
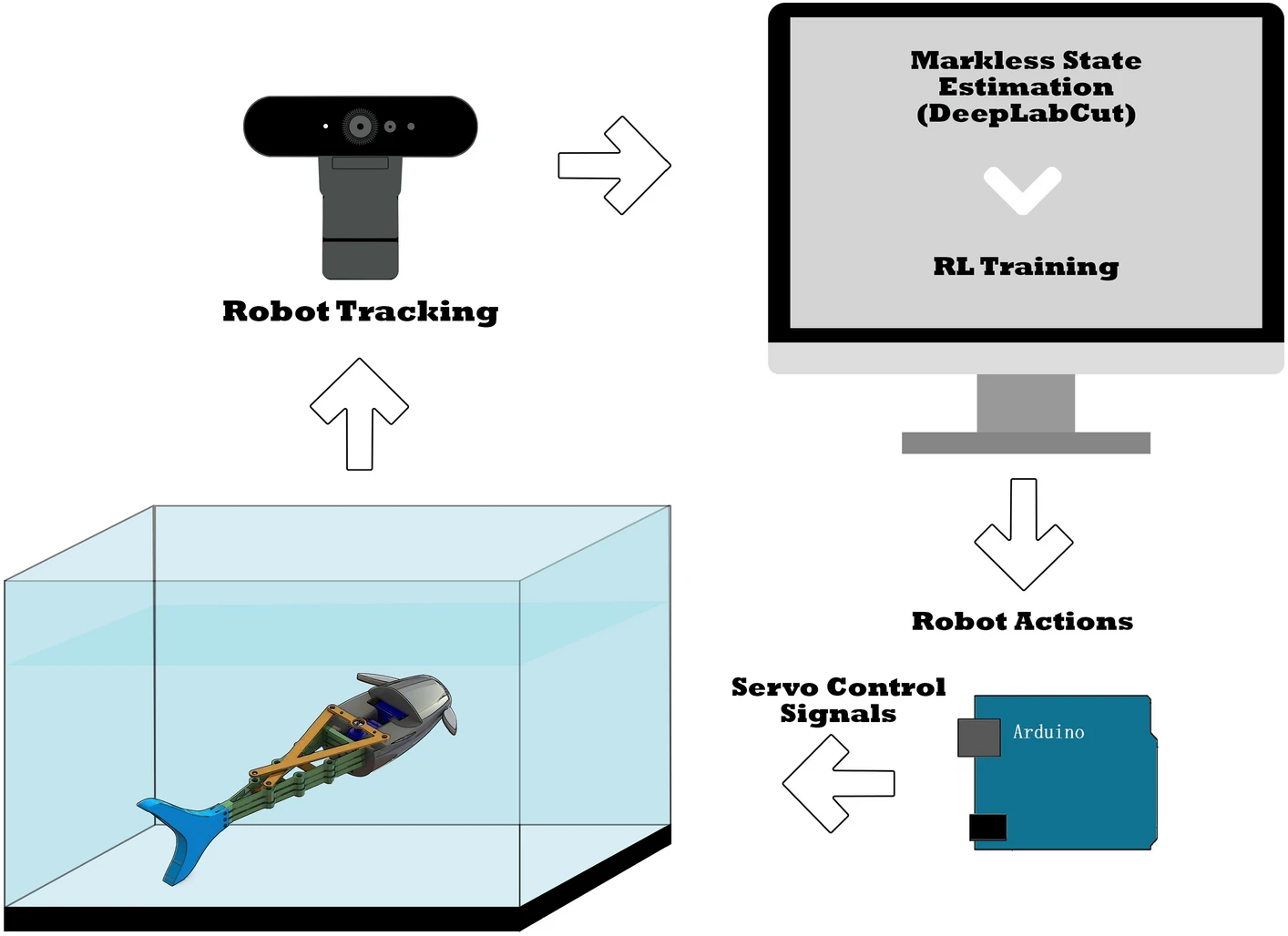
Soft robots provide a pathway to accurately mimic biological creatures and be integrated into their environment with minimal invasion or disruption to their ecosystem. These robots made from soft deforming materials possess structural properties and behaviors similar to the bodies and organs of living creatures. However, they are difficult to develop in terms of integrated actuation and sensing, accurate modeling, and precise control. This article presents a soft-rigid hybrid robotic fish inspired by the Pangasius fish. The robot employs a flexible fin ray tail structure driven by a servo
This paper introduces a memristor based ternary adder, which is an essential building block for any arithmetic ternary operations. The proposed ternary adder circuit tries to achieve the theoretical advantages of the ternary system, increase the density and decrease the processing time by using the memristor properties such as its hysteresis and nanotechnology. The general block diagram of the proposed circuit is illustrated based on memristors and its operation has been validated via different examples using PSPICE where simulation results show a great match. © 2013 IEEE.
Area and power consumption are the main challenges in Network on Chip (NoC). Indeed, First Input First Output (FIFO) memory is the key element in NoC. Increasing the FIFO depth, produces an increas in the performance of NoC but at the cost of area and power consumption. This paper proposes a new hybrid CMOS-Memristor based FIFO architecture that consumes low power and has a small size compared to the conventional CMOS-based FIFOs. The predicted area is approximately equal to the half of that wasted in conventional FIFOs. The implementation of FIFO controller module is implemented using HDL

Fractional Order Systems: Optimization, Control, Circuit Realizations and Applications consists of 21 contributed chapters by subject experts. Chapters offer practical solutions and novel methods for recent research problems in the multidisciplinary applications of fractional order systems, such as FPGA, circuits, memristors, control algorithms, photovoltaic systems, robot manipulators, oscillators, etc. This book is ideal for researchers working in the modeling and applications of both continuous-time and discrete-time dynamics and chaotic systems. Researchers from academia and industry who

This paper presents a high-efficiency bow-tie antenna for ambient RF energy harvesting at the 2.4 GHz band. Moreover, a rectifier circuit that converts the AC into DC is proposed. The antenna is fed via a CPW transmission line where a quarter wavelength transformer is inserted to match the slot bow-tie with the 50-ohm transmission line. The structure is simulated using CST software, and results are validated using HFSS. The antenna's directivity, efficiency, and bandwidth are 6.63 dBi, 89.9 %, and 0.946 GHz respectively, as simulated using CST. The antenna is fabricated on a single-layer
In this work different control schemes are proposed to study the problem of generalized synchronization (GS) between integer-order and fractional order chaotic systems with different dimensions. Based on Lyapunov stability theory of integer-order differential systems, fractional Lyapunov-based approach and nonlinear controllers, different criterions are derived to achieve generalized synchronization. The effectiveness of the proposed control schemes are verified by numerical examples and computer simulations. © Springer International Publishing AG 2017.
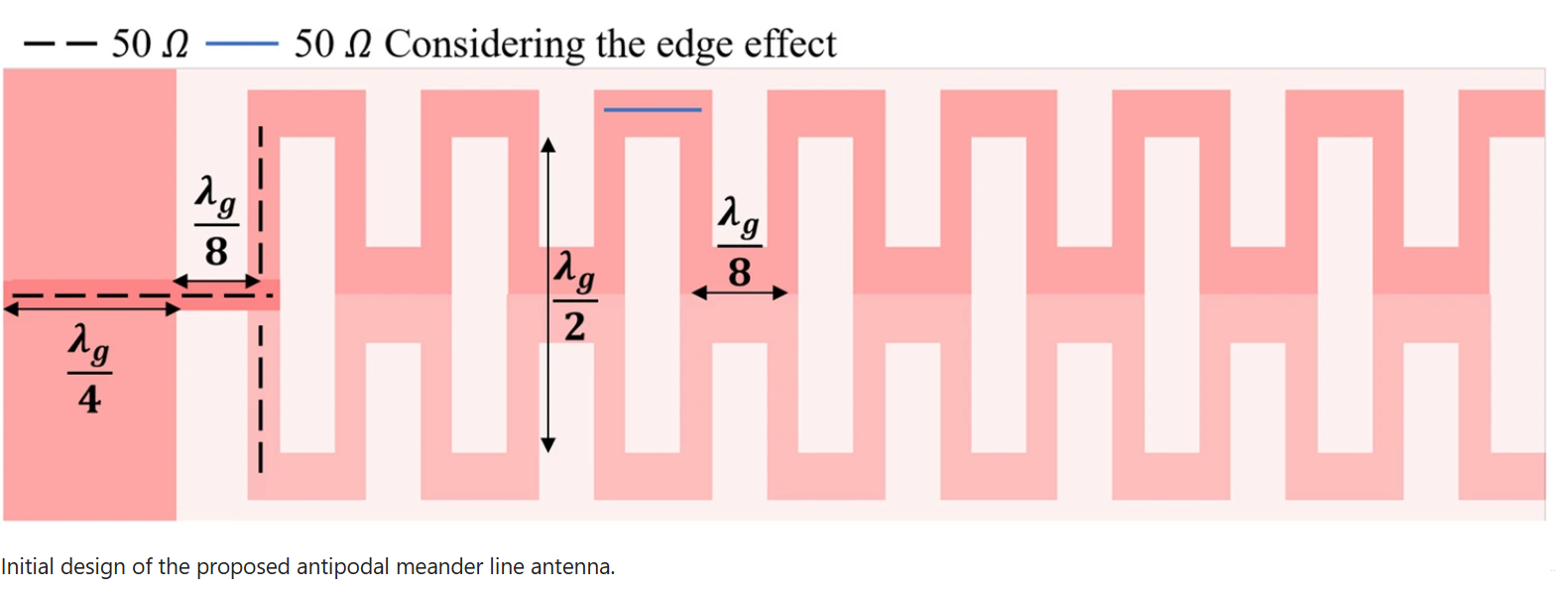
This paper introduces a planar antipodal meander line antenna fabricated using RO3003 substrate. The proposed antenna is designed to radiate in the end-fire direction, achieving a maximum measured gain of 10.43 dBi within its working bandwidth, which ranges from 2.24 GHz to 2.7 GHz, covering long-range WLAN/WiMAX applications. A systematic procedure is adopted in the design process to prove its tunability to cover other application requirements in terms of gain and bandwidth. The proposed design steps show that the bandwidth and the gain can independently be controlled by adjusting specific

Light trapping as a result of embedding plasmonic nanoparticles (NPs) into photovoltaics (PVs) has been recently used to achieve better optical performance compared to conventional PVs. This light trapping technique enhances the efficiency of PVs by confining incident light into hot-spot field regions around NPs, which have higher absorption, and thus more enhancement of the photocurrent. This research aims to study the impact of embedding metallic pyramidal-shaped NPs inside the PV’s active region to enhance the efficiency of plasmonic silicon PVs. The optical properties of pyramidal-shaped

This paper proposes a metamaterial Terahertz sensor with detected sensitivity for biomedical applications. The proposed sensor consists of two interdigitated golden C-shaped structures on top of Teflon substrate that is backed by a gold layer. The absorption spectrum contains a peak resonance corresponding to the maximum absorption of the sensor. The proposed sensor has a maximum narrow-band absorption at 3.35 THz, with an average sensitivity of 2.256 THz/RIU and a quality factor of 22.3. The developed model is checked for the range of refractive index range between n= 1.3 to n= 1.4 to check

Plasmonic Photovoltaics (PVs) are an effective method for increasing optical absorption by adding metallic nanoparticles to the photovoltaic active layer. The role of these nanoparticles is confining the incident light near them in the PV cell, resulting in thin film PVs of enhanced efficiency. Therefore, different materials and new NPs shapes are used for this purpose. In this research, a step pyramid is introduced as a novel structure for nanoparticles for enhancing plasmonic PVs by embedding an array of the proposed step pyramid nanoparticles within the PV cell. Therefore, the extinction