
Artificial Intelligence
Prediction model for the compressive strength of green concrete using cement kiln dust and fly ash
Integrating artificial intelligence and green concrete in the construction industry is a challenge that can help to move towards sustainable construction. Therefore, this research aims to predict the compressive strength of green concrete that includes a ratio of cement kiln dust (CKD) and fly ash (FA), then recommend the optimum sustainable mixture design. The artificial neural network (ANN) and multiple linear regression techniques are used to build prediction models and statistics using MATLAB and IBM SPSS software. The input parameters are based on 156 data points of concrete components
Analysis of compressive strength of glass fiber reinforced concrete using design of experiments
Although there are many studies on Fiber Reinforced Concrete (FRC), determining the factors having the highest impact on compressive strength of fiber reinforced concrete has little attention. In this paper a full factorial L16OA design is used to analyze the early compressive strength of Glass Fiber Reinforced Concrete (GFRC). This is to find the factors tat are significantly affecting the early compressive strength of concrete. The affecting factors were identified through Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) and main effects plots considering the interactions between the factors and the compressive

Decision Support Framework for the Choice of Delay Analysis Techniques Used in Extension of Time Claims
One of the inevitable challenges that face the construction industry is the delay of project completion. The current state of the industry makes the need for delay analysis apparent, however the process of choosing the most reliable delay analysis technique can get very complex in some situations. This research aims to develop a framework to identify and analyze the most important factors to consider when choosing a delay analysis technique. The most reliable technique is decided based on a weighted multicriteria decision matrix. The proposed numerical weight for each factor and the pointing
Flexural behavior of recycled aggregate concrete beams strengthened with carbon fiber reinforced polymer
Using recycled aggregate in the construction of reinforced concrete (RC) buildings has become essential to reduce the waste produced from demolished buildings. In this paper, the influence of using carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP) in strengthening of RC beams with recycled coarse aggregate (RCA), as a partial/full replacement for natural coarse aggregate (NCA), was experimentally investigated. Twelve RC beams with various RCA ratios (0%, 30%, 70%, and 100%) were prepared and tested under four-point loading. Four beams without CFRP were tested till failure while the other eight beams were
Optimizing the coagulation/flocculation process for the treatment of slaughterhouse and meat processing wastewater: experimental studies and pilot-scale proposal
The slaughterhouse industry generates substantial wastewater rich in proteins, lipids, fibers, and carbohydrates. This study integrates experimental investigations into artificial neural network (ANN) optimization and commerce design studies for treating slaughterhouse and meat processing wastewater (SMW). Batch coagulation/flocculation experiments identified optimal conditions for three coagulants: Ferric Chloride (FeCl3·6H2O), Poly Aluminum Chloride (PAC), and Aluminum Sulfate Al2(SO4)3, aiming for optimum removal of chemical oxygen demand (COD), total suspended solids (TSS), and total
Impact of filling period of the grand Ethiopian renaissance dam on hydropower generation and hydropower water footprint of Aswan high dam
The existence of the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD) has a significant impact on Egypt's water share and future water usage. The filling time of the reservoir will have a great impact on the Nile River of the downstream users, especially Egypt. Many of the GERD impacts on Egypt have been previously studied, but no study has addressed the effect of the GERD existence on the hydropower water footprint of the Aswan High dam. This research is studying and simulating the effect of the different GERD reservoir filling scenarios on the water footprint of the hydropower generated from the High
Numerical modeling of sheathed screw connections in CFS shear walls
Screw connections within sheathed cold formed steel (CFS) shear walls experience in-plane shear that acts in a parallel direction to the sheathing's free edge. Yet, many investigations focused on connections where shear loads applied perpendicular to the sheathing's free edge. Although the modes of failure in perpendicular testing are comparable to those ones in CFS shear walls, the load deformation behavior and strength might not be precisely predicted. Thus, the purpose of this study is to create a finite element (FE) model to simulate screw connections under parallel loading. The element
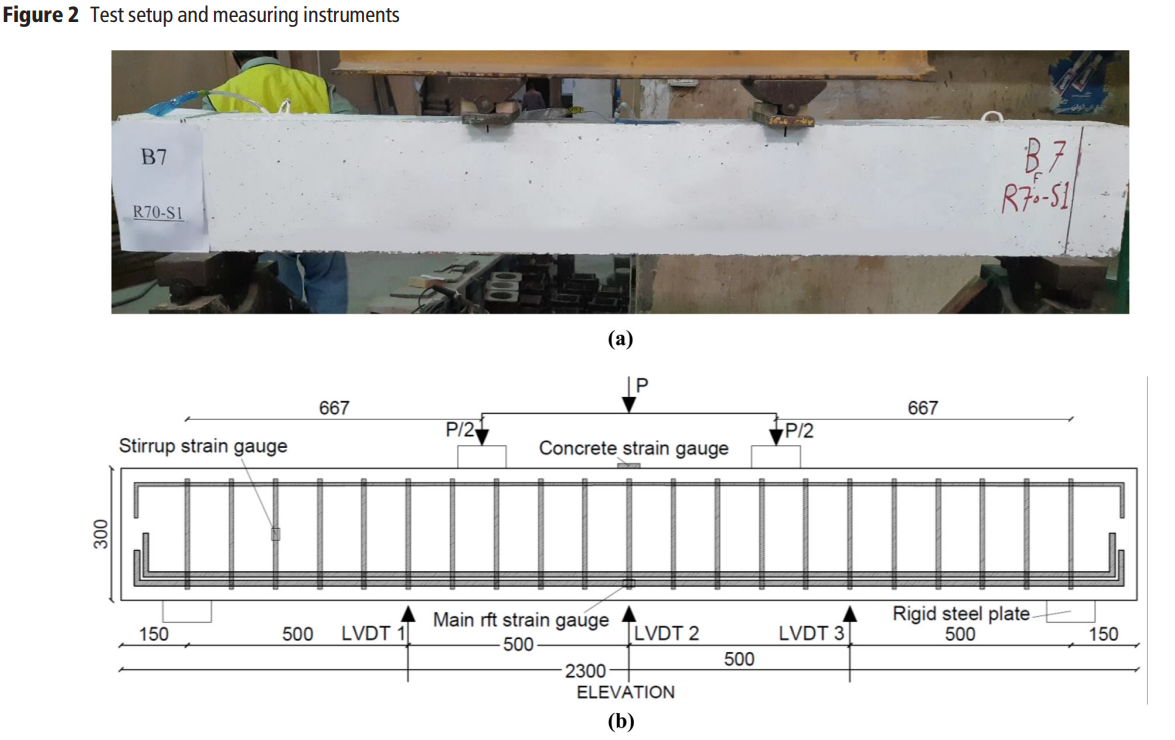
Experimental and numerical investigation of preloaded recycled concrete beams strengthened with CFRP
Purpose: The use of recycled coarse aggregate in concrete structures promotes environmental sustainability; however, performance of these structures might be negatively impacted when it is used as a replacement to traditional aggregate. This paper aims to simulate recycled concrete beams strengthened with carbon fiber-reinforced polymer (CFRP), to advance the modeling and use of recycled concrete structures. Design/methodology/approach: To investigate the performance of beams with recycled coarse aggregate concrete (RCAC), finite element models (FEMs) were developed to simulate 12 preloaded
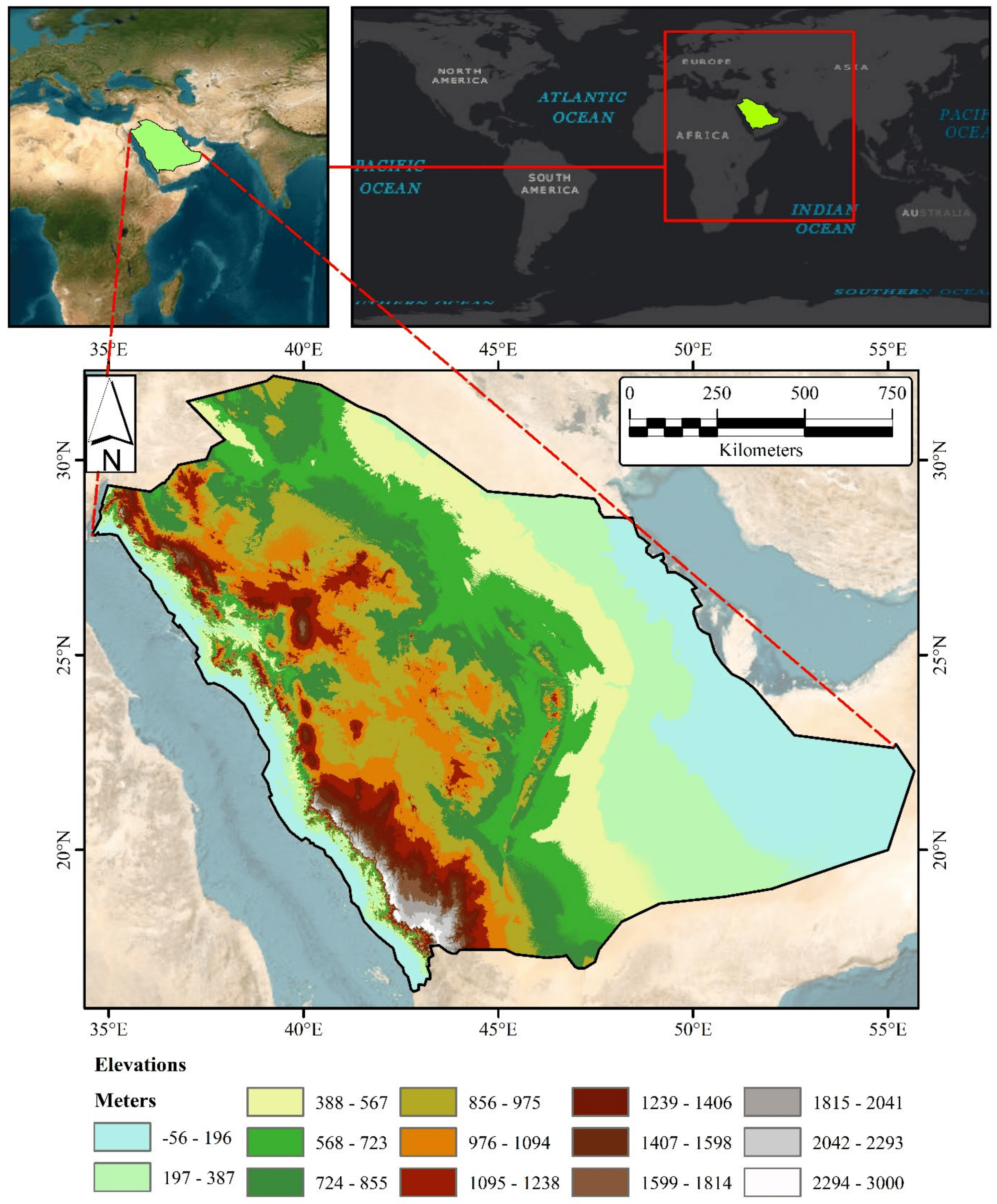
Evaluation of Geospatial Interpolation Techniques for Enhancing Spatiotemporal Rainfall Distribution and Filling Data Gaps in Asir Region, Saudi Arabia
Providing an accurate spatiotemporal distribution of rainfall and filling data gaps are pivotal for effective water resource management. This study focuses on the Asir region in the southwest of Saudi Arabia. Given the limited accuracy of satellite data in this arid/mountain-dominated study area, geospatial interpolation has emerged as a viable alternative approach for filling terrestrial records data gaps. Furthermore, the irregularity in rain gauge data and the yearly spatial variation in data gaps hinder the creation of a coherent distribution pattern. To address this, the Centered Root
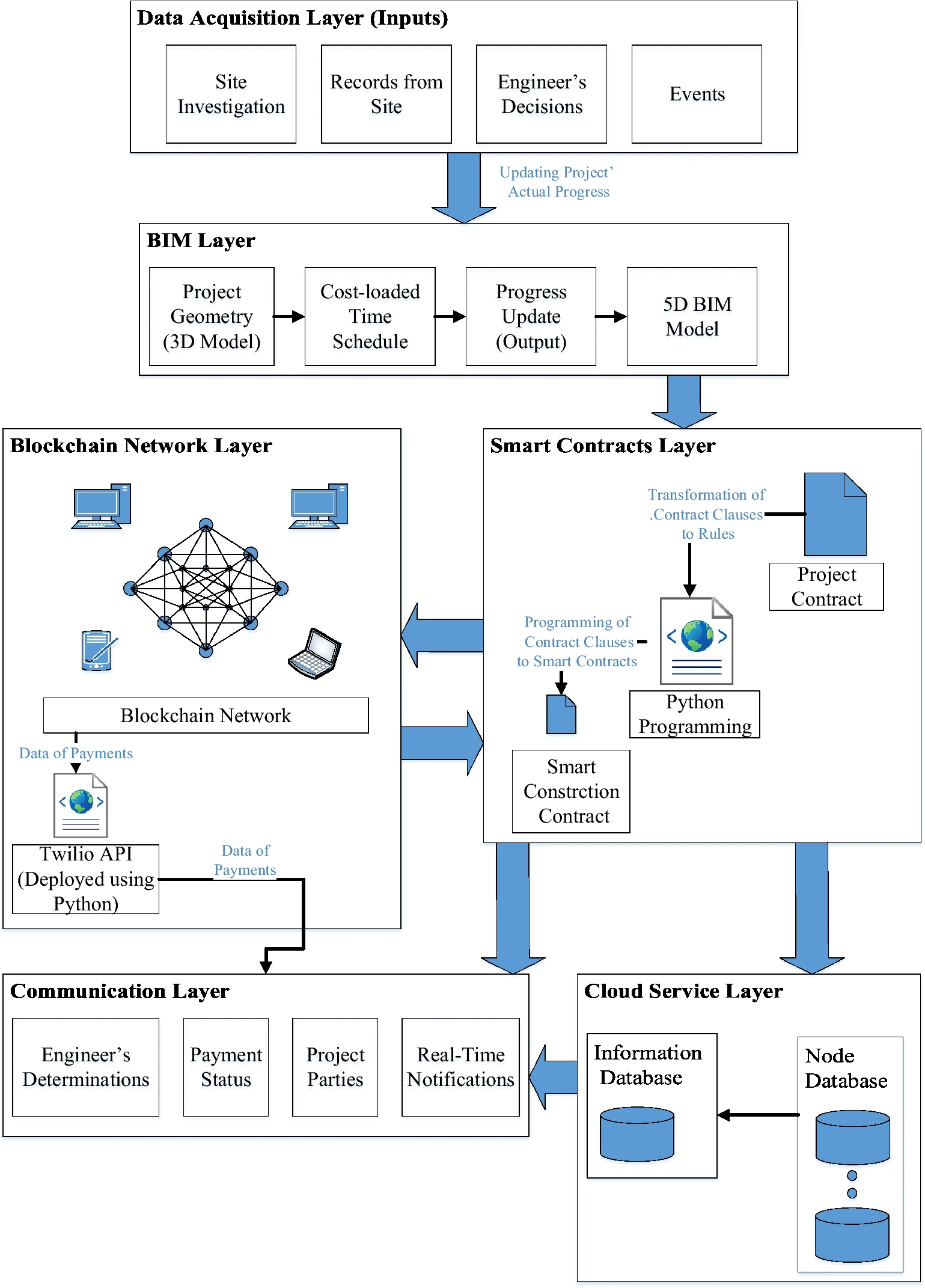
A framework for smart construction contracts using BIM and blockchain
Poor payment practices are perceived as one of the biggest challenges facing the construction industry. Since payments are issued according to project contract terms, the project’s cash flow is inherently affected by the contract and how parties fulfill their obligations. This research proposes a framework for payment automation in construction projects to achieve smart construction contracts. Payments are automatically issued upon satisfying contract conditions using blockchain. Cryptocurrency is proposed to be utilized in the framework to execute the contract terms with no need for a third