper aims to propose an efficient optimization
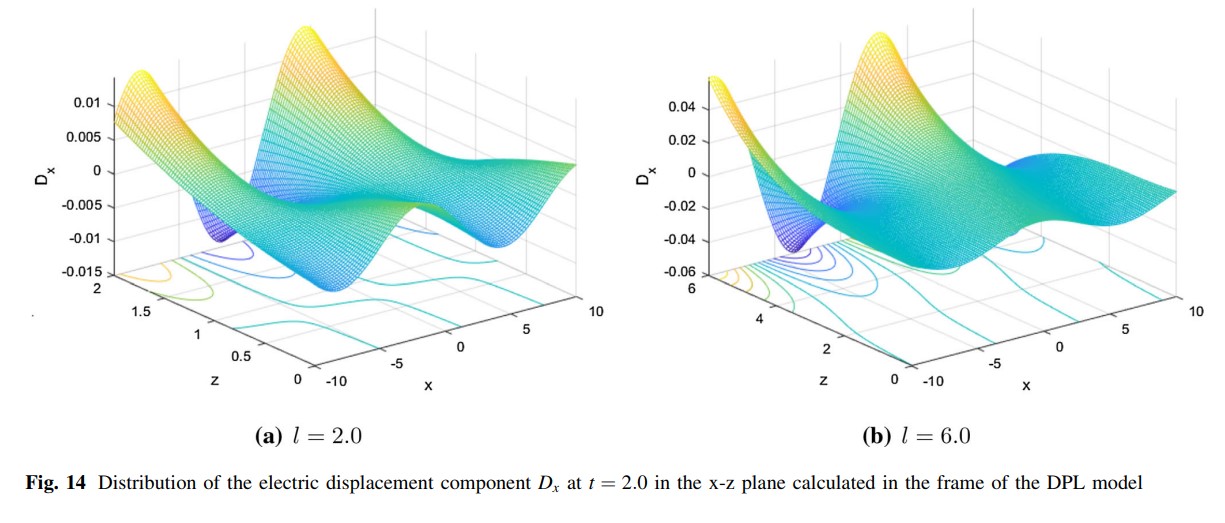
The system of equations of the generalized piezothermoelasticity in anisotropic medium with dual-phase-lag model is established. The exact expressions for displacement components, the temperature, stress components, electric potential and electric displacements are given in the physical domain and illustrated graphically. These expressions are calculated numerically for the problem. Comparisons are made with the results predicted by Lord–Shulman theory and dual-phase-lag model. It is shown that the results from both theories are close to each other for thin slabs, while they differ
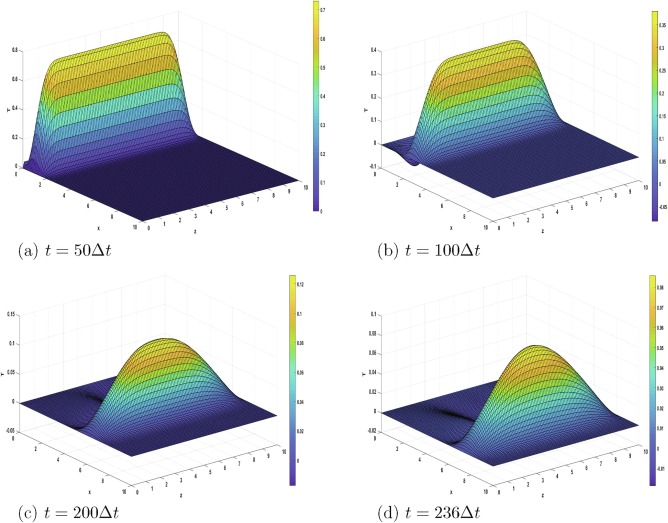
We present a numerical solution by finite differences to a linear, plane, initial-boundary-value problem of thermo-piezoelasticity in a quarter-space, within the dual-phase-lag model. Motion is excited by a one-period heat regime applied to one boundary of the medium. The relation between the two relaxation times is clarified in order to obtain wave-like solutions. An explicit, three-level numerical scheme is proposed to solve the problem under concrete initial and boundary conditions. The obtained results are discussed and three-dimensional plots of the unknown functions are presented. They

The aim of this empirical article is identifying and showing the key challenges and core problems faced by private universities with international affiliation, located in west Cairo, when applying online educational learning in the context of COVID-19. As well, it aims to assist in assembling the lessons learned to maximize the learning impact. a mixed-methods approach was used and it included: (1) observations complemented with five in-depth interviews with experienced faculty members and decision-makers (2) followed by a survey to comprehend the drivers of students’ satisfaction concerning
The unsteady flow field variations between healthy and diseased three-dimensional rigid posterior cerebral artery are numerically investigated. The Computational hemodynamic simulations have been known to provide valuable clinical information to researchers and surgeons that proved to be crucial for the assessment of medical risks, pre-surgical conditioning and treatment planning. The wall shear stress (WSS) and wall pressure are the most important hemodynamic variables, and both are used to give accurate description about the health status of the artery. The results showed that at the
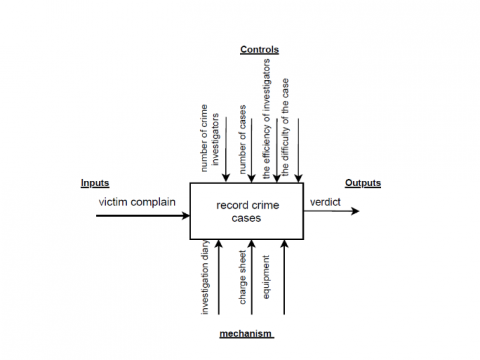
Crime records management is a system that helps police keep records of citizens’ complaints files, investigation evidence and processes. In addition, it helps police keep records of the criminals who have been arrested or who are to be arrested. This paper aims to model the Crime Record Management System (CRMS) using various Unified Modeling Language (UML) diagrams, to demonstrate an explicit visualization of the system. Also, showing the communication among different actors, and the sequence of activities and interactions. The perspective of modeling the CRMS is by covering four stages, which
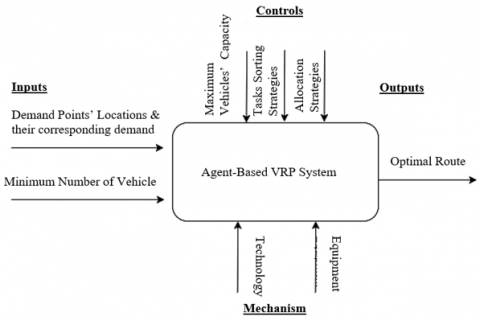
The Vehicle Routing Problem (VRP) is among the most studied optimization problems in the field of supply chain management. Typically, VRP requires dispatching a fleet of vehicles from a central depot to deliver demand to pre-determined spatially dispersed customers, with the objective of minimizing the total routing cost, and the constraint of not exceeding vehicles' capacities. Agent Based Modelling (ABM) assists industries in the use of technology to support their decision-making process. This paper proposes a model of an Agent Based Vehicle Routing Problem System. The system under study is
Molten salt has been realized as a potential candidate as a clean non-pollutant heat transfer fluid for concentrated solar power plants because of its high heat capacity and broad ranges of operational temperatures. In this study, the Nusselt number of the commercially known Hitec molten salt is numerically assessed, using k-ϵ model turbulence model with non-equilibrium wall functions, for the ranges of 104-105 Reynolds number and 104-105 W/m2 uniform surface heat flux. Moreover, the present work is compared against previously published work with success. The proposed numerical model provides
A new Finite element model for HVAC applications is introduced. The model incorporates flow turbulence, buoyancy effects and unsteadiness. Also, the model accommodates complicated boundaries due to complex geometries and perforated tiles. Experimental validation is provided and extensive results for flow and temperature contours are presented. Temporal and spatial resolution prove that the model can capture important HVAC features as thermal comfort, buoyancy induced flow, complex boundaries. © 2020 IEEE.