
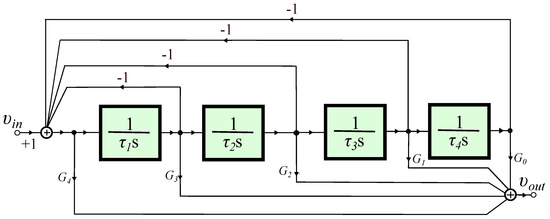
Fractional-order Butterworth filters of order 1 + (Formula presented.) (0
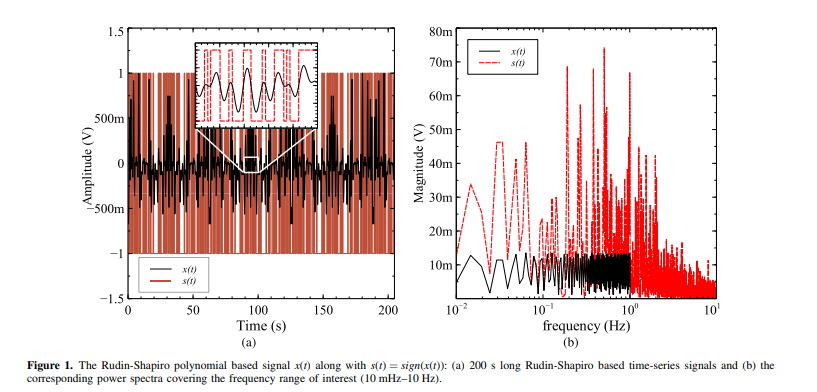
Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) has become an increasingly important diagnostic and monitoring tool in many industries. An obstacle that arises when employing EIS in low and ultra low sub-Hz frequencies is the long measurement time associated with using the conventional frequency-sweep method. One possible solution to this problem is to use wide-band signals that cover at once the entire frequency range of interest. In this work, we explore and validate the use of such a signal obtained from the Rudin-Shapiro polynomial over the frequency range 10 mHz to 10 Hz. The proposed signal
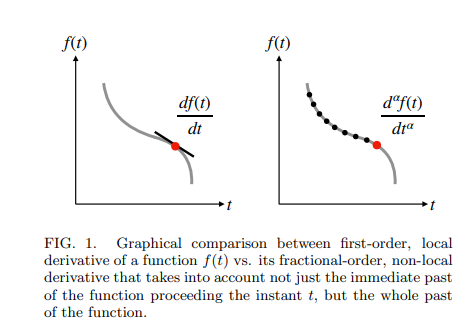
Electrochemical capacitors are a class of energy devices in which complex mechanisms of accumulation and dissipation of electric energy take place when connected to a charging or discharging power system. Reliably modeling their frequency-domain and time-domain behaviors is crucial for their proper design and integration in engineering applications, knowing that electrochemical capacitors in general exhibit anomalous tendency that cannot be adequately captured with the traditional RC-based models. In this study, we first review some of the widely used fractional-order models for the
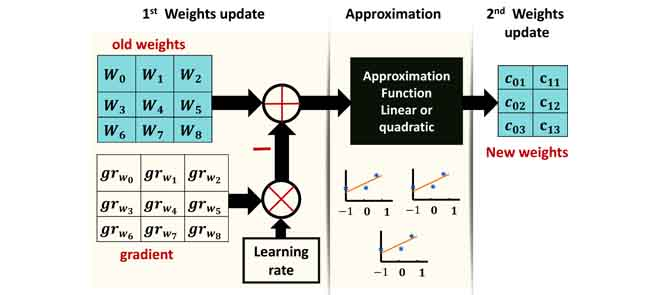
Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) are computationally and memory intensive, which present a big challenge for hardware, especially for resource-constrained devices such as Internet-of-Things (IoT) nodes. This paper introduces a new method to improve DNNs performance by fusing approximate computing with data reuse techniques for image recognition applications. First, starting from the pre-Trained network, then the DNNs weights are approximated based on the linear and quadratic approximation methods during the retraining phase to reduce the DNN model size and number of arithmetic operations. Then, the
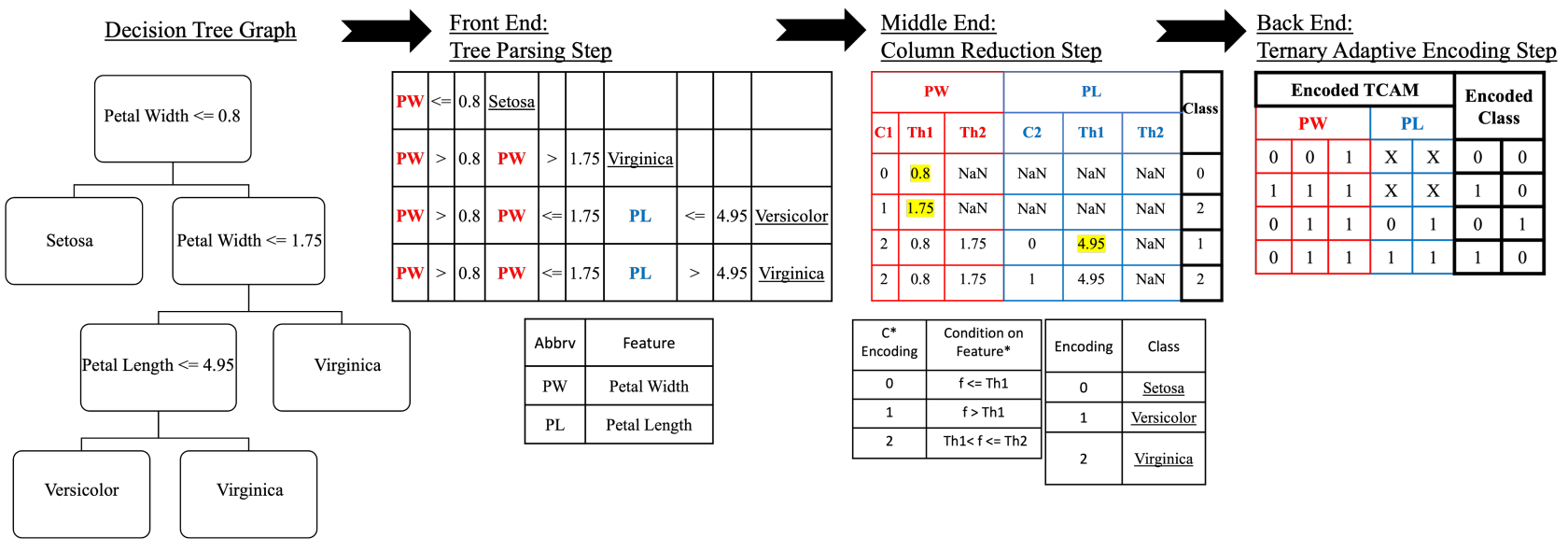
Decision trees are powerful tools for data classification. Accelerating the decision tree search is crucial for on-the-edge applications with limited power and latency budget. In this article, we propose a content-addressable memory compiler for decision tree inference acceleration. We propose a novel 'adaptive-precision' scheme that results in a compact implementation and enables an efficient bijective mapping to ternary content addressable memories while maintaining high inference accuracies. We also develop a resistive-based functional synthesizer to map the decision tree to resistive
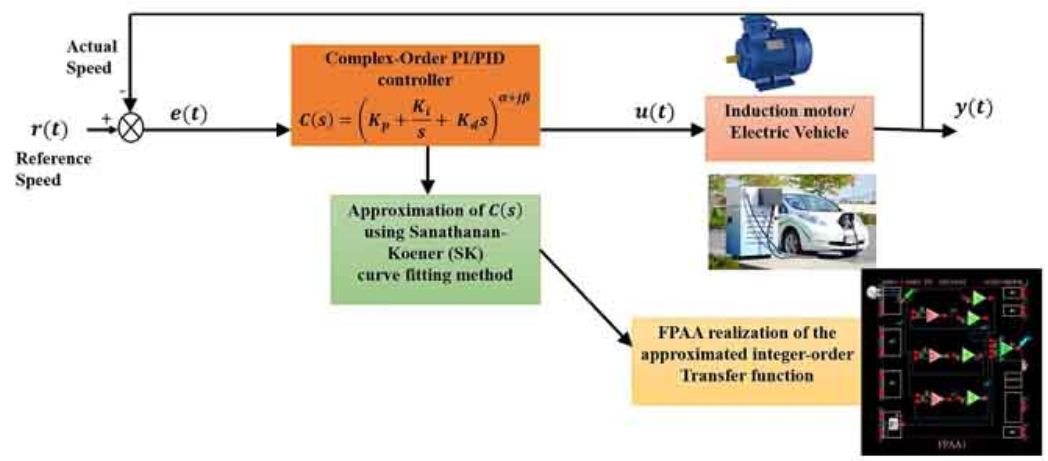
Complex-order controllers are a generalized version of conventional integer-order controllers and are known to offer greater flexibility, better robustness, and improved system performance. This paper discusses the design of complex-order PI/PID controllers to control the speed of an induction motor drive and an electric vehicle. The speed-tracking performance of the complex-order controllers is compared with fractional-order controllers and conventional integer-order controllers. Implementing complex-order controllers is challenging due to commercial complex-order fractance element

An updated definition of group delay bandwidth in analog filters is introduced in this work. Unlike existing definitions, this new definition considers simultaneously the value of the group delay and filter gain, leading to minimized distortion in the filter output. In addition, it offers the capability of handling wide-band signals without introducing errors in the shape of their envelopes. Selected first- and second-order filters are studied and simulation results are provided to validate the efficiency of the new definition. © 2024 The Author(s). International Journal of Circuit Theory and

A theoretical study of the behavior of some elementary first- and second-order functions, which are suitable for realizing negative group delay, is performed in this work. As both the gain and phase responses are simultaneously considered, important derivations related to the actual bandwidth of operation are derived accompanied by useful design tips. The presented theory is supported by simulation and experimental results obtained through the utilization of typical active-RC filter structures, as well as from a field-programmable analog array device. © The Author(s) 2024.
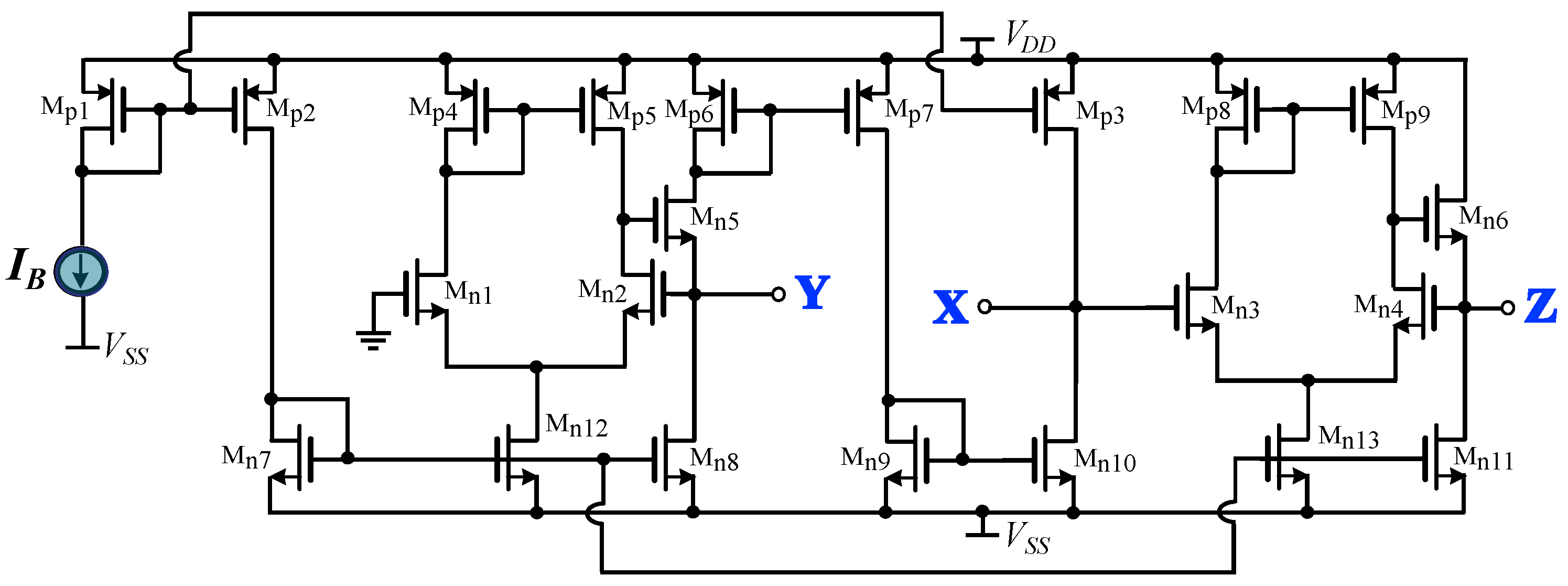
A generalized structure for implementing fractional-order controllers is introduced in this paper. This is achieved thanks to the consideration of the controller transfer function as a ratio of integer and non-integer impedances. The non-integer order impedance is implemented using RC networks, such as the Foster and Cauer networks. The main offered benefit, with regards to the corresponding convectional implementations, is the reduced active and, also, passive component count. To demonstrate the versatility of the proposed concept, a controller suitable for implementing a cardiac pacemaker
Retraction to: Neural Comput & Applic (2018) 29:67–78https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2711-z. The Editor-in-Chief and the publisher have retracted this article. The article was submitted to be part of a guest-edited issue. An investigation by the publisher found a number of articles, including this one, with a number of concerns, including but not limited to compromised editorial handling and peer review process, inappropriate or irrelevant references or not being in scope of the journal or guest-edited issue. Based on the investigation’s findings the Editor-in-Chief therefore no longer has