
This paper proposes Parallelized Linear Time-Variant Acceleration Coefficients and Inertial Weight of Particle Swarm Optimization algorithm (PLTVACIW-PSO). Its designed has introduced the benefits of Parallel computing into the combined power of TVAC (Time-Variant Acceleration Coefficients) and IW (Inertial Weight). Proposed algorithm has been tested against linear, non-linear, traditional, and multiswarm based optimization algorithms. An experimental study is performed in two stages to assess the proposed PLTVACIW-PSO. Phase I uses 12 recognized Standard Benchmarks methods to evaluate the
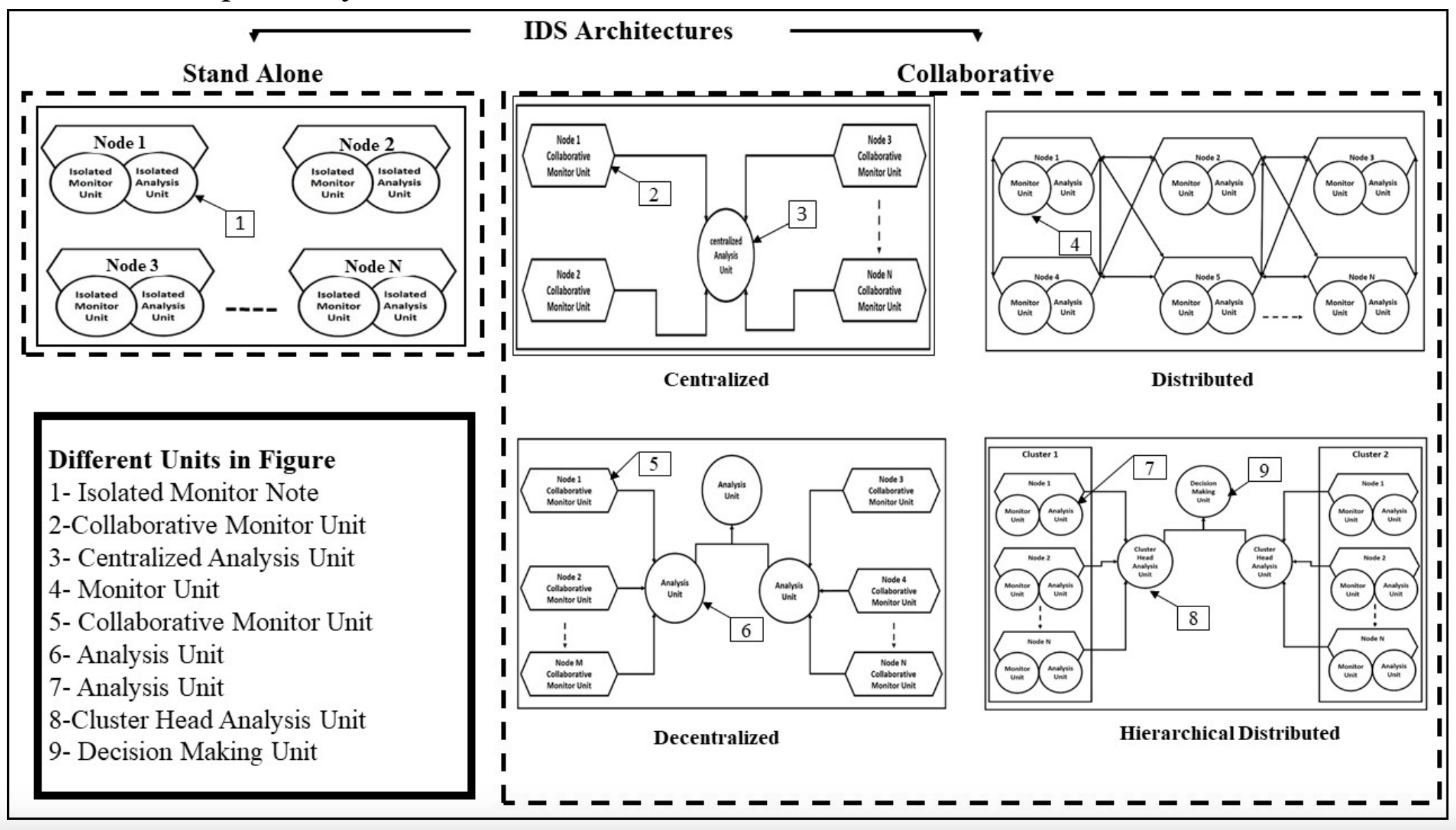
Ad hoc networks have been through extensive research in the last decade. Even with their desirable characteristics, major issues related to their security need to be considered. Various security solutions have been proposed to reduce the risks of malicious actions. They mainly focus on key management, authentication, secure localization, and aggregation techniques. These techniques have been proposed to secure wireless communications but they can only deal with external threats. Therefore, they are considered the first line of defense. Intrusion detection systems are always required to
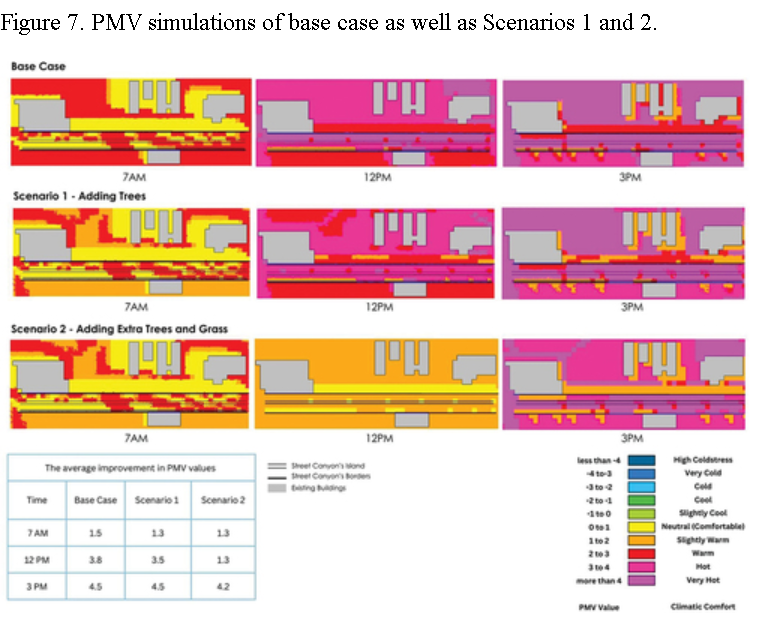
Climate change is a major issue all over the world which has a great impact on global warming especially in countries with hot arid climates like Egypt. With rapid urbanization, streets in Greater Cairo and new cities are mostly car-oriented, which increases the Urban Heat Island(UHI) and, hence, affects the overall outdoor thermal comfort. Looking at the urban development in recent years, almost 10 new private universities are in operation in Cairo’s new cities together with a number of large recreational projects where they lack the appropriate vegetation surrounding their borders which in

[No abstract available]
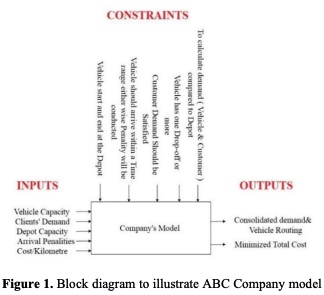
Route optimization is tactically important for companies that must fulfill the demands of different customers with fleet of vehicles, considering multiple factors like: The cost of the resources (vehicles) involved and the operating costs of the entire process. As a case study, a third-party logistics service provider, ABC Company, is introduced to implement optimization on. Furthermore, ABC Company's problem is defined as route optimization and load consolidation problems that will be solved as heterogeneous vehicle routing problem with soft time windows (HVRPSTW). In this paper's case
The number of words should not exceed 350. A three-dimensional numerical model for HVAC induced flow is presented. The nonlinear set of buoyancy driven incompressible flow equations, augmented with those of energy and k-ϵ turbulence model is solved. Various relevant are discussed. These challenges include avoiding expensive commercial packages, modelling complex boundaries, and capturing near wall gradients. Adaptive time stepping is employed to optimize computational effort. Threedimensional simulation requirements are addressed using parallel computations. Twodimensional and three
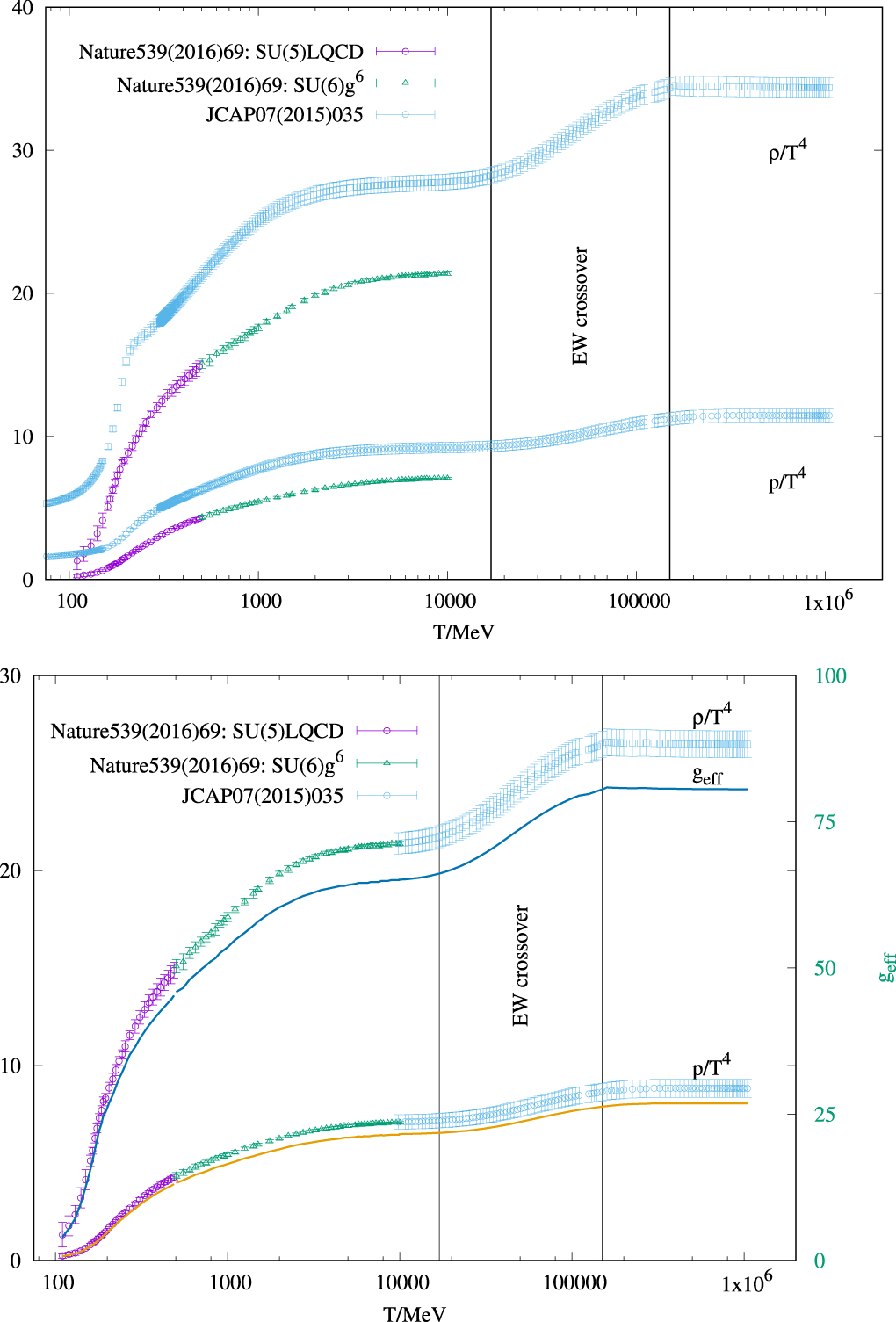
Various thermodynamic quantities for baryon-free matter are calculated by combining the most reliable non-perturbative and perturbative calculations, especially the most recent ones including as many quark flavors as possible. We extend these calculations by including other degrees of freedom (dof), such as photons, neutrinos, leptons, electroweak particles and Higgs bosons, which allows us to consider temperatures up to the TeV-scale. The calculations show that similar to QCD, the EW phase transition is also a crossover. We have found that while the equation of state for the hadronic matter
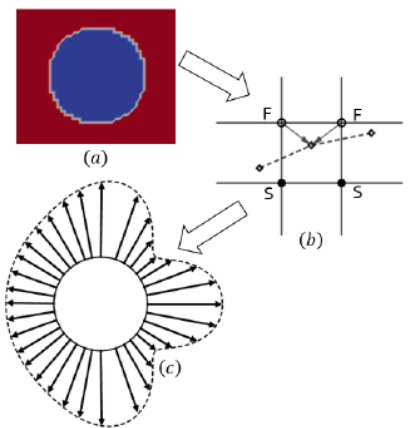
This work introduces an immersed boundary method for two-dimensional simulation of incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. The method uses flow field mapping on the immersed boundary and performs a contour integration to calculate immersed boundary forces. This takes into account the relative location of the immersed boundary inside the background grid elements by using inverse distance weights, and also considers the curvature of the immersed boundary edges. The governing equations of the fluid mechanics are solved using a Galerkin-Least squares finite element formulation. The model is
In this work, we are proposing a silicon (Si) based concentric tube broadband absorber. The proposed broadband absorber is composed of consecutive concentric tubes of intrinsic Si and doped-Si (D-Si) layers. The structure exhibits a broadband performance within a wide range of mid-IR wavelength spectrum extending from 3 to 7 µm with an absorption peak that varies between 0.88 and 0.97 in the case of S-polarized incident light. We report that light coupling to the proposed concentric tube metamaterial absorber structure over a broad wavelength range is a result of exhibiting multiple resonance
This paper presents a real-time vision framework that detects and tracks vehicles from stationary camera. It can be used to calculate statistical information such as average traffic speed and flow as well as in surveillance tasks. The framework consists of three main stages. Vehicles are first detected using Haar-like features. In the second phase, an adaptive appearance-based model is built to dynamically keep track of the detected vehicles. This model is also used in the third phase of data association to fuse the detection and tracking results. The use of detection results to update the