
Artificial Intelligence
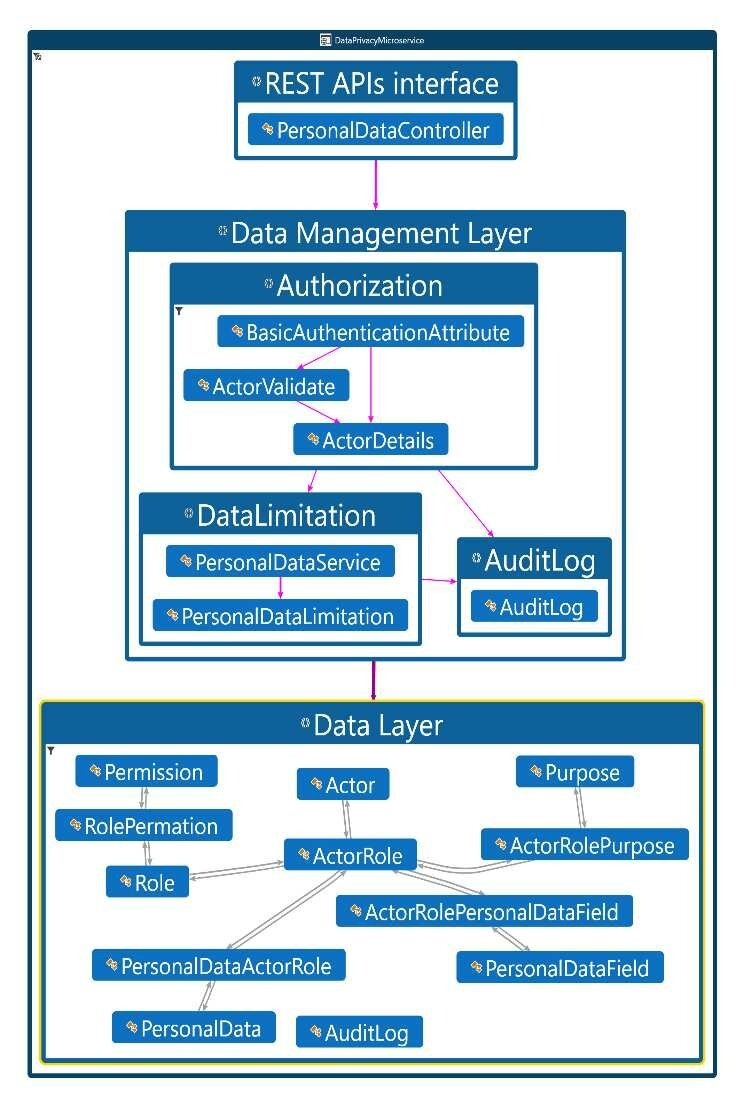
Privacy by Design: A Microservices-Based Software Architecture Approach
Data privacy regulations have increased significantly recently. As a result, privacy by design (PbD) has become a critical consideration for enterprises that handle personal data. PbD is no longer a plain principle. Rather than that, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) addresses PbD as a required legal requirement for controllers who may face fines for non-compliance with the GDPR. In this paper, we propose a practical solution, 'PbD Microservice,' that can help organizations to achieve privacy regulatory compliance. We will focus on GDPR, one of the most important regulations that
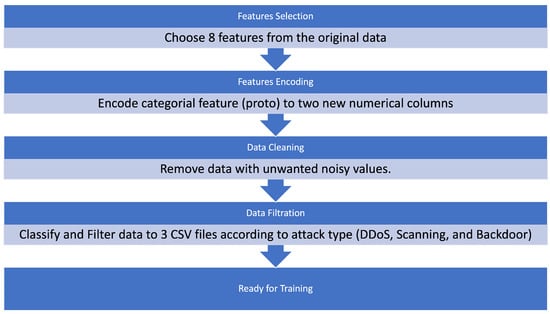
Anomaly Detection of Zero-Day Attacks Based on CNN and Regularization Techniques
The rapid development of cyberattacks in the field of the Internet of things (IoT) introduces new security challenges regarding zero-day attacks. Intrusion-detection systems (IDS) are usually trained on specific attacks to protect the IoT application, but the attacks that are yet unknown for IDS (i.e., zero-day attacks) still represent challenges and concerns regarding users’ data privacy and security in those applications. Anomaly-detection methods usually depend on machine learning (ML)-based methods. Under the ML umbrella are classical ML-based methods, which are known to have low
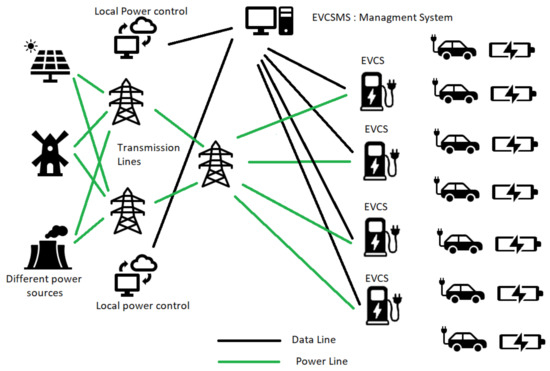
Intrusion Detection for Electric Vehicle Charging Systems (EVCS)
The market for Electric Vehicles (EVs) has expanded tremendously as seen in the recent Conference of the Parties 27 (COP27) held at Sharm El Sheikh, Egypt in November 2022. This needs the creation of an ecosystem that is user-friendly and secure. Internet-connected Electric Vehicle Charging Stations (EVCSs) provide a rich user experience and add-on services. Eventually, the EVCSs are connected to a management system, which is the Electric Vehicle Charging Station Management System (EVCSMS). Attacking the EVCS ecosystem remotely via cyberattacks is rising at the same rate as physical attacks
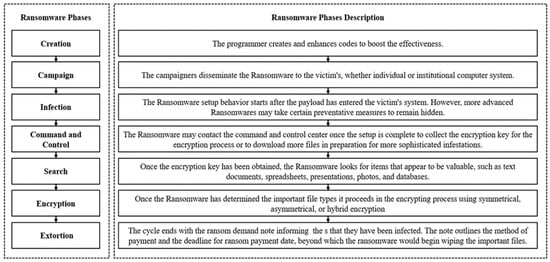
A New Scheme for Ransomware Classification and Clustering Using Static Features
Ransomware is a strain of malware that disables access to the user’s resources after infiltrating a victim’s system. Ransomware is one of the most dangerous malware organizations face by blocking data access or publishing private data over the internet. The major challenge of any entity is how to decrypt the files encrypted by ransomware. Ransomware’s binary analysis can provide a means to characterize the relationships between different features used by ransomware families to track the ransomware encryption mechanism routine. In this paper, we compare the different ransomware detection
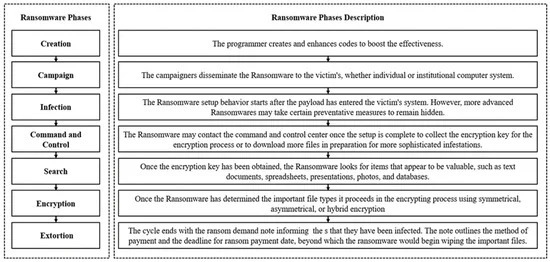
Ransomware Clustering and Classification using Similarity Matrix
Ransomwares are amongst the most dangerous malwares that face and affect any business by restricting data access or leaking sensitive information over the internet. Ransomwares binary analysis can provide a way to define the relationships between distinct features employed by ransomware families. Malware classification and clustering systems offer an effective malware indexing with search functionalities, similarity checking, samples classification and clustering. Most studies focus on the static and dynamic features extraction, machine and deep learning or visualization techniques used to
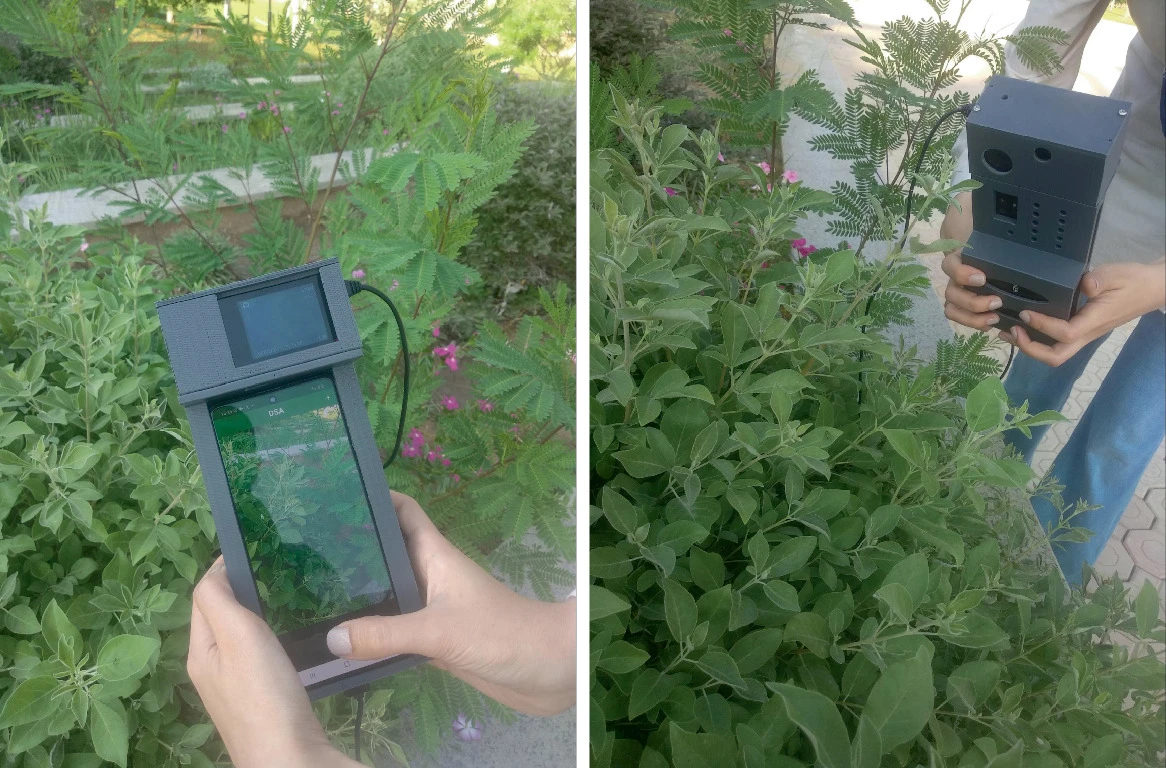

Rice Plant Disease Detection and Diagnosis Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks and Multispectral Imaging
Rice is considered a strategic crop in Egypt as it is regularly consumed in the Egyptian people’s diet. Even though Egypt is the highest rice producer in Africa with a share of 6 million tons per year [5], it still imports rice to satisfy its local needs due to production loss, especially due to rice disease. Rice blast disease is responsible for 30% loss in rice production worldwide [9]. Therefore, it is crucial to target limiting yield damage by detecting rice crops diseases in its early stages. This paper introduces a public multispectral and RGB images dataset and a deep learning pipeline
Autonomous Traffic-Aware and QoS-Constrained Capacity Cell Shutdown for Green Mobile Networks
Energy efficiency of Radio Access Networks (RANs) is increasingly becoming a global strategic priority for Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) and governments to attain sustainable and uninterruptible network services. In this work, we propose an autonomous Machine Learning (ML)-based framework to maximize RAN energy efficiency via underutilized radio resource shutdown while maintaining an adequate network capacity with a preset Quality-Of-Service (QoS) level. This is achieved by dynamically switching radio resources on and off according to service demand. Training on a live network dataset and

A distributed real-time recommender system for big data streams
Recommender Systems (RS) play a crucial role in our lives. As users become continuously connected to the internet, they are less tolerant of obsolete recommendations made by an RS. Online RS has to address three requirements: continuous training and recommendation, handling concept drifts, and the ability to scale. Streaming RS proposed in the literature address the first two requirements only. That is because they run the training process on a single machine. To tackle the third challenge, we propose a Splitting and Replication mechanism for distributed streaming RS. Our mechanism is inspired

A Framework for Democratizing Open-Source Decision-Making using Decentralized Autonomous Organization
The open Source Software (OSS) became the backbone of the most heavily used technologies, including operating systems, cloud computing, AI, Blockchain, Bigdata Systems, IoT, and many more. Although the OSS individual contributors are the primary power for developing the OSS projects, they do not contribute to the OSS project's decisionmaking as much as their contributions in the OSS Projects development. This paper proposes a framework to democratize the OSS Project's decision-making using a blockchain-related technology called Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO). Using DAO
Anomaly-Based Intrusion Detection for Blackhole Attack Mitigation
In the contemporary environment, mobile ad hoc networks (MANETs) are becoming necessary. They are absolutely vital in a variety of situations where setting up a network quickly is required; however, this is infeasible due to low resources. Ad hoc networks have many applications: education, on the front lines of battle, rescue missions, etc. These networks are distinguished by high mobility and constrained compute, storage, and energy capabilities. As a result of a lack of infrastructure, they do not use communication tools related to infrastructure. Instead, these networks rely on one another