
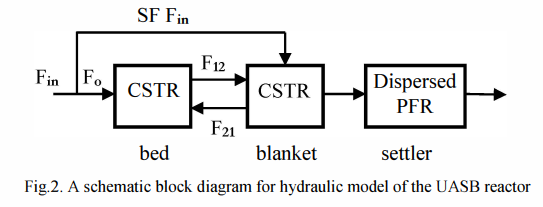
This paper introduces a dynamic model to adequately describe an Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB) reactor. Some available models of a UASB reactor are discussed in order to modify their drawbacks and propose a new improved model with less complexity and more reliability. The developed model is a combination of two recent models introduced in Sweden. According to this model, a UASB rector is divided hydraulically into three compartments with integration of a kinetic model. Simulations are performed to investigate the validity of the developed model which indicates a good agreement with
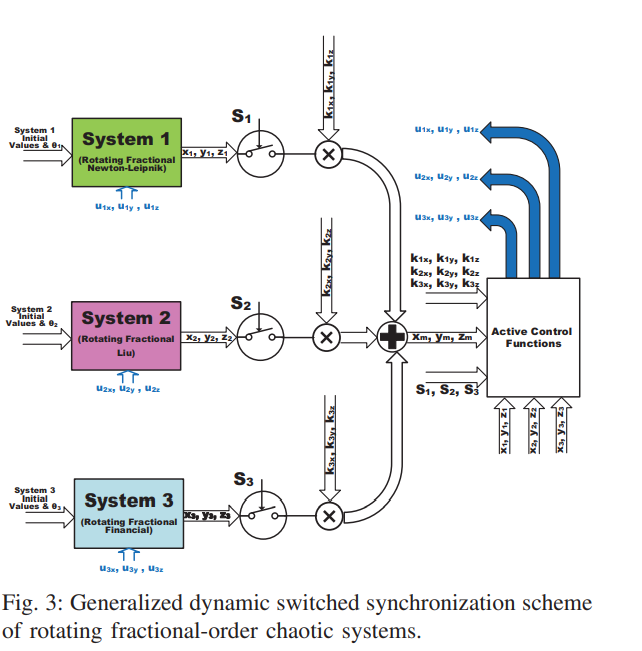
This paper proposes generalized controllable strange attractors through dynamic rotation of fractional-order chaotic systems. Dynamic rotation angle enables the generation of multi-scroll and multi-wing attractors from single and double-scroll ones. The rotating systems are integrated with a generalized dynamic switched synchronization scheme. Dynamic control switches determine whether each system plays the role of master or slave. Based on dynamic scaling factors, the master can be one system or a combination of several ones with new strange attractors. The rotating fractional-order systems
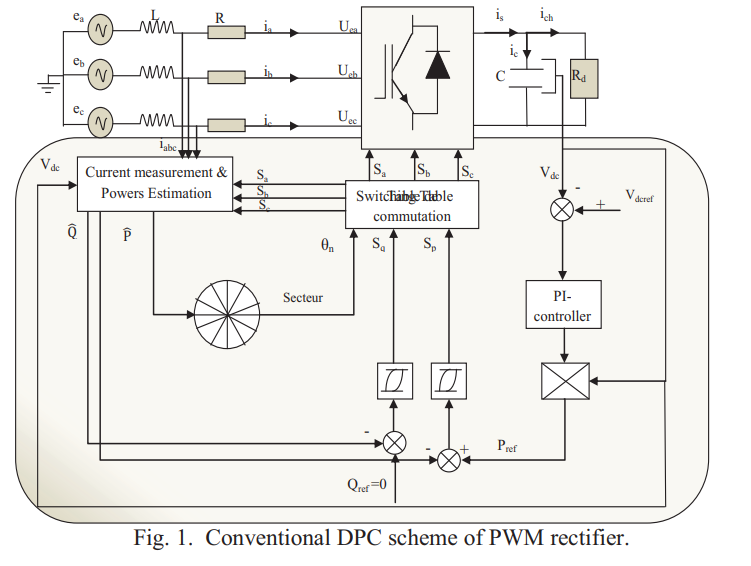
This article proposes a new simple scheme for direct power control of a PWM rectifier without a switch table and voltage sensor. The selection of the switching state of the converter is based on the transition of a Petri net, using the instantaneous active and reactive power tracking errors and the angular position of the network line voltage estimated as variables of Controller input based on Petri nets. Simulation and experimental results demonstrated better performance and verified the validity of the new command with the Petri nets applied to the bridge rectifier connected to the
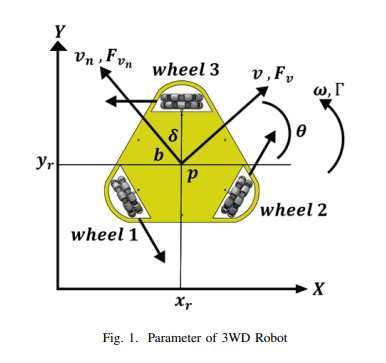
Omni mobile robots are one of the mobile robots that interact with humans in many areas where it is needed to be collaborative and accurate. Committing robotics with artificial intelligence-based controllers became nowadays mandatory for more association of these robots with distinct environments. This paper proposes the distinction of the 3WD Omni Vision feedback model between Simscape and actual information to obtain a surmised model. Study applying some artificial control procedures on this model for path planning and speed control as the artificial neural system and PSO optimization
The active control of flow around an airfoil through morphing is numerically investigated. The lock-in phenomenon was predicted while using a fixed grid. Galerkin/Least-Squares Finite Element Method was used to simulate incompressible flow over an airfoil with leading edge morphing at a Reynolds number, Re = 5000, and angle of attack, α = 6°. The numerical simulation was carried out using the in-house FORTRAN code. The code was validated with the literature by simulating the flow over an oscillating cylinder. The paperwork implemented a locally oscillating surface on the airfoil with a
Detection of lane boundaries is the primary role for monitoring an autonomous car's trajectory. Three lane identification methodologies are explored in this paper with experimental illustration: Edge detection, Hough transformation, and Birds eye view. The next step after obtaining the boundary points is to add a regulation rule to effectively trigger the regulation of steering and velocity to the motors. A comparative analysis is made between different steering controllers like PID or by using PID with a pure pursuit controller for the Lane Keeping Assist (LKA) system. A camera that sends
In recent years, the massive growth in the scale of data is being a key factor in the needed data processing approaches. The efficiency of the algorithms of knowledge extraction depends significantly on the quality of the raw data, which can be improved by employing preprocessing techniques. In the field of energy consumption, the forecasting of power cost needed plays a vital role in determining the expected profit. To achieve a forecasting with higher accuracy, it is needed to deal with the large amount of data associated with power plants. It is shown in the literature that the use of
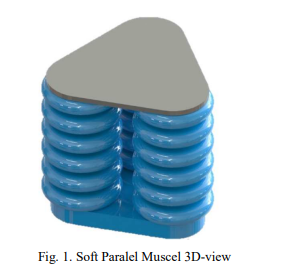
Recently, soft robotics represents a new era of advanced robotics systems. Based on the flexible nature of soft robots, they are more adequate to have safe interaction with humans and handle complex or delicate objects. Due to the nature of soft robotics, there is a crucial need to propose new designs, fabrication, and control systems suitable for the flexibility nature. In this research project, a novel three parallel soft muscle actuator is proposed. The proposed design and analytical models for predicting actuation behavior are based on a set of design parameters. First, the actuator
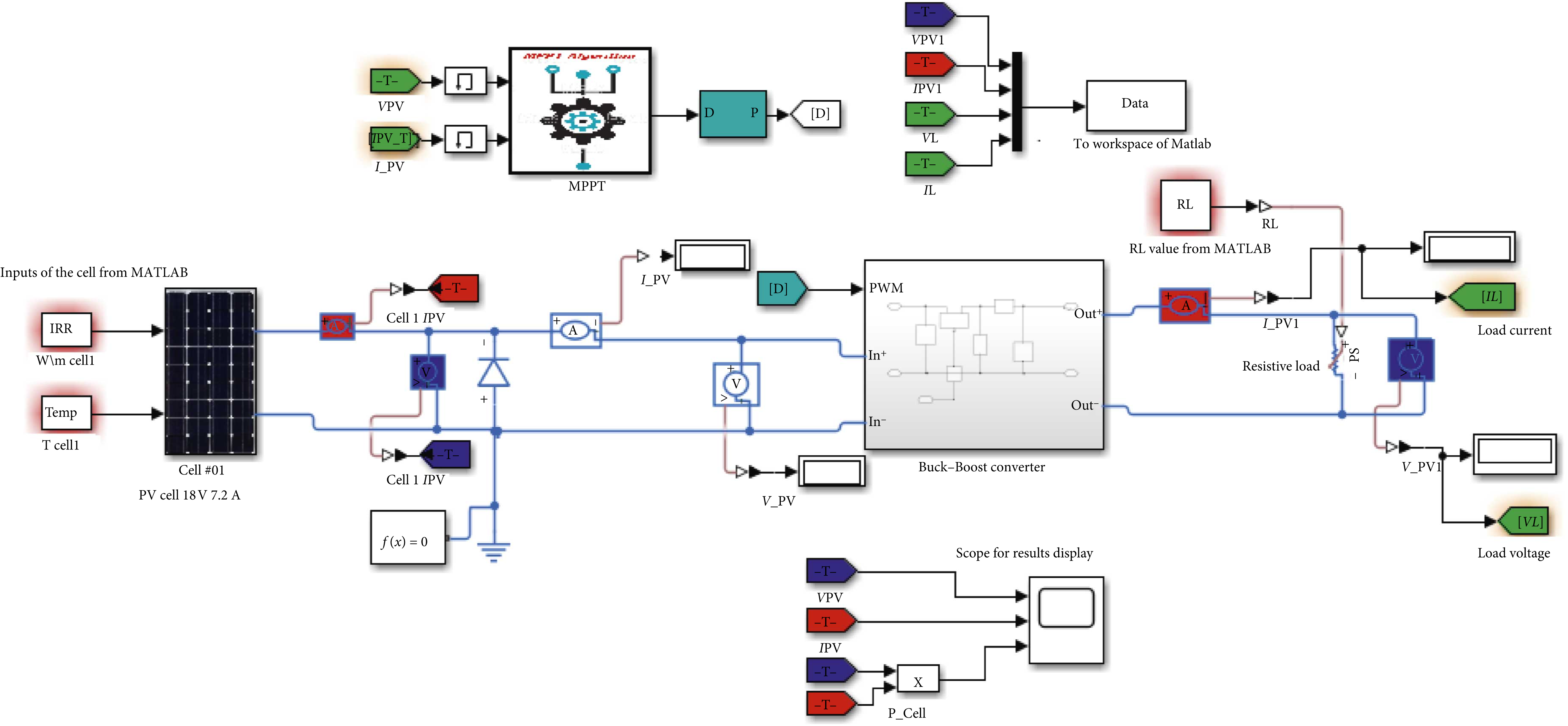
This paper seeks to improve the photovoltaic (PV) system efficiency using metaheuristic, optimized fractional order incremental conductance (FO-INC) control. The proposed FO-INC controls the output voltage of the PV arrays to obtain maximum power point tracking (MPPT). Due to its simplicity and efficiency, the incremental conductance MPPT (INC-MPPT) is one of the most popular algorithms used in the PV scheme. However, owing to the nonlinearity and fractional order (FO) nature of both PV and DC-DC converters, the conventional INC algorithm provides a trade-off between monitoring velocity and
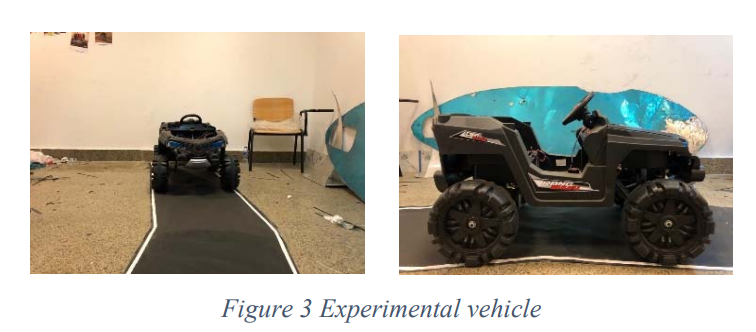
In this paper we implement and evaluate two ways of controlling the steering angle of an autonomous vehicle, PID control with manual tuning followed by gradient descent algorithm tuning-which is able to enhance the performance through self-adjusting the controller parameters-and using supervised machine learning through the end-to-end deep learning for self-driving car which implement Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) to predict the steering angle for a given instance of a track. The verification testing went through two phases: software simulation using python for first run testing and C++