
Artificial Intelligence
Smart cloud platform for data management in the age of the internet of vehicles
Smart cars, with the emergence of the Internet of Vehicles (IoV), are expected to generate huge volumes of data at rates that typical data management systems will not be able to handle. Such data can be extremely useful to both analytics and machine learning applications. This paper discusses and demonstrates the process of architecting and building a scalable data management system for the IoV in a smart city environment, using Apache Spark, Apache Kafka and Apache Cassandra, which results in a scalable, resilient and fault-Tolerant data management system that facilitates performing big data

Design for Ergonomics: Application of Single- Passenger Electric Car via Design of Experiments
Design for Ergonomics is still an important concept in new product development. Although some assessment tools could predict if a certain posture is convenient, determining the ergonomics for a new product is still challenging. In this paper, a full factorial L32 Orthogonal Array design is used in the conceptual design phase for a single- passenger electric car. Design of experiments is used to find the significant variables affecting the comfort of the driver at different confidence levels. The significant variables are identified through Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) and response graph/

Integration of simulation modelling and lean management to improve patient flow at outpatient clinics
The outpatient clinics suffer from various inefficiencies such as long queues, long waiting times and low utilisation of medical resources. Simulation modelling and process improvement techniques have been applied separately to tackle such inefficiencies. This paper demonstrates how simulation modelling and lean management can be integrated to improve the patient flow and performance of outpatient clinics. The proposed framework for integrating lean and simulation consists of three main phases where the first phase includes the system description, data collection and analysis, and simulation

Design of a Fuzzy Type-2 Controller for 1-DOF Pitch Axis Twin Rotor System
This paper presents the design, manufacturing, modeling, and control of a novel 1-DOF pitch axis Twin Rotor system. An IMU sensor is used to precisely access the desired pitch angle of the system. A type-2 fuzzy controller is designed and implemented to achieve fast rise time and low overshoot, which are the desired response specifications for the system. In terms of overshoot and settling time, the performance of the type-2 fuzzy-PID controller is compared to that of the type-l fuzzy-PID controller and the conventional PID controller. The type-2 fuzzy-PID controller's performance is promising
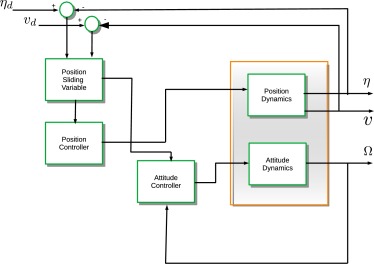
Sliding mode controller design for unmanned aerial vehicles with unmodeled polytopic dynamics
Unmodeled dynamics is one of the problems found in mathematical modeling of many kinds of physical systems, such as electrical and mechanical systems. For this reason, robust control is a solution for this kind of problem, considering the unmodeled dynamics as a matched uncertainty. Unmodeled dynamics affect the robust stability and robust performance of many mechanical systems, reducing the overall efficiency of the designed controller. Therefore, the sliding mode controller (SMC) is designed for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) with unmodeled polytopic dynamics. In this case, this kind of
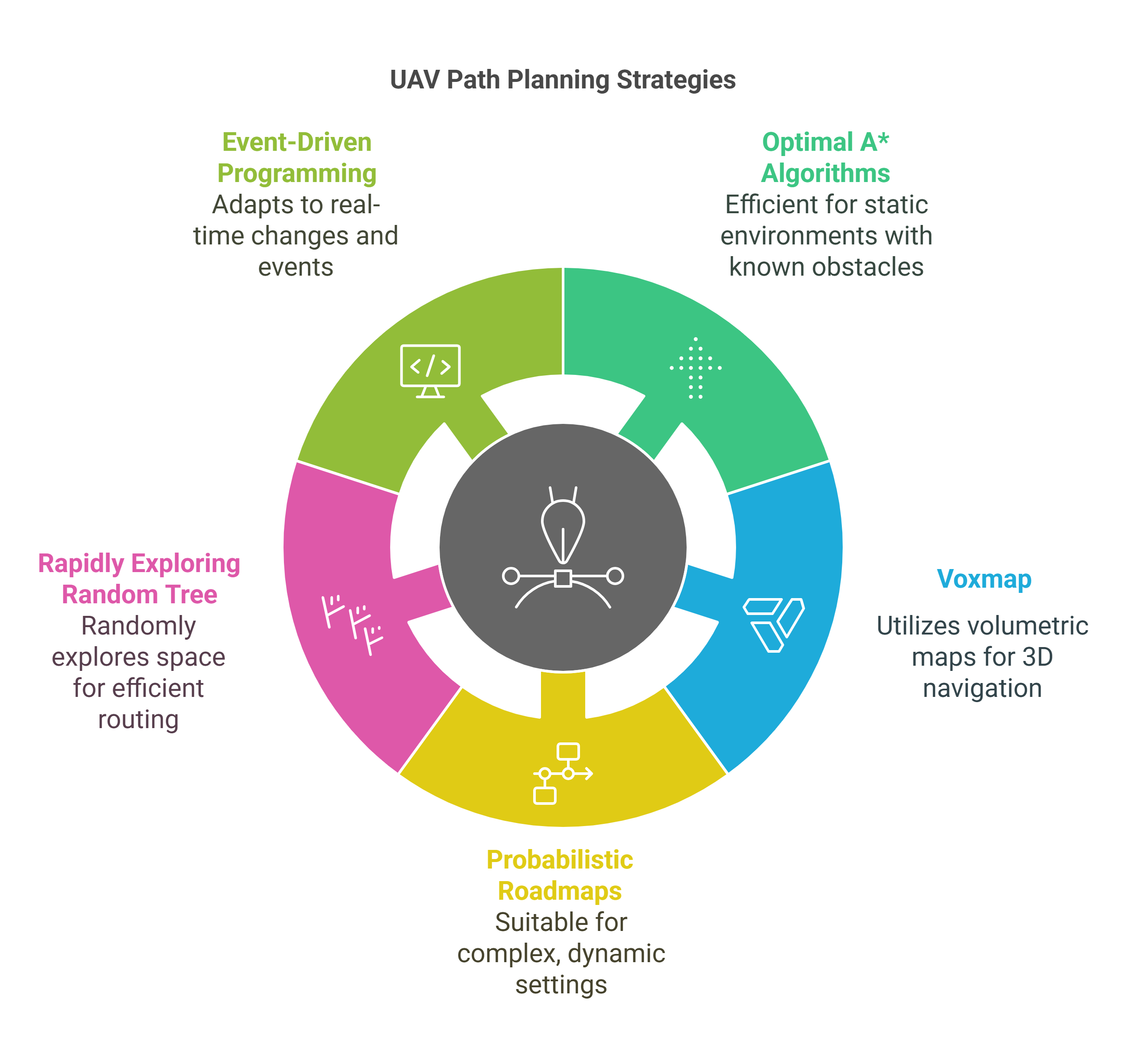
Event-driven programming-based path planning and navigation of UAVs around a complex urban environment
This chapter focuses on path planning techniques for autonomous navigation of small unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) in complex urban environments. It is difficult for UAVs to navigate at low altitudes in dynamic or complex urban environments because they encounter large structures, unpredictable or unrecognized environments, or other UAVs or obstacles flying in their path. Path planning is the core capability of an autonomous UAV to adapt dynamically in changing environments. This chapter will study and implement different path planning algorithms, slowly increasing complexity from optimal A
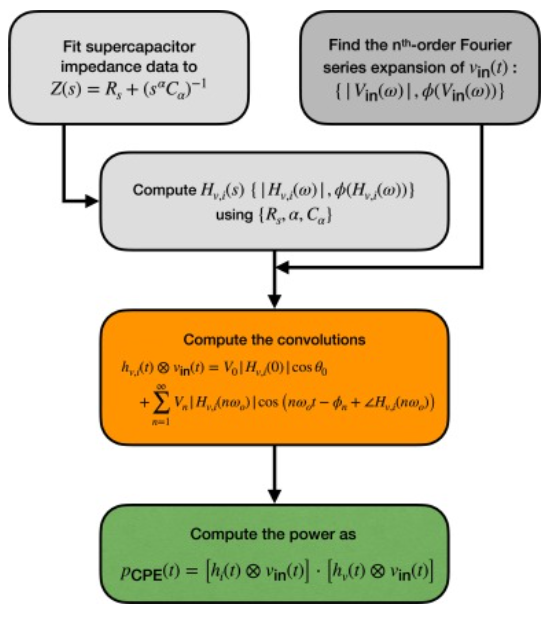
Time-domain response of supercapacitors using their impedance parameters and Fourier series decomposition of the excitation signal
Supercapacitors are mostly recognized for their high power density capabilities and fast response time when compared to secondary batteries. However, computing their power in response to a given excitation using the standard formulæof capacitors is misleading and erroneous because supercapacitors are actually non-ideal capacitive devices that cannot be characterized with a single constant capacitance. In this study we show how to estimate accurately the time-domain power and energy of supercapacitors in response to any excitation signal represented in terms of its Fourier series coefficients
Robust adaptive supervisory fractional order controller for optimal energy management in wind turbine with battery storage
To address the challenges of poor grid stability, intermittency of wind speed, lack of decision-making, and low economic benefits, many countries have set strict grid codes that wind power generators must accomplish. One of the major factors that can increase the efficiency of wind turbines (WTs) is the simultaneous control of the different parts in several operating area. A high performance controller can significantly increase the amount and quality of energy that can be captured from wind. The main problem associated with control design in wind generator is the presence of asymmetric in the
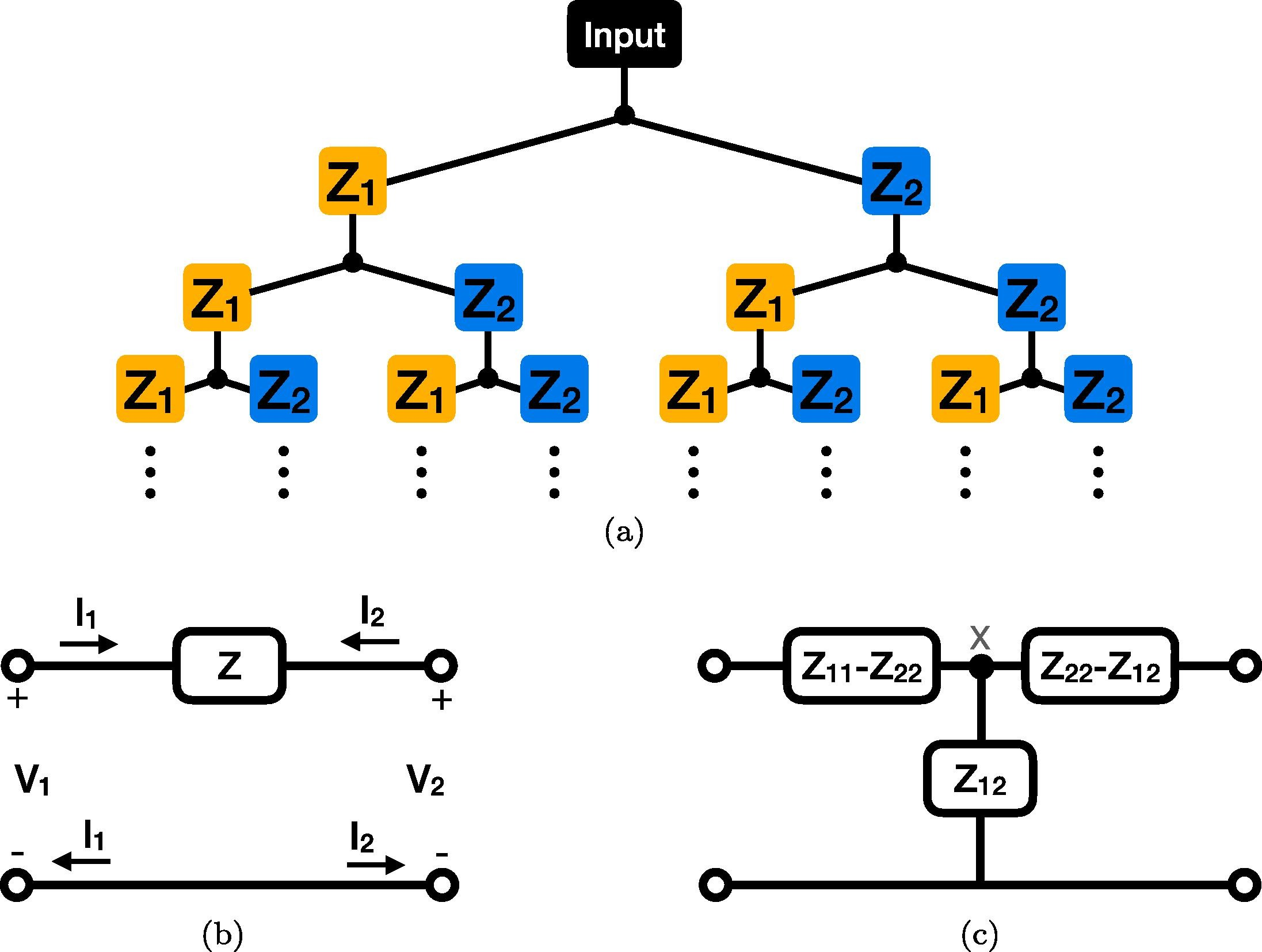
Generalizing the Warburg impedance to a Warburg impedance matrix
We seek to generalize and study the well-known Warburg impedance element, which has an impedance proportional to 1/s (s=jω is the complex frequency), to a two-port impedance network. For this purpose, we consider an infinite binary tree structure inside which each impedance is treated as a two-port network. We obtain a Warburg impedance matrix, which is both symmetrical and reciprocal, and study its equivalent circuit behavior. Interestingly, the equivalent circuit contains two resistors and a Cole–Davidson type impedance proportional to 1+2/(τs), where τ is a time constant. Simulation results

Synthesis of resonance-based common-gate fully differential band-pass filters
We propose a class of fully differential filters based on a common-gate differential amplifier cell in three different topologies. Our focus is on the synthesis of second-order band-pass filters and we found 53 possible circuits. All filters are resonance-based and have electronically tunable gain. Post layout simulations in 65-nm CMOS technology are provided to validate the proper function of these filters. © 2022 Elsevier B.V.