
Artificial Intelligence
Automated Deep Learning Pipeline for Accurate Segmentation of Aortic Lumen and Branches in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: A Two-Step Approach
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA) is a serious medical condition characterized by the abnormal enlargement of the abdominal aorta. If left untreated, AAA can have life-threatening consequences. Accurate segmentation of the aorta in Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) images plays a vital role in treatment planning for AAA. However, manual and semi-automatic segmentation methods suffer from limitations in terms of time and accuracy. This study presents a deep learning pipeline that aims to fully automate the precise and efficient segmentation of the aorta and its branches within CTA images. A
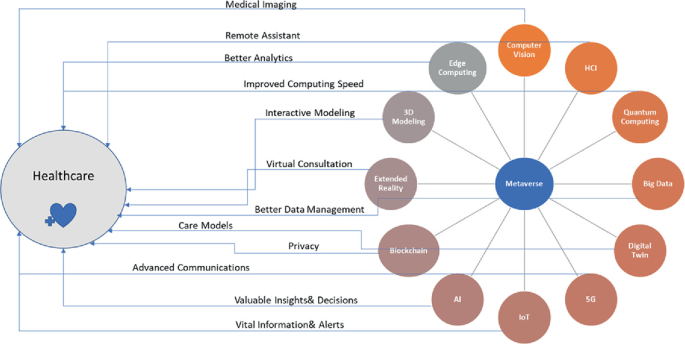
The Implication of Metaverse in the Traditional Medical Environment and Healthcare Sector: Applications and Challenges
There are a lot of studies that have been presenting the idea of the metaverse since 2021. It's the term for the next-generation mobile computing platform, which will be extensively utilized in the future and refers to the internet accessed through VR and AR glasses. The range of illnesses people face today is different from what it was decades ago. Cancer, COPD, diabetes, heart disease, and asthma are just few of the many non-communicable diseases that pose a serious risk to human health in the modern world. As a result, efforts toward chronic disease prevention and management need to be
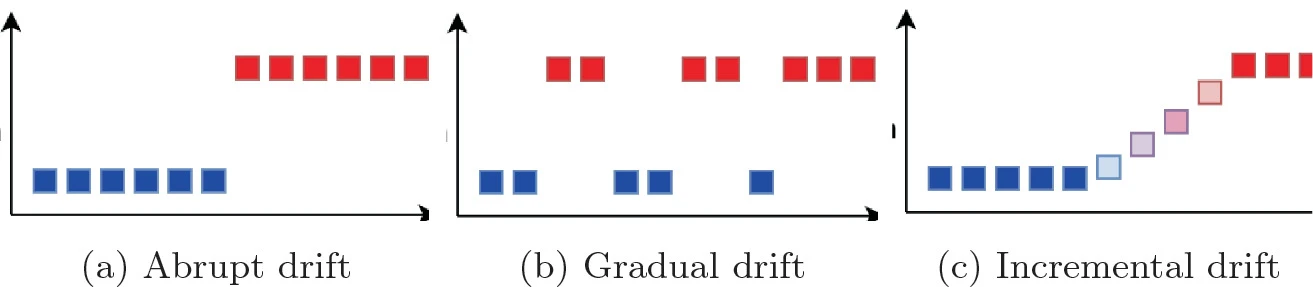
Benchmarking Concept Drift Detectors for Online Machine Learning
Concept drift detection is an essential step to maintain the accuracy of online machine learning. The main task is to detect changes in data distribution that might cause changes in the decision boundaries for a classification algorithm. Upon drift detection, the classification algorithm may reset its model or concurrently grow a new learning model. Over the past fifteen years, several drift detection methods have been proposed. Most of these methods have been implemented within the Massive Online Analysis (MOA). Moreover, a couple of studies have compared the drift detectors. However, such
Optimizing truss members using Machine Learning
This paper aims to produce an optimization methodology for a truss for minimal stress on critical sections using Machine learning models. This is done by varying the height and length of the truss span and applying live loads on different joints. The optimization of the truss is done through feed forward with back propagation artificial neural network model, The optimized truss is modelled and analysed using finite element and stiffness software. The paper presents the results and identifies the best dimensions for the truss design with a safety factor. © The Authors.
Sludge as an Alternative to Cement for Canal Lining
Plain concrete is used for water canal lining due to its low permeability to reduce water losses due to seepage. However, cement manufacture has a negative environmental impact as it produces large amount of CO2 emissions in addition to high energy consumption. In this study, bio-sludge of sewage plants was used an alternative for cement, mixed with sand and crushed stone, and used as an alternative to plan concrete for canal lining. An experimental testing program was designed based on percentages of sludge and soil equal to 2.5%, 5%, and 10% by weight. For each sludge mix, properties were
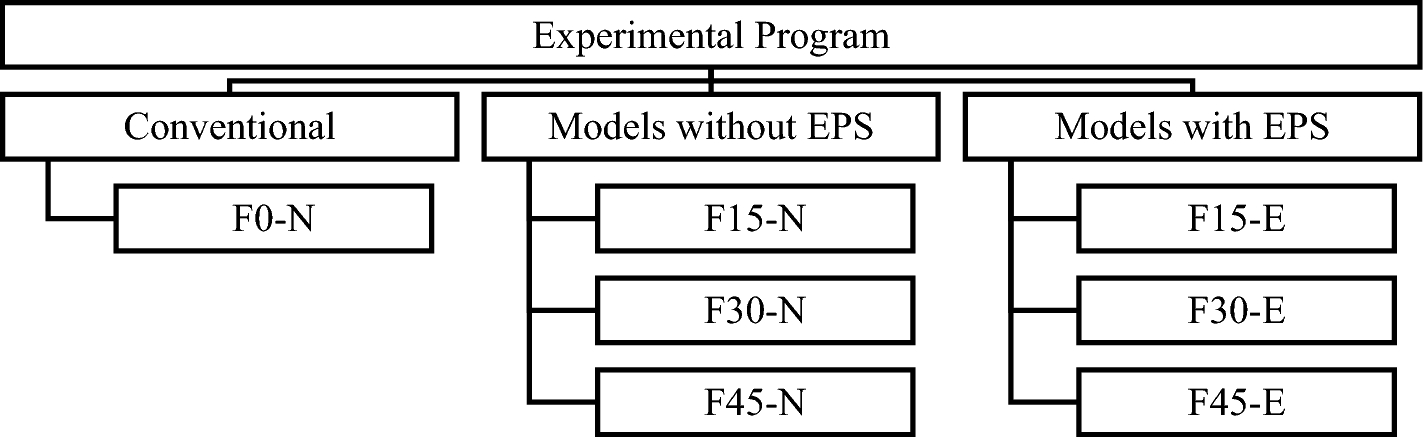
Shell folded footings using different angles and EPS cavity filling: experimental study
Shell folded footings have drawn the interest of researchers for decades as an alternative to typical flat isolated footings because folded footings can reduce the needed amount of reinforced concrete in addition to enhancing the overall geotechnical performance of the supporting soil medium. The main setback of utilizing such folded footings is the relatively complex geometry of the bottom cavity, which requires proper compaction of the soil used to fill that cavity. Current geosynthetic materials such as geofoam or expanded polystyrene (EPS) proved efficiency in many geotechnical
Decision Analysis for the Influence of Incorporating Waste Materials on Green Concrete Properties
Concrete industry is challenged by sustainability and technical concerns. Sustainability includes minimization of raw material usage, energy consumption, and emission of greenhouse gases, while technical concerns comprise the enhancement of mechanical properties and durability such as compressive strength, resistance to chloride, acids, and elevated temperatures. Therefore, recycling of industrial waste in manufacturing of green concrete has become a robust viable alternative to disposal, due to the limited natural resources and raw materials which contribute to sustainable construction
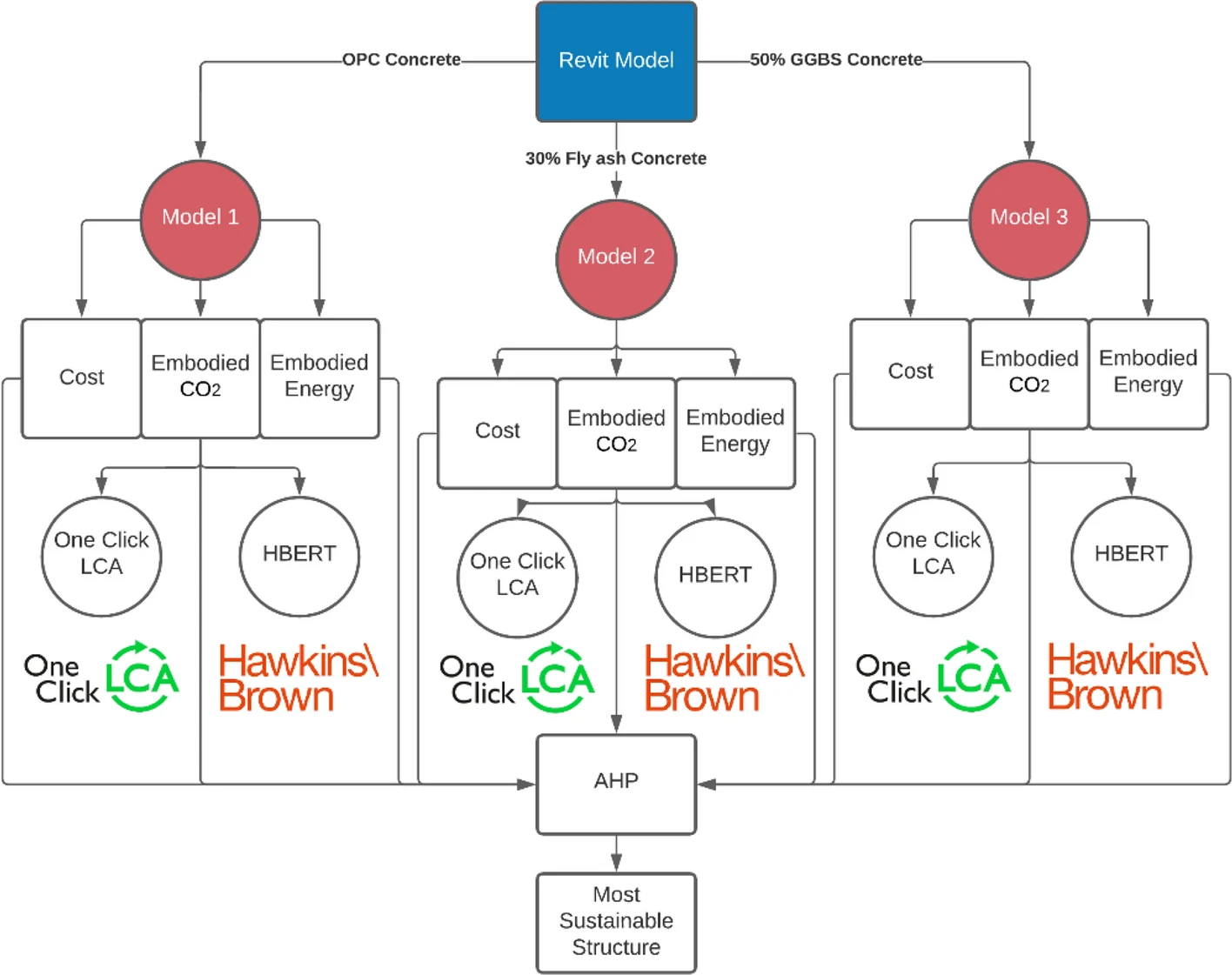
Sustainable assessment of concrete structures using BIM–LCA–AHP integrated approach
Recently, sustainability has become one of the most critical goals to be accomplished in the construction industry to mitigate its environmental impacts, energy consumption, waste, and cost. Therefore, this research aims to assess the sustainability of concrete structures using the Building Information Modeling and Life Cycle Assessment (BIM–LCA) approach. It can aid to rank and select the type of concrete based on sustainability criteria including CO2 emissions, embodied energy, and cost using analytical hierarchy process (AHP) method. One-Click LCA tool has been used for the recognition of
Ethiopian Dam Optimum Hydraulic Operating Conditions to Reduce Unfavorable Impacts on Downstream Countries
As noted by several researchers, the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD) on the Blue Nile River is expected to have unfavorable consequences for downstream countries like Egypt and Sudan. To limit GERD's negative effects on downstream countries, its operation should be secure, and its upstream water level should be ideal. However, none of the studies carried out the ideal operating scenarios from the perspective of controlling the number of gate openings. Accordingly, this study evaluates the optimal operating scenarios of the GERD and its impact on downstream countries by adopting a
Sand-Biosolids Mixture Characterization and Potential
Biosolid-sludge of sewage treatment plants was mixed with clean coarse sands to reduce soil permeability and assess the potential of utilizing such mix for several geotechnical applications. One of the applications was to develop a soil mix with low permeability for use in roadway embankments subjected to torrents from sudden heavy rain in desert areas. The main purpose was to address a sustainable and eco-friendly mix to be used as an additional protection to the current boulder lining for such embankments. In this study, biosolid sludge was mixed with medium dense sand using percentages