
Energy and Water
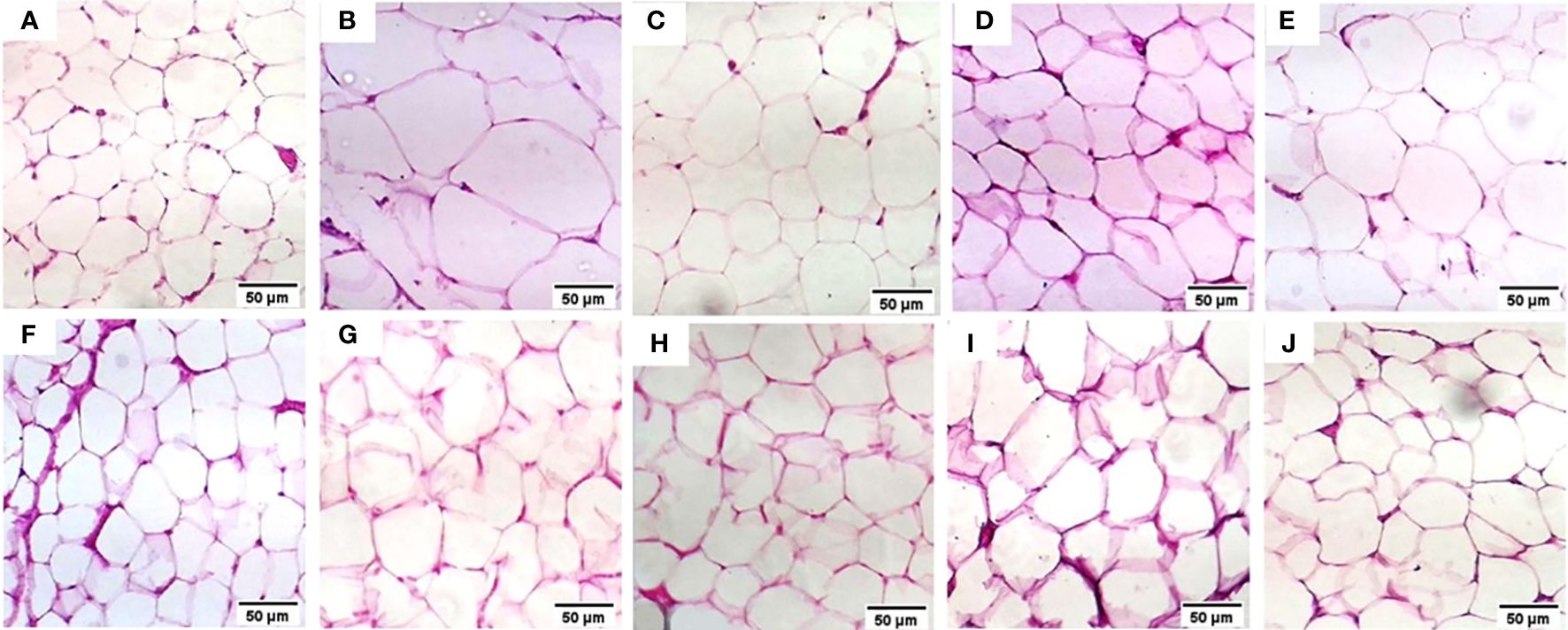
Comprehensive machine learning models for predicting therapeutic targets in type 2 diabetes utilizing molecular and biochemical features in rats
Introduction: With the increasing prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), there is an urgent need to discover effective therapeutic targets for this complex condition. Coding and non-coding RNAs, with traditional biochemical parameters, have shown promise as viable targets for therapy. Machine learning (ML) techniques have emerged as powerful tools for predicting drug responses. Method: In this study, we developed an ML-based model to identify the most influential features for drug response in the treatment of type 2 diabetes using three medicinal plant-based drugs (Rosavin, Caffeic
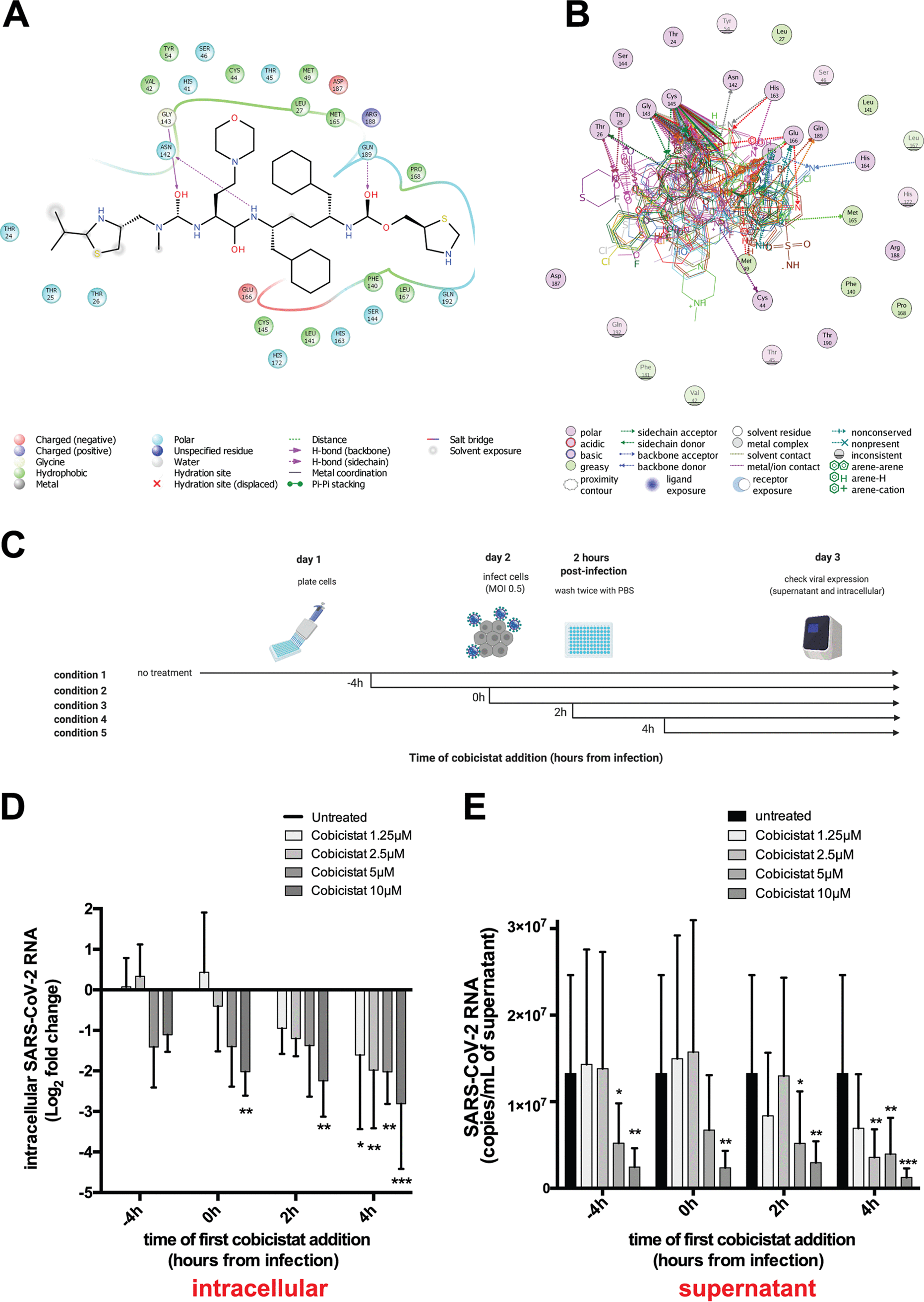
The FDA-Approved Drug Cobicistat Synergizes with Remdesivir to Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 Replication in Vitro and Decreases Viral Titers and Disease Progression in Syrian Hamsters
Combinations of direct-acting antivirals are needed to minimize drug resistance mutations and stably suppress replication of RNA viruses. Currently, there are limited therapeutic options against the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), and testing of a number of drug regimens has led to conflicting results. Here, we show that cobicistat, which is an FDA-approved drug booster that blocks the activity of the drug-metabolizing proteins cytochrome P450-3As (CYP3As) and P-glycoprotein (P-gp), inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication. Two independent cell-to-cell membrane fusion
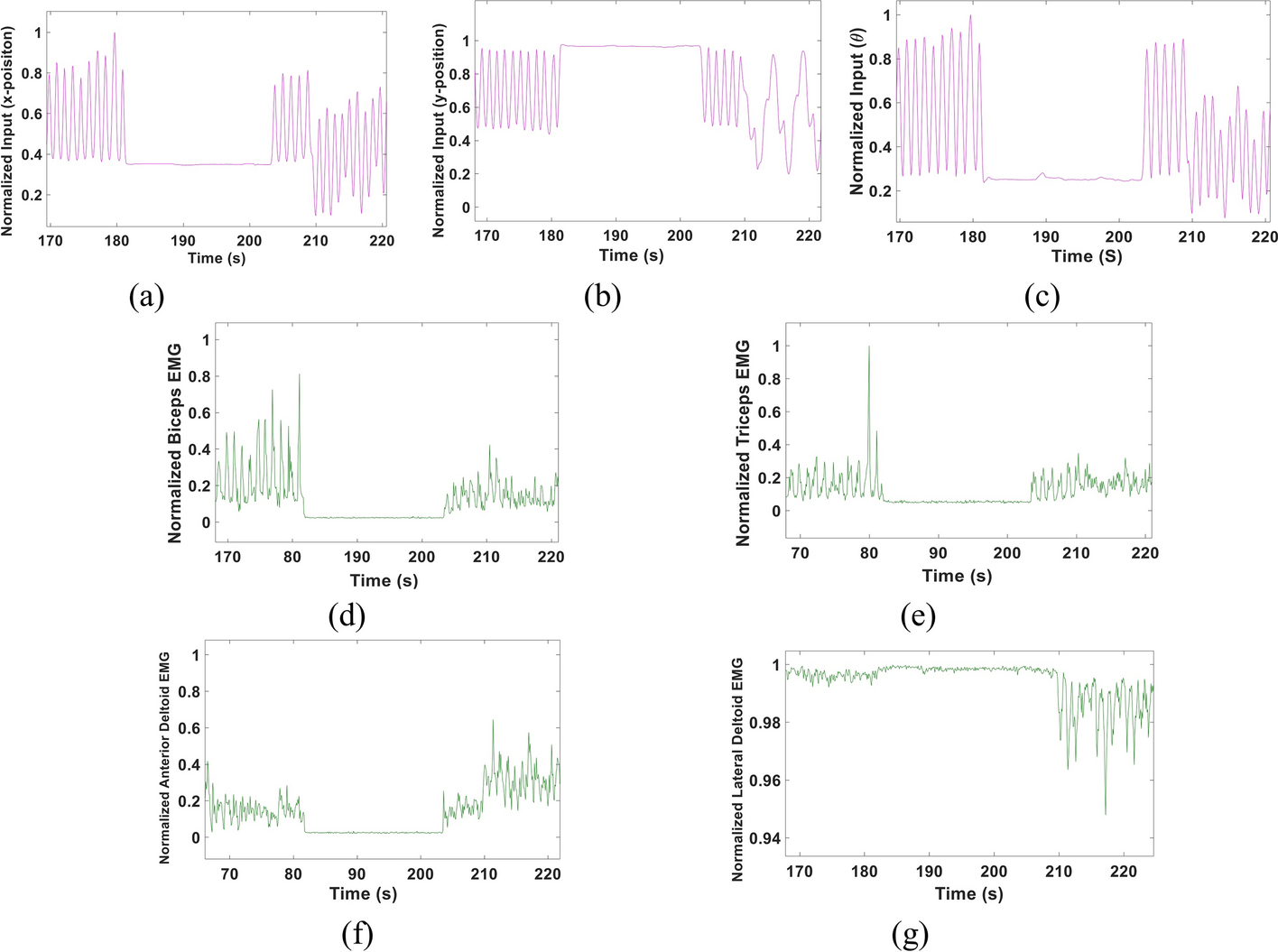
A multi-Kalman filter-based approach for decoding arm kinematics from EMG recordings
Background: Remarkable work has been recently introduced to enhance the usage of Electromyography (EMG) signals in operating prosthetic arms. Despite the rapid advancements in this field, providing a reliable, naturalistic myoelectric prosthesis remains a significant challenge. Other challenges include the limited number of allowed movements, lack of simultaneous, continuous control and the high computational power that could be needed for accurate decoding. In this study, we propose an EMG-based multi-Kalman filter approach to decode arm kinematics; specifically, the elbow angle (θ), wrist
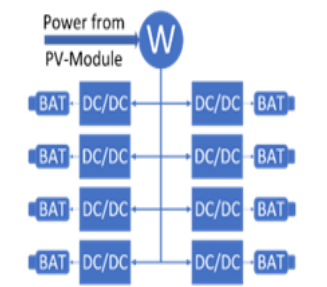
Developing Role Model of PV Powered Battery Swapping Stations for e-scooters in Urban Regions
Electric vehicles (EVs) can only provide lower carbon emissions than conventional, internal combustion-powered vehicles if they are charged using green energy. They also have the drawback of long charging times to 'refuel' them. To combat these two problems, a solar-powered battery charging and swapping station was developed using centered-human design and systems engineering. The design focuses on electric two-wheeled vehicles (e-scooters) due to the easier handling of their light and low-capacity batteries compared to electric cars. These stations are easy to maintain and manage and can be
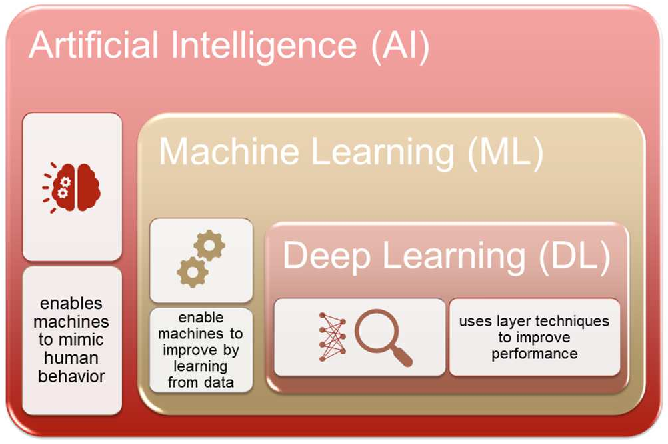
AI for Automated Thoracic Disease Assessment from X-Ray Imaging: a Review
With the increasing availability of digital X-ray imaging, artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a promising tool for automating the assessment of thoracic diseases. The objective of this study is to systematically review the artificial intelligence (AI) and deep learning methods proposed for the automated assessment of thoracic diseases from chest X-ray images. A thorough search of the relevant literature was conducted, and studies that met the inclusion criteria were critically reviewed. Information on the datasets, model architectures, evaluation metrics, and results was extracted
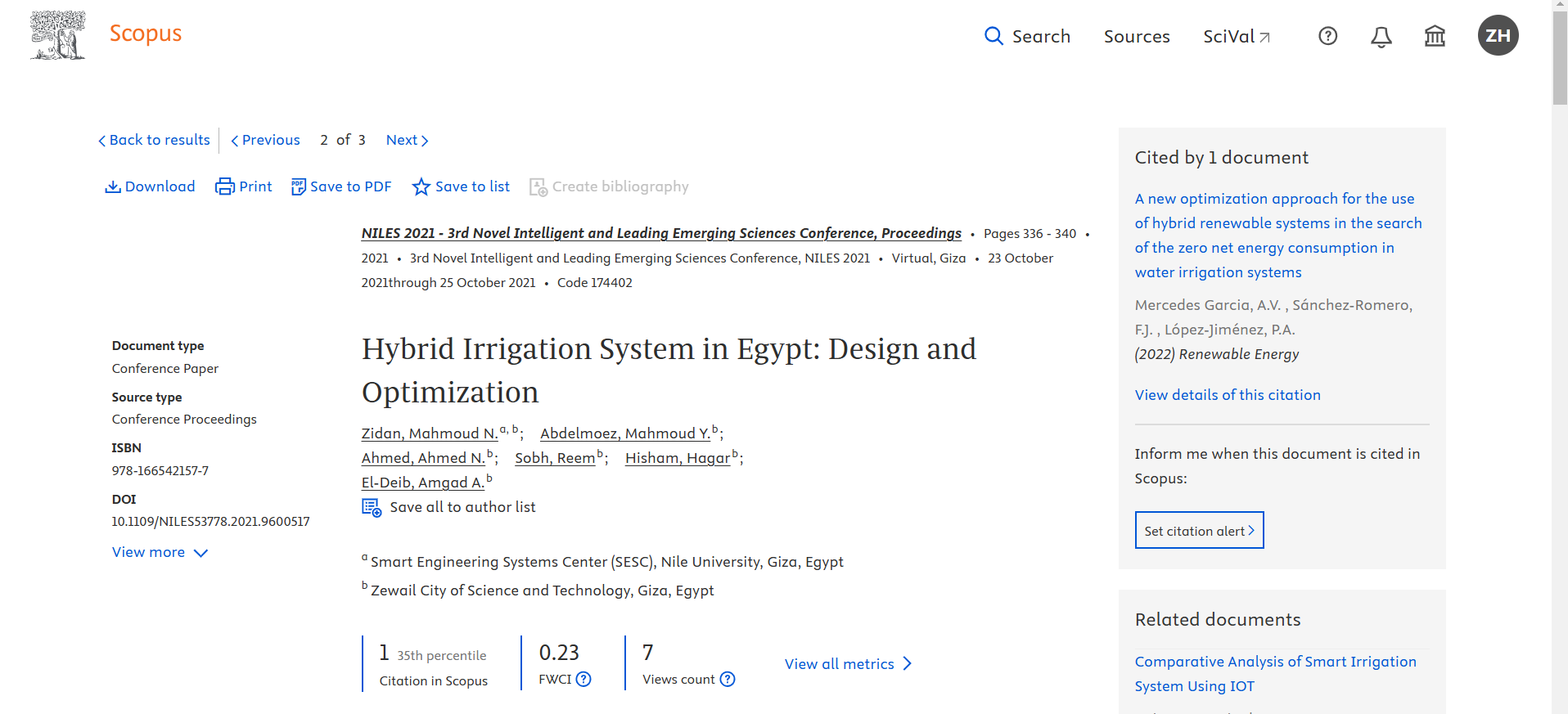
Hybrid Irrigation System in Egypt: Design and Optimization
This presents a hybrid photovoltaic/diesel system simulated as an alternative to the diesel generators required for water pumping systems. This hybrid system is designed to overcome the limitations of the fluctuating price and availability of diesel generators, ensure a reliable supply without interruptions, and improve the overall system efficiency. The system configuration offers an economical benefits over fully renewable hybrid systems or PV only systems. The novelty of the system design lies in minimizing its complexity in terms of design size and control while using a 10 KW photovoltaic
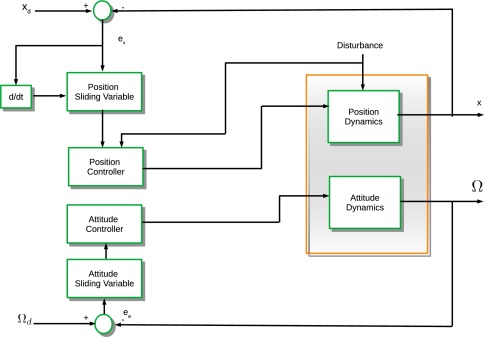
Robust fractional-order sliding mode control design for UAVs subjected to atmospheric disturbances
Trajectory tracking of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) has been studied nowadays because it is necessary to design new controllers under different conditions. Severe atmospheric conditions are one of the major problems to overcome according to the path of the UAV. Conditions such as wind speed that can vary according to the weather conditions can affect the flight performance and of course in extreme cases can lead to stability problems. Some kinds of severe conditions are storms, snow, and hurricanes. These conditions are considered as disturbances in the roll, pitch, and yaw orientations of
Di- and tri- cyclic aromatic hydrocarbons removal using different prepared materials based Sargassum dentifolium algae, and iron oxide
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are highly toxic and carcinogenic compounds as they are low water solubility, hardly degradable and may persist in the environment for many years. Therefore, this study was directed to PAHs ‘anthracene and naphthalene’ removal using a combination method between adsorption and degradation using sunlight. Three adsorbent materials, iron oxide (Fe) alone, Sargassum dentifolium (S) alone, and mixture of Iron oxide and Sargassum dentifolium (FeS) were prepared. Afterwards, optimisation process was performed for the three adsorbent forms through some
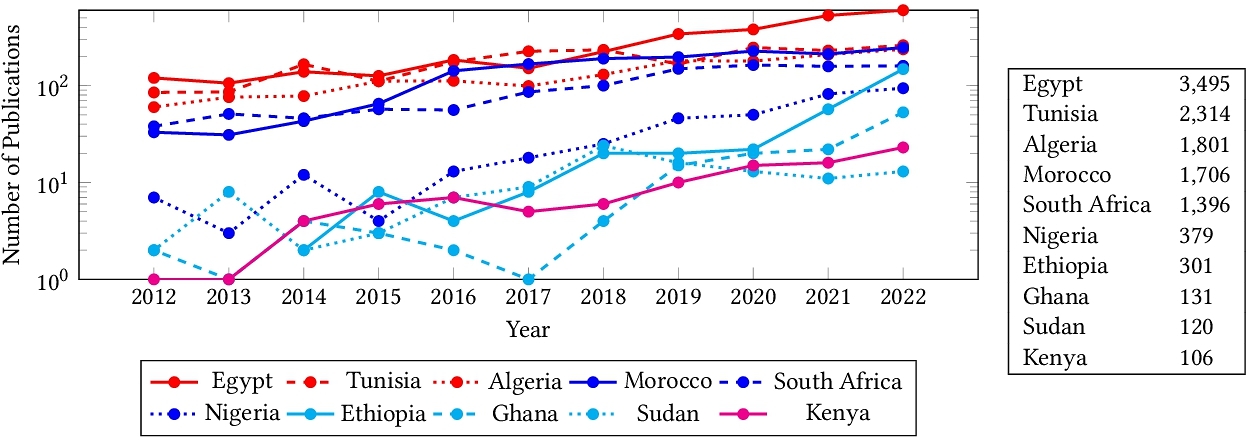
The State of Computer Vision Research in Africa
Despite significant efforts to democratize artificial intelligence (AI), computer vision which is a sub-field of AI, still lags in Africa. A significant factor to this, is the limited access to computing resources, datasets, and collaborations. As a result, Africa's contribution to top-tier publications in this field has only been 0.06% over the past decade. Towards improving the computer vision field and making it more accessible and inclusive, this study analyzes 63,000 Scopus-indexed computer vision publications from Africa. We utilize large language models to automatically parse their
Numerical Investigation of Hydrogen-Enriched Diesel Addition Effects in a Furnace Burner: Flame Temperatures and Exhaust Emissions
In this work, the effects of adding hydrogen to diesel non-premixed combustion with air in a cylindrical furnace burner are investigated. A numerical model is developed to study the effects of hydrogen addition on combustion flame temperature and exhaust emissions. Different hydrogen addition ratios of 5%, 10%, 15%, and 20% by volume in the burning mixture are considered. The turbulence-chemistry interaction is modelled through the eddy dissipation combustion model to predict the concentration of exhaust emissions and the temperature of the combustion flame. The air-fuel equivalence ratio is