
Mechanical Design
Decision Analysis for the Influence of Incorporating Waste Materials on Green Concrete Properties
Concrete industry is challenged by sustainability and technical concerns. Sustainability includes minimization of raw material usage, energy consumption, and emission of greenhouse gases, while technical concerns comprise the enhancement of mechanical properties and durability such as compressive strength, resistance to chloride, acids, and elevated temperatures. Therefore, recycling of industrial waste in manufacturing of green concrete has become a robust viable alternative to disposal, due to the limited natural resources and raw materials which contribute to sustainable construction
Sand-Biosolids Mixture Characterization and Potential
Biosolid-sludge of sewage treatment plants was mixed with clean coarse sands to reduce soil permeability and assess the potential of utilizing such mix for several geotechnical applications. One of the applications was to develop a soil mix with low permeability for use in roadway embankments subjected to torrents from sudden heavy rain in desert areas. The main purpose was to address a sustainable and eco-friendly mix to be used as an additional protection to the current boulder lining for such embankments. In this study, biosolid sludge was mixed with medium dense sand using percentages
Prediction model for the compressive strength of green concrete using cement kiln dust and fly ash
Integrating artificial intelligence and green concrete in the construction industry is a challenge that can help to move towards sustainable construction. Therefore, this research aims to predict the compressive strength of green concrete that includes a ratio of cement kiln dust (CKD) and fly ash (FA), then recommend the optimum sustainable mixture design. The artificial neural network (ANN) and multiple linear regression techniques are used to build prediction models and statistics using MATLAB and IBM SPSS software. The input parameters are based on 156 data points of concrete components
Analysis of compressive strength of glass fiber reinforced concrete using design of experiments
Although there are many studies on Fiber Reinforced Concrete (FRC), determining the factors having the highest impact on compressive strength of fiber reinforced concrete has little attention. In this paper a full factorial L16OA design is used to analyze the early compressive strength of Glass Fiber Reinforced Concrete (GFRC). This is to find the factors tat are significantly affecting the early compressive strength of concrete. The affecting factors were identified through Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) and main effects plots considering the interactions between the factors and the compressive
Flexural behavior of recycled aggregate concrete beams strengthened with carbon fiber reinforced polymer
Using recycled aggregate in the construction of reinforced concrete (RC) buildings has become essential to reduce the waste produced from demolished buildings. In this paper, the influence of using carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP) in strengthening of RC beams with recycled coarse aggregate (RCA), as a partial/full replacement for natural coarse aggregate (NCA), was experimentally investigated. Twelve RC beams with various RCA ratios (0%, 30%, 70%, and 100%) were prepared and tested under four-point loading. Four beams without CFRP were tested till failure while the other eight beams were
Optimizing the coagulation/flocculation process for the treatment of slaughterhouse and meat processing wastewater: experimental studies and pilot-scale proposal
The slaughterhouse industry generates substantial wastewater rich in proteins, lipids, fibers, and carbohydrates. This study integrates experimental investigations into artificial neural network (ANN) optimization and commerce design studies for treating slaughterhouse and meat processing wastewater (SMW). Batch coagulation/flocculation experiments identified optimal conditions for three coagulants: Ferric Chloride (FeCl3·6H2O), Poly Aluminum Chloride (PAC), and Aluminum Sulfate Al2(SO4)3, aiming for optimum removal of chemical oxygen demand (COD), total suspended solids (TSS), and total
Numerical modeling of sheathed screw connections in CFS shear walls
Screw connections within sheathed cold formed steel (CFS) shear walls experience in-plane shear that acts in a parallel direction to the sheathing's free edge. Yet, many investigations focused on connections where shear loads applied perpendicular to the sheathing's free edge. Although the modes of failure in perpendicular testing are comparable to those ones in CFS shear walls, the load deformation behavior and strength might not be precisely predicted. Thus, the purpose of this study is to create a finite element (FE) model to simulate screw connections under parallel loading. The element
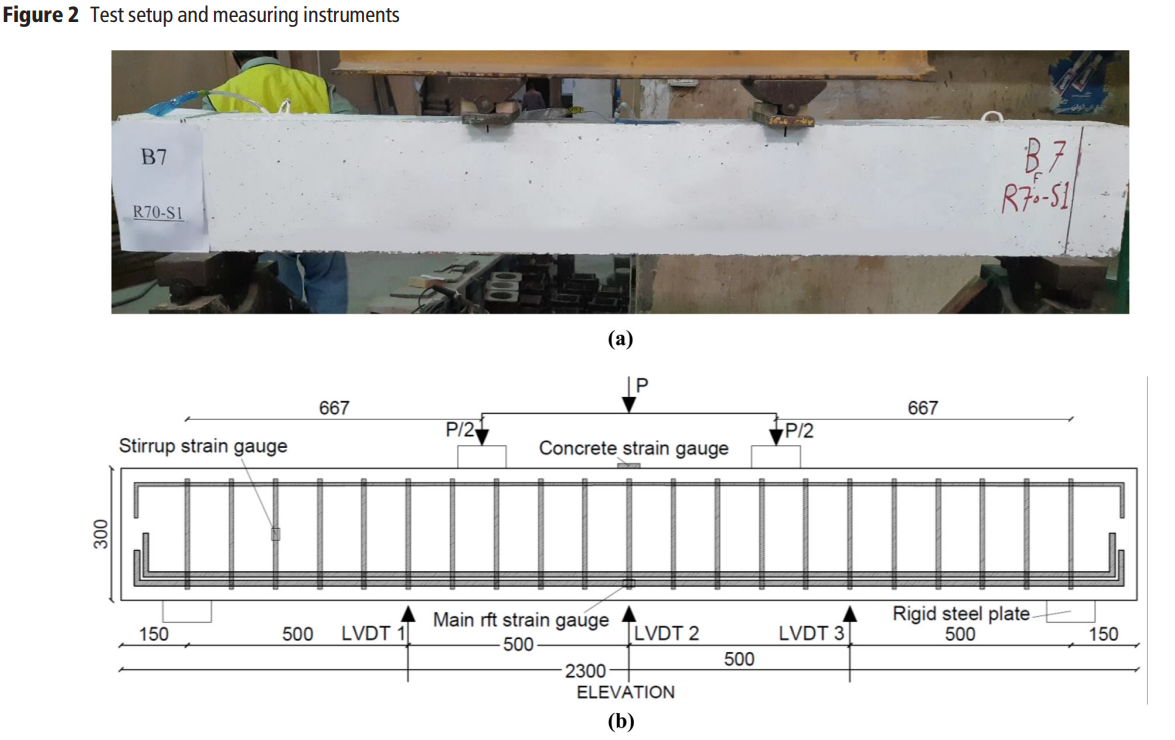
Experimental and numerical investigation of preloaded recycled concrete beams strengthened with CFRP
Purpose: The use of recycled coarse aggregate in concrete structures promotes environmental sustainability; however, performance of these structures might be negatively impacted when it is used as a replacement to traditional aggregate. This paper aims to simulate recycled concrete beams strengthened with carbon fiber-reinforced polymer (CFRP), to advance the modeling and use of recycled concrete structures. Design/methodology/approach: To investigate the performance of beams with recycled coarse aggregate concrete (RCAC), finite element models (FEMs) were developed to simulate 12 preloaded
Impact assessment of implementing virtual reality in the Egyptian construction industry
Construction projects in Egypt are becoming more complex as the need for mega projects increases to meet the Egyptian 2030 vision. Meanwhile, the advancement of Virtual Reality technologies is apparent in the 21st century. This paper aims to assess the impact of implementing virtual reality in the Egyptian construction industry. An application using Fuzor VDC and Oculus Quest 2 has been developed elaborating the technology's use. The application includes 4D simulation and meetings in virtual reality. Furthermore, a survey is conducted to measure the impact of implementation on key project
Organizational learning via gamification for employer brand management
Purpose: This paper aims to deepen our understanding of how serious games could be used for learning in organizations to empower brand performance and image sustaining competitive advantage from a Resource Based View (RBV) perspective and to examine the practical implications of the evolving technologies for employers. Design/methodology/approach: The research methodology is based on a qualitative approach adopting the case study research method (Yin, 2003). Data were collected through fifteen semi-structured interviews (a total of twelve hours) with the involved departments (particularly