
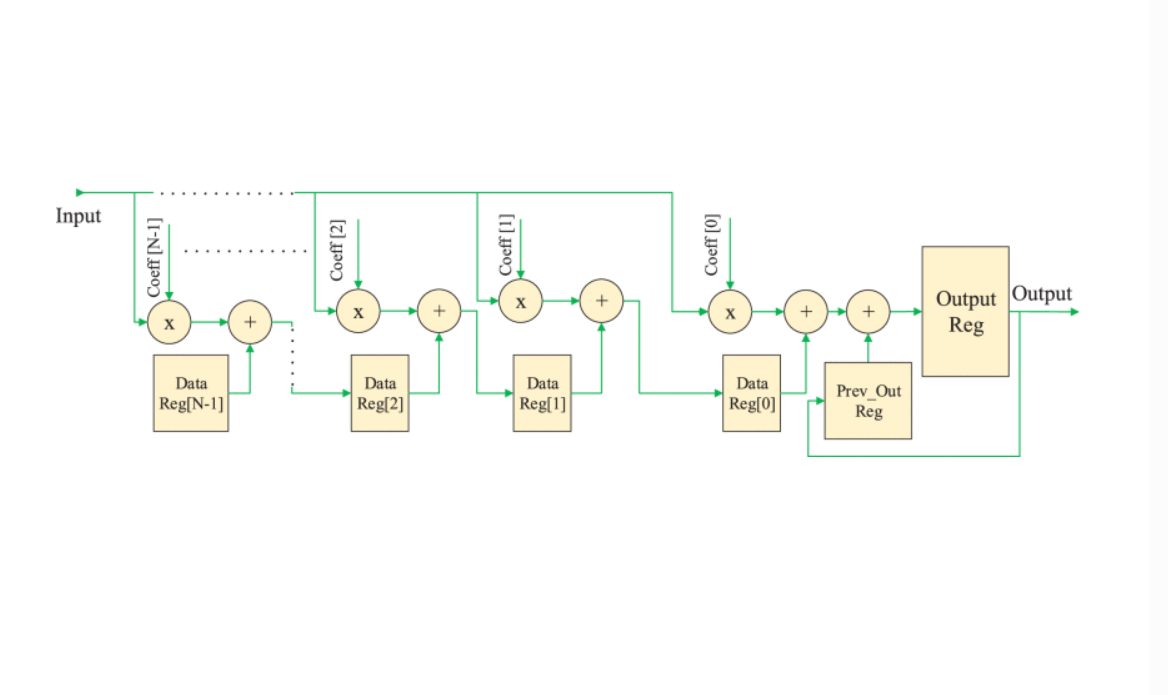
Hardware accelerators outperform CPUs in terms of performance by parallelizing the algorithm architecture and using the device’s programmable resources. FPGA is a type of hardware accelerator that excels not only in performance but also in energy efficiency. So, it provides a suitable platform for implementing complicated fractional-order systems. This paper proposes a novel phase-based optimization method to implement fractional operators using FIR and IIR filters. We also compare five fractional operator implementation methods on FPGA regarding resource utilization, execution time, power
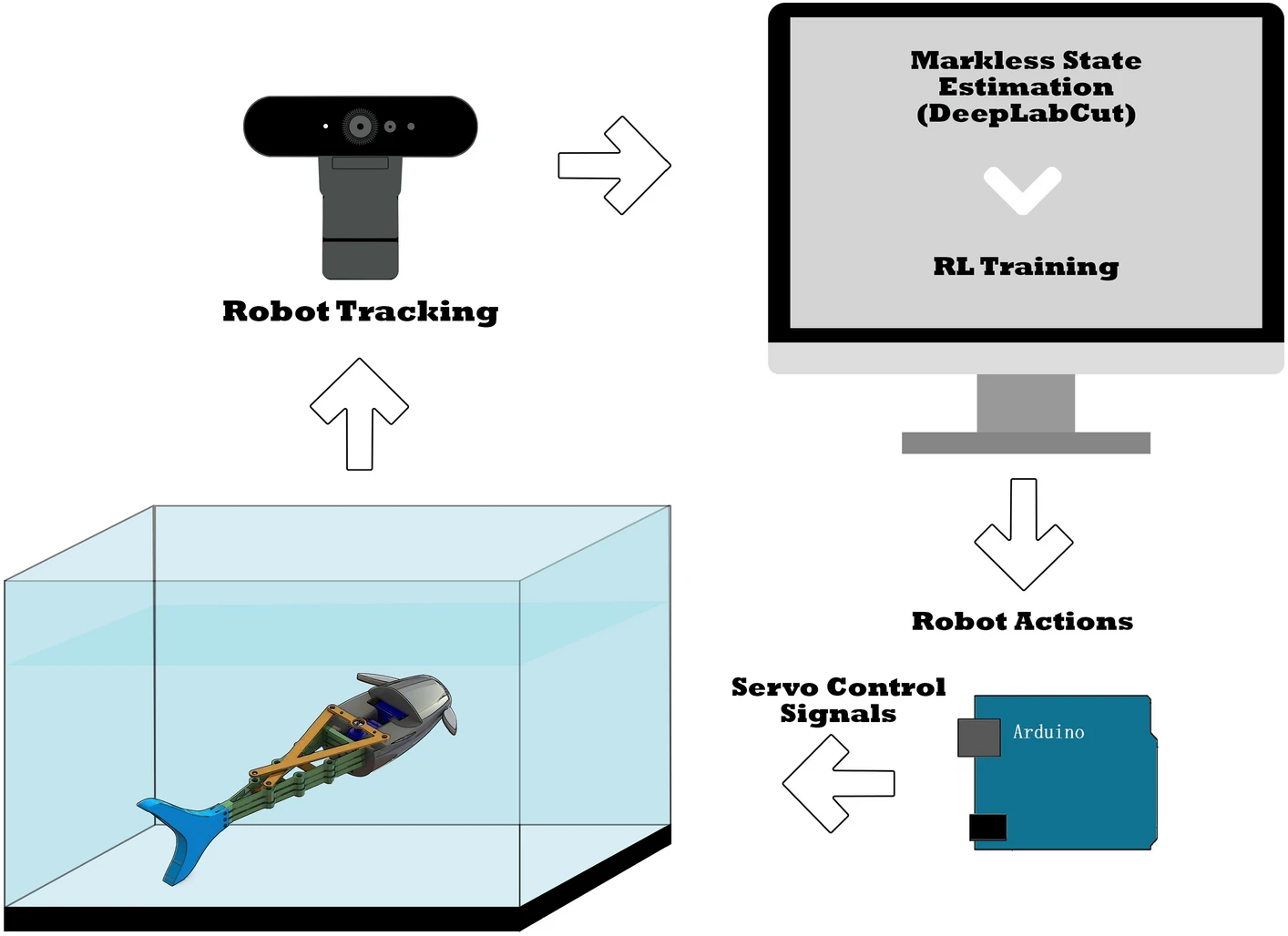
Soft robots provide a pathway to accurately mimic biological creatures and be integrated into their environment with minimal invasion or disruption to their ecosystem. These robots made from soft deforming materials possess structural properties and behaviors similar to the bodies and organs of living creatures. However, they are difficult to develop in terms of integrated actuation and sensing, accurate modeling, and precise control. This article presents a soft-rigid hybrid robotic fish inspired by the Pangasius fish. The robot employs a flexible fin ray tail structure driven by a servo

Fractional Order Systems: Optimization, Control, Circuit Realizations and Applications consists of 21 contributed chapters by subject experts. Chapters offer practical solutions and novel methods for recent research problems in the multidisciplinary applications of fractional order systems, such as FPGA, circuits, memristors, control algorithms, photovoltaic systems, robot manipulators, oscillators, etc. This book is ideal for researchers working in the modeling and applications of both continuous-time and discrete-time dynamics and chaotic systems. Researchers from academia and industry who
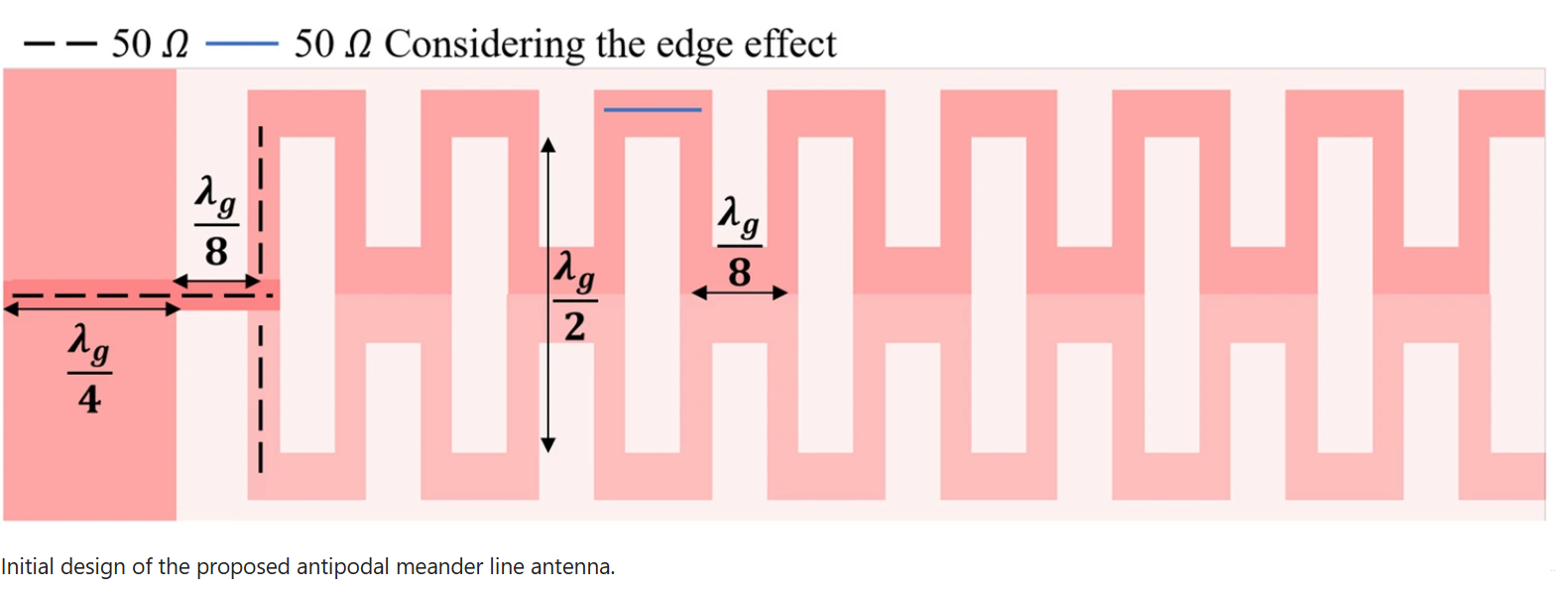
This paper introduces a planar antipodal meander line antenna fabricated using RO3003 substrate. The proposed antenna is designed to radiate in the end-fire direction, achieving a maximum measured gain of 10.43 dBi within its working bandwidth, which ranges from 2.24 GHz to 2.7 GHz, covering long-range WLAN/WiMAX applications. A systematic procedure is adopted in the design process to prove its tunability to cover other application requirements in terms of gain and bandwidth. The proposed design steps show that the bandwidth and the gain can independently be controlled by adjusting specific

Plasmonic Photovoltaics (PVs) are an effective method for increasing optical absorption by adding metallic nanoparticles to the photovoltaic active layer. The role of these nanoparticles is confining the incident light near them in the PV cell, resulting in thin film PVs of enhanced efficiency. Therefore, different materials and new NPs shapes are used for this purpose. In this research, a step pyramid is introduced as a novel structure for nanoparticles for enhancing plasmonic PVs by embedding an array of the proposed step pyramid nanoparticles within the PV cell. Therefore, the extinction

This paper introduces an efficient prediction algorithm tailored for advanced and high efficiency video coding, encompassing both H.264 and H.265. The proposed approach aims at replacing the standard intra prediction methodology by employing a streamlined prediction mode, which significantly reduces computational overhead and system complexity while eliminating the requirement for mode decision. By leveraging block comparison criteria, the designed method combines neighboring blocks in a linear fashion to accurately represent the target block. Extensive comparisons are conducted with the H.264
We investigate a one-dimensional restriction of a nonlinear model of thermo-electroelasticity in extended thermodynamics and in the quasi-electrostatic regime (see Ghaleb et al. in Int J Eng Sci 119:29–39, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijengsci.2017.06.010). An additional dependence of the thermal conductivity and the thermal relaxation time on temperature and heat flux is introduced. The aim of the present work is to assess the effect of some quadratic nonlinear couplings between the mechanical, thermal and electric fields. Such couplings are known to have a crucial effect on the stability
A 2D first order linear system of partial differential equations of plane strain thermoelasticity within the frame of extended thermodynamics is presented and analyzed. The system is composed of the equations of classical thermoelasticity in which displacements are replaced with velocities, complemented with Cattaneo evolution equation for heat flux. For a particular choice of the characteristic quantities and for positive thermal conductivity, it is shown that this system may be cast in a form that is symmetric t-hyperbolic without further recurrence to entropy principle. While hyperbolicity
[No abstract available]

Mathematical Techniques of Fractional Order Systems illustrates advances in linear and nonlinear fractional-order systems relating to many interdisciplinary applications, including biomedical, control, circuits, electromagnetics and security. The book covers the mathematical background and literature survey of fractional-order calculus and generalized fractional-order circuit theorems from different perspectives in design, analysis and realizations, nonlinear fractional-order circuits and systems, the fractional-order memristive circuits and systems in design, analysis, emulators, simulation