
Artificial Intelligence
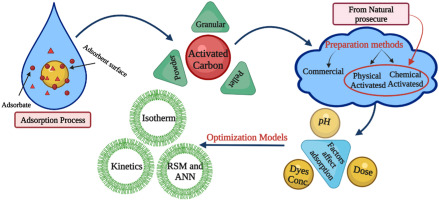
Review of activated carbon adsorbent material for textile dyes removal: Preparation, and modelling
Water contamination with colours and heavy metals from textile effluents has harmed the ecology and food chain, with mutagenic and carcinogenic effects on human health. As a result, removing these harmful chemicals is critical for the environment and human health. Various standard physicochemical and biological treatment technologies are used; however, there are still some difficulties. Adsorption is described as a highly successful technology for removing contaminants from textile-effluents wastewater compared to other methods. Several adsorbent materials, including nanomaterials, natural

Applied Techniques for Wastewater Treatment: Physicochemical and Biological Methods
Polluted water is one of the significant challenges facing the world nowadays, especially with the noticed water shortage recorded in the last period. Different treatment methods, physicochemical and biological, were presented for pollutant removal from polluted wastewater. This review discusses the treatment methods starting from the biological part to help reduction of organics, which are solids that appear in the wastewater. After that, the physicochemical techniques will be discussed as a second part of the treatment process to minimize the heavy metal, dyes, and other pollutants
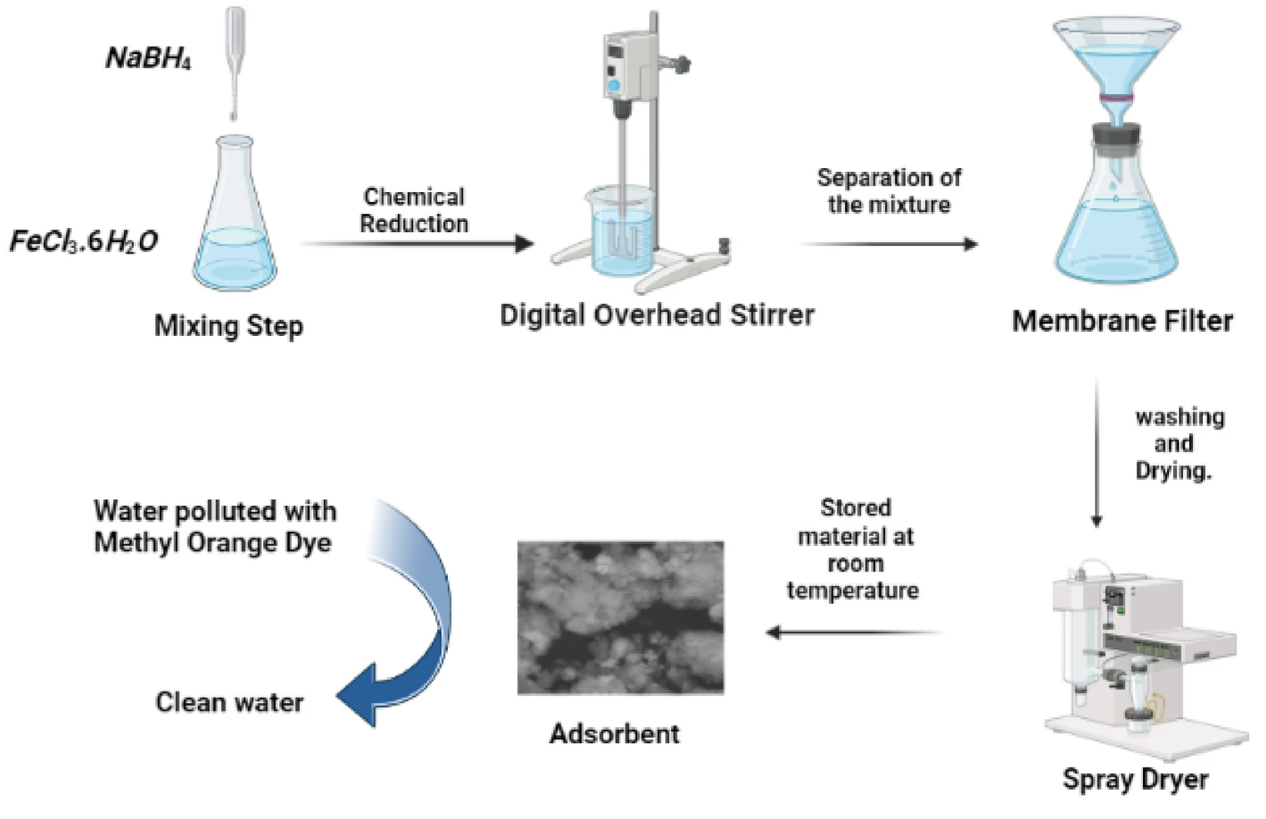
Preparation and Characterization of nZVI, Bimetallic Fe 0-Cu, and Fava Bean Activated Carbon-Supported Bimetallic AC-F e 0-Cu for Anionic Methyl Orange Dye Removal
Early detection of hypo/hyperglycemia using a microneedle electrode array-based biosensor for glucose ultrasensitive monitoring in interstitial fluid
Diabetes is a common chronic metabolic disease with a wide range of clinical symptoms and consequences and one of the main causes of death. For the management of diabetes, painless and continuous interstitial fluid (ISF) glucose monitoring is ideal. Here, we demonstrate continuous diabetes monitoring using an integrated microneedle (MN) biosensor with an emergency alert system. MNs are a novel technique in the field of biomedical engineering because of their ability to analyze bioinformation with minimal invasion. In this work we developed a poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) based MN glucose

Integrated Analysis of Bulk and Single-Cell Transcriptomics in Cervical Cancer: Insights into BPGM, EGLN3, and SUN1
Cervical cancer (CC) is considered a significant global health threat to women therefore there is a need for personalized treatment strategy based on individual-specific gene expression patterns to enhance recovery and survival rates. Although a few studies have linked bisphosphoglycerate mutase (BPGM) expression with CC, its precise role in CC progression remains unclear. In this study, we conducted an integrated analysis for both bulk and single-cell RNA sequencing data to investigate the involvement of BPGM in CC. On the bulk RNA level, the Wilcoxon test result showed a significant
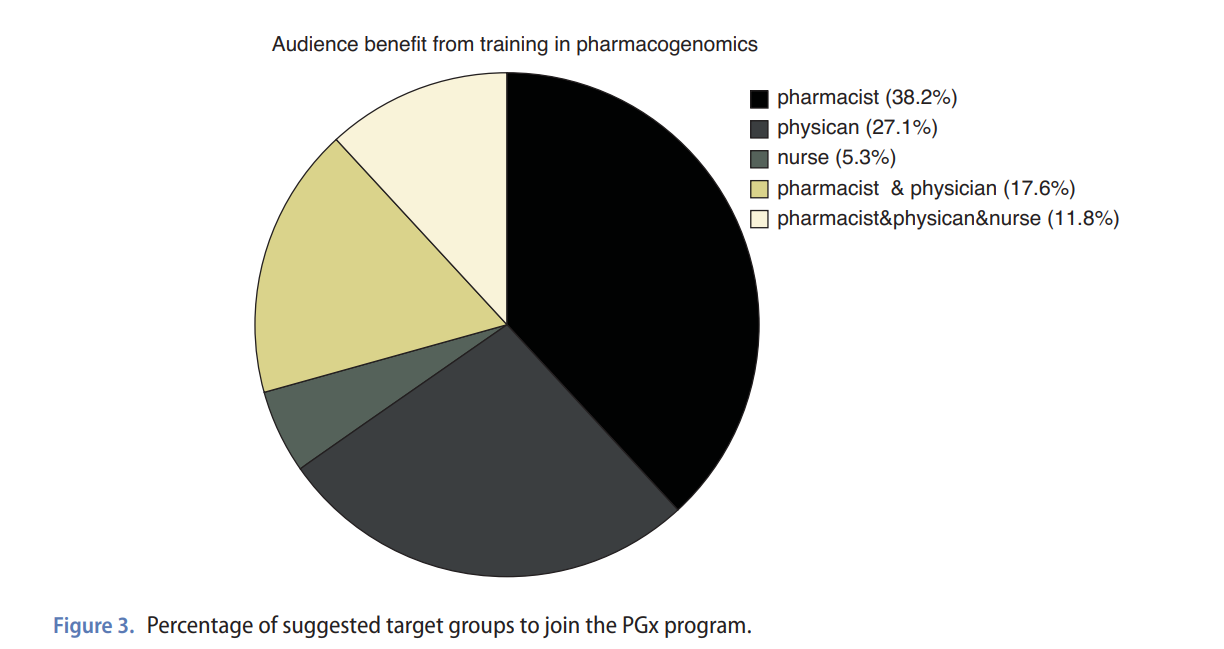
Analysis of the current situation of pharmacogenomics in terms of educational and healthcare needs in Egypt and Lebanon
Pharmacogenomics (PGx) is a practice that investigates the link between genetic differences and drug response in patients. This can improve treatment effectiveness and reduce harmful side effects. However, has yet to be adequately realized in developing nations. Three surveys were conducted between November 2022 to March 2023 in Egypt and Lebanon. The first survey assessed availability of PGx testing in different healthcare facilities; the second one assessed knowledge, interest and attitude toward learning about PGx among pharmacists and physicians; and the third one assessed interest in
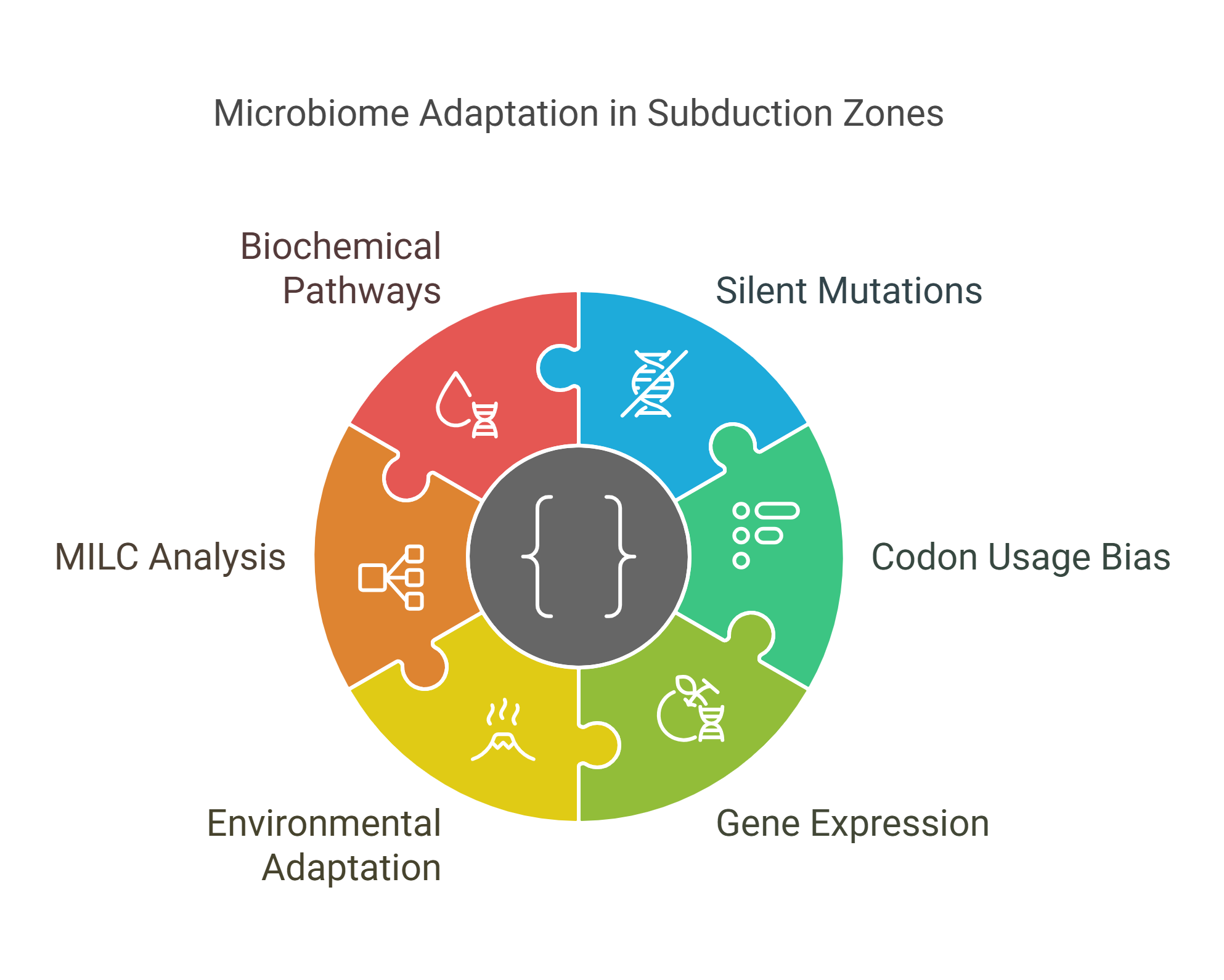
The Melody of Silent Mutations: Microbiome Adaptation Across the Subduction Zone
Silent mutations generate synonymous codons that encode the same amino acid however, they may be silent yet operative. These synonymous codons are used in unequal frequencies resulting in a phenomenon known as codon usage bias (CUB). It drives gene expression towards highly expressed and adaptation genes. In this study we investigated CUB in one of the largest, most dynamic exotic niches, the volcanic subduction zones in Costa Rica. CUB analysis in such challengingly inaccessible sites can help distinguish highly expressed genes under certain environmental factors, elucidating molecular
Chronic tobacco smoking and neurocognitive impairments in adolescents and young adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis
There is a lack of robust research investigating the association between neurocognitive impairments and chronic tobacco smoking in adolescents/young adults. Therefore, a systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted to examine this association by pooling cross-sectional studies published from 1980 to 2023. The systematic review assessed the neurocognitive performances between chronic tobacco smokers and non-smokers in each study. The meta-analysis included six studies that compared chronic tobacco smokers against non-smokers using neuropsychological tests covering three neurocognitive
Identification and expression analysis of SBP-Box-like (SPL) gene family disclose their contribution to abiotic stress and flower budding in pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan)
The SPL gene family (for Squamosa Promoter-binding like Proteins) represents specific transcription factors that have significant roles in abiotic stress tolerance, development and the growth processes of different plants, including initiation of the leaf, branching and development of shoot and fruits. The SPL gene family has been studied in different plant species; however, its role is not yet fully explored in pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan). In the present study, 11 members of the CcSPL gene family were identified in C. cajan. The identified SPLs were classified into nine groups based on a
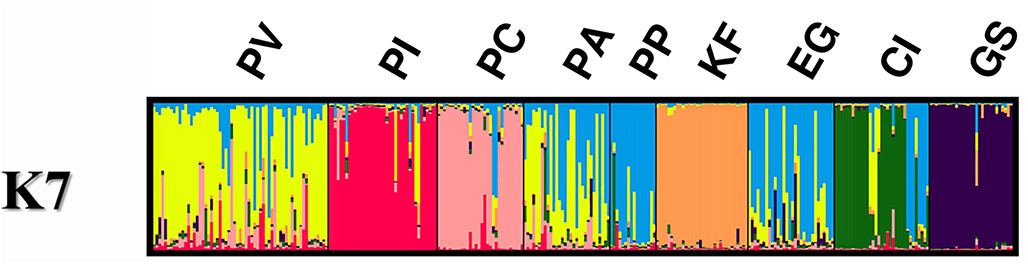
Phylogeographic and population genetic structure of hound-like native dogs of the Mediterranean Basin
The dog was probably the first domesticated animal. Despite extensive archaeological and genetic investigations, the origin and the evolution of the extant dogs are still being debated. Dog breeds that have over time been selected for hunting share common ancestral traits. This study represents the first comprehensive attempt to survey at the genomic and mitochondrial level eight hound-like dogs breeds indigenous to the Mediterranean Basin to determine if they share common ancient origins. Results from the microsatellite analysis indicate that all the dog populations have a low inbreeding