
Artificial Intelligence
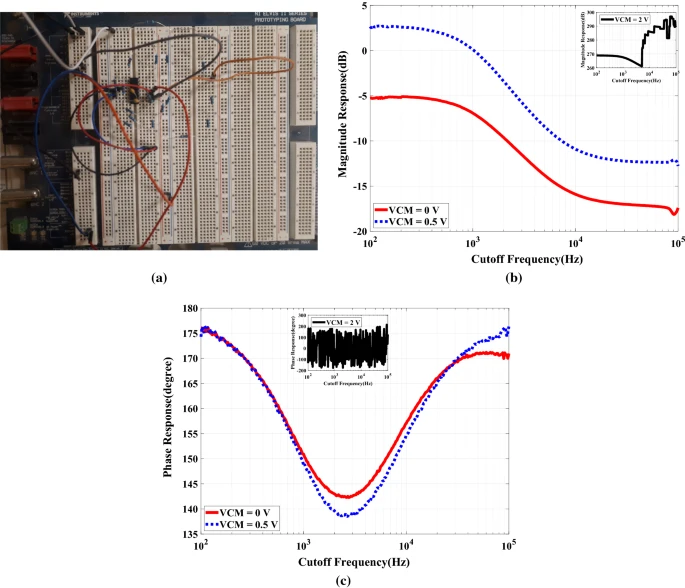
Active and passive sensitivity analysis for the second-order active RC filter families using operational amplifier: a review
This work is a review article that sheds light on the active and passive sensitivities of the active RC filters based on opamp. This work provides a detailed analysis through different filters realization criteria and sensitivity summary tables and quantitative insight by discussing the most significant. However, some are almost forgotten, filters families in the literature over decades. A detailed mathematical analysis for the passive sensitivity to compare the filters’ realizations is presented. The concept of dealing between filter design theory and filter design circuit realization is
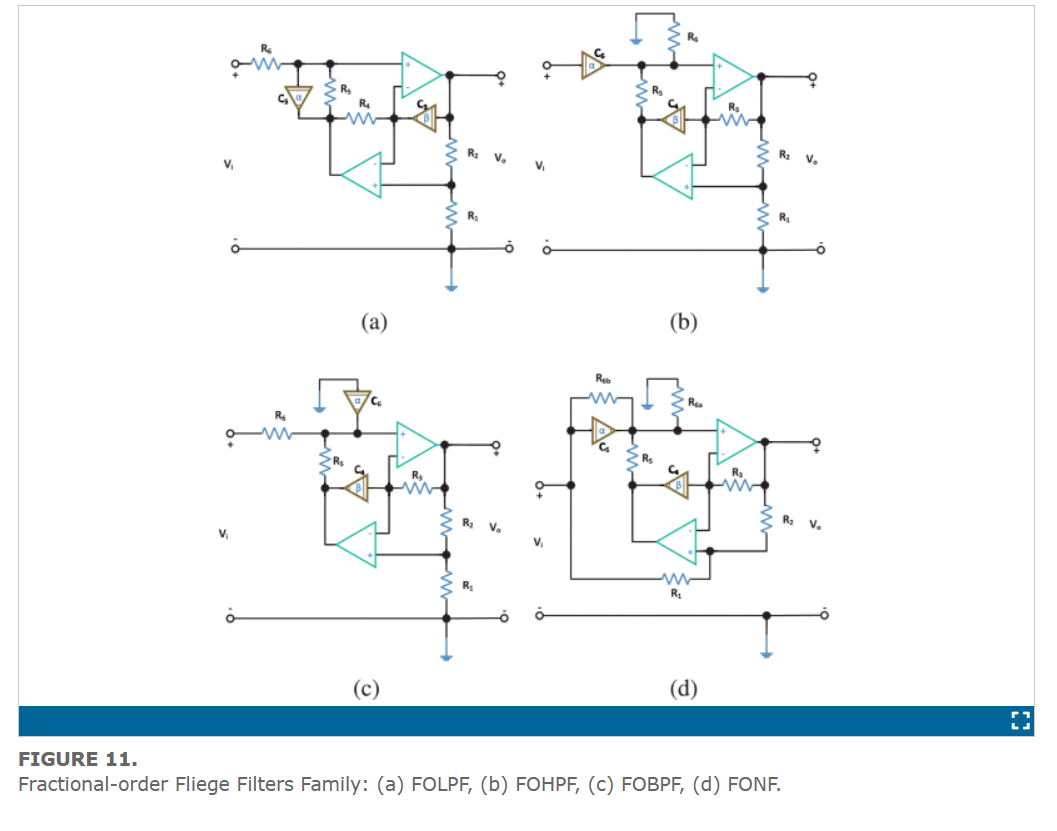
On the Design Flow of the Fractional-Order Analog Filters Between FPAA Implementation and Circuit Realization
This work explicitly states the design flows of the fractional-order analog filters used by researchers throughout the literature. Two main flows are studied: the FPAA implementation and the circuit realization. Partial-fraction expansion representation is used to prepare the approximated fractional-order response for implementation on FPAA. The generalization of the second-order active RC analog filters based on opamp from the integer-order domain to the fractional-order domain is presented. The generalization is studied from both mathematical and circuit realization points of view. It is
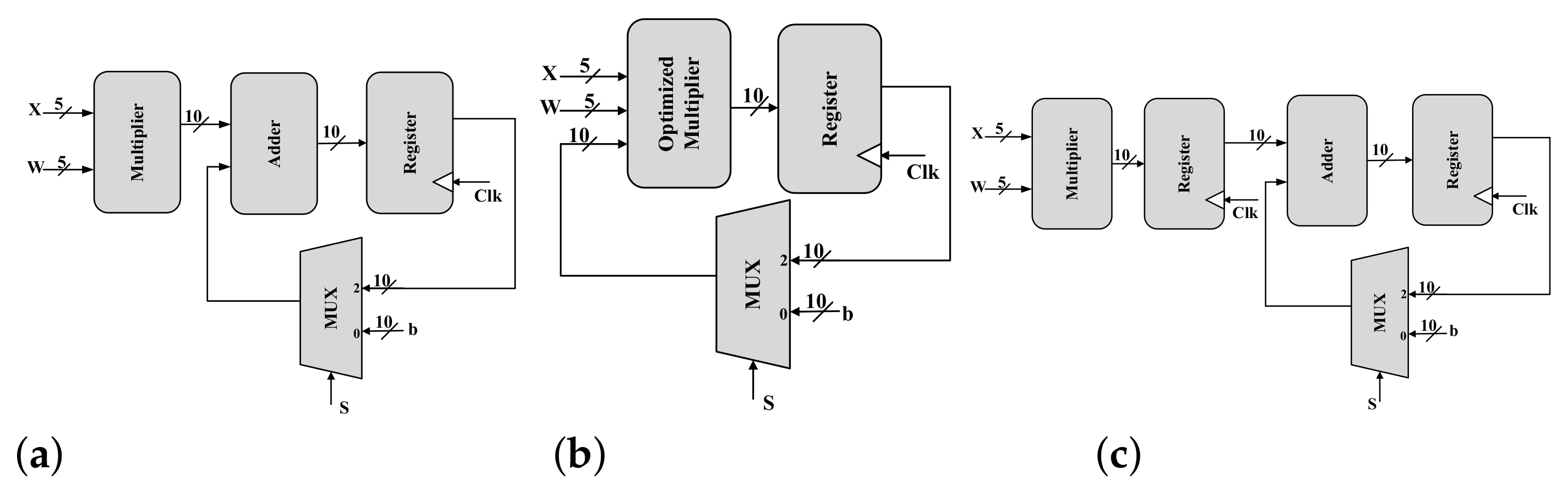
CNTFET-Based Ternary Multiply-and-Accumulate Unit
Multiply-Accumulate (MAC) is one of the most commonly used operations in modern computing systems due to its use in matrix multiplication, signal processing, and in new applications such as machine learning and deep neural networks. Ternary number system offers higher information processing within the same number of digits when compared to binary systems. In this paper, a MAC is proposed using a CNTFET-based ternary logic number. Specifically, we build a 5-trit multiplier and 10-trit adder as building blocks of two ternary MAC unit designs. The first is a basic MAC which has two methods to
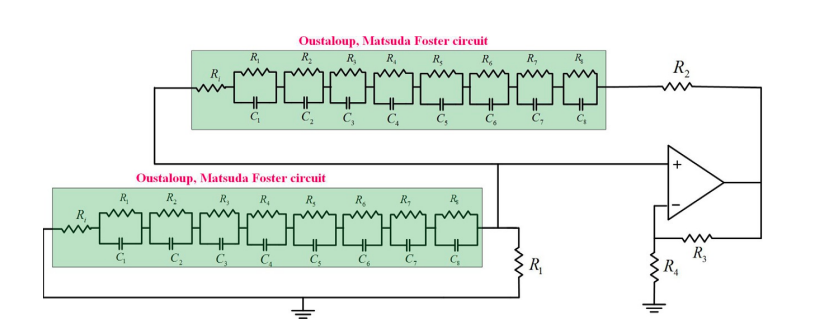
On the Approximation of Fractional-Order Circuit Design
Despite the complex nature of fractional calculus, it is still fairly possible to reduce this complexity by using integer-order approximation. Each integer-order approximation has its own trade-offs from the complexity, sensitivity, and accuracy points of view. In this chapter, two different fractional-order electronic circuits are studied: the Wien oscillator and the CCII-based KHN filter with two different fractional elements of orders α and β. The investigation is concerned with changes in the response of these two circuits under two approximations: Oustaloup and Matsuda. A detailed review
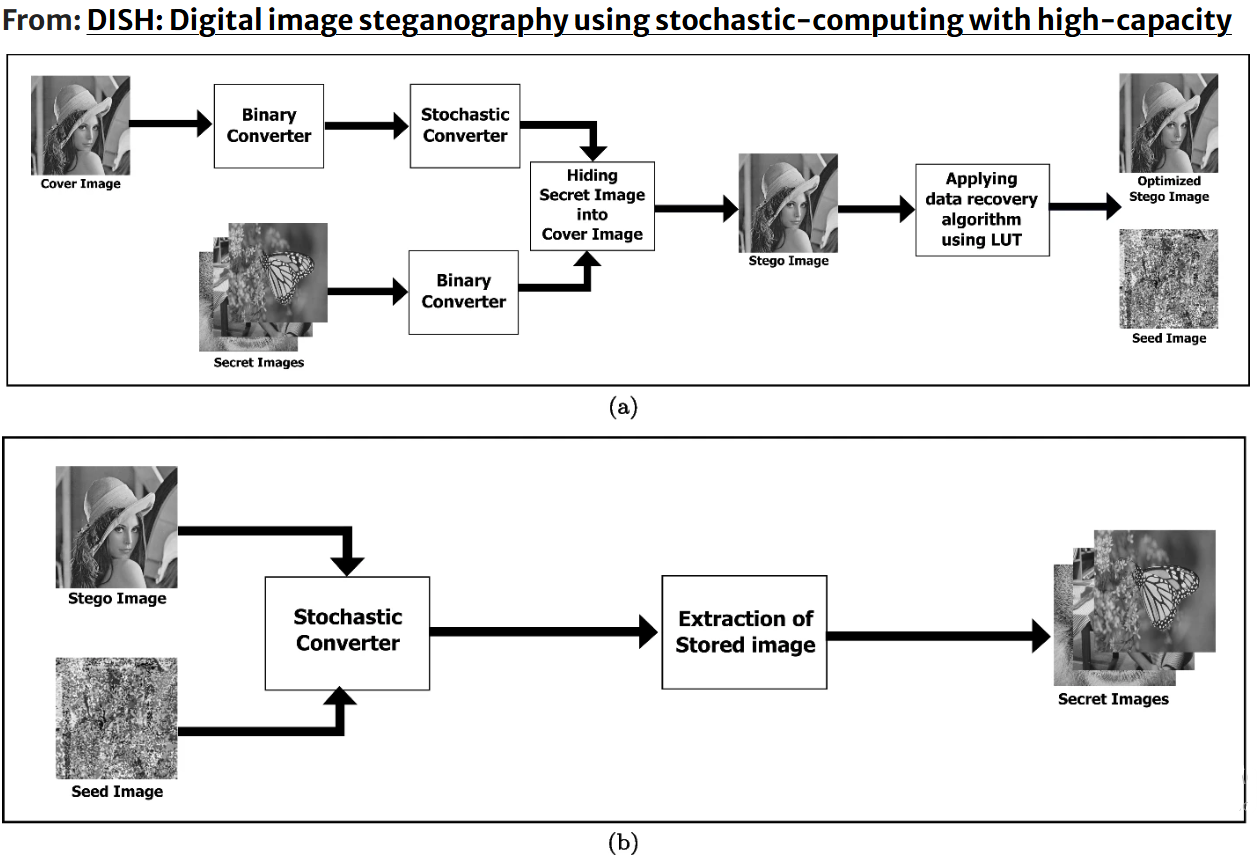
DISH: Digital image steganography using stochastic-computing with high-capacity
Stochastic computing is a relatively new approach to computing that has gained interest in recent years due to its potential for low-power and high-noise environments. It is a method of computing that uses probability to represent and manipulate data, therefore it has applications in areas such as signal processing, machine learning, and cryptography. Stochastic steganography involves hiding a message within a cover image using a statistical model. Unlike traditional steganography techniques that use deterministic algorithms to embed the message, stochastic steganography uses a probabilistic
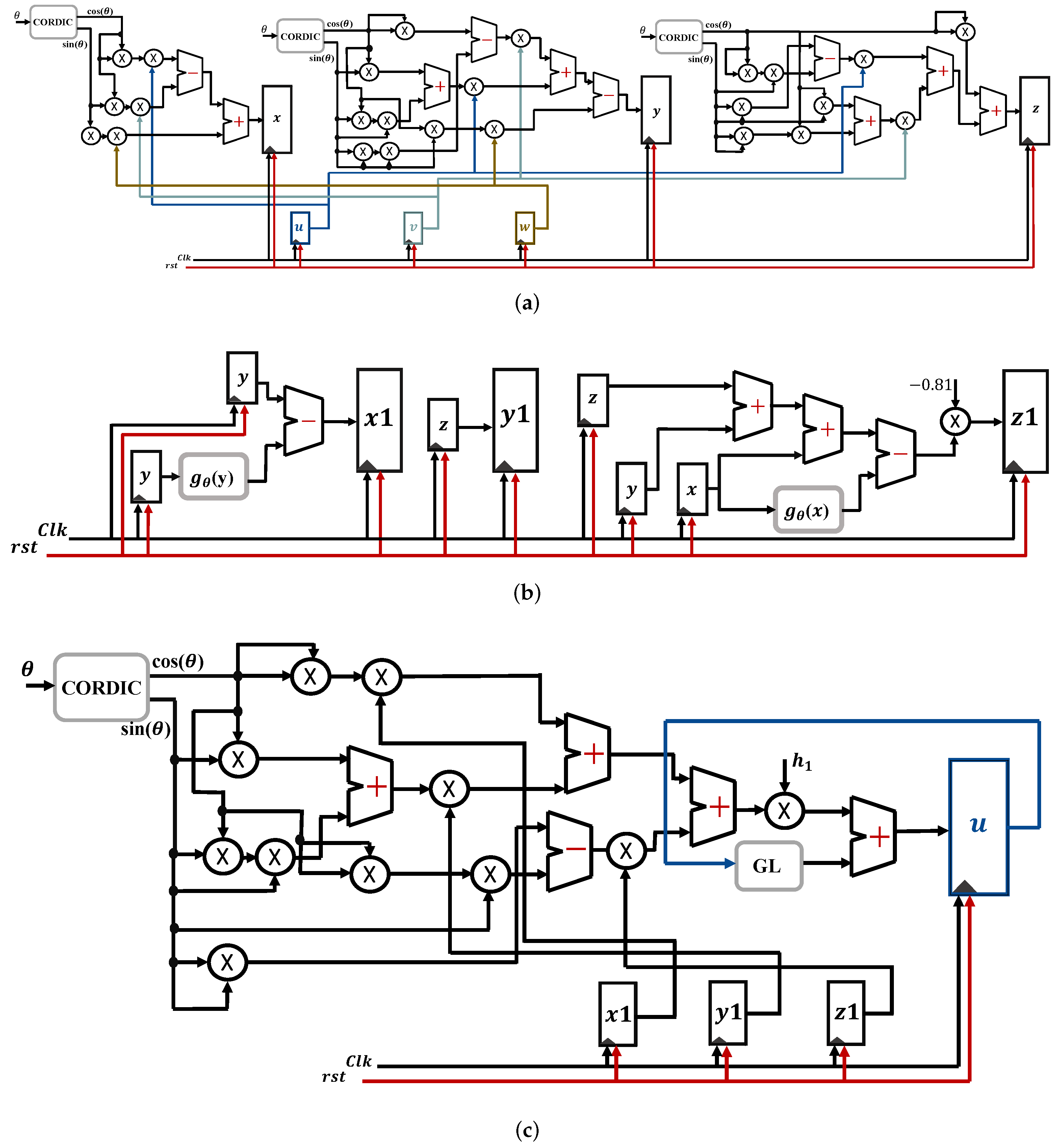
CORDIC-Based FPGA Realization of a Spatially Rotating Translational Fractional-Order Multi-Scroll Grid Chaotic System
This paper proposes an algorithm and hardware realization of generalized chaotic systems using fractional calculus and rotation algorithms. Enhanced chaotic properties, flexibility, and controllability are achieved using fractional orders, a multi-scroll grid, a dynamic rotation angle(s) in two- and three-dimensional space, and translational parameters. The rotated system is successfully utilized as a Pseudo-Random Number Generator (PRNG) in an image encryption scheme. It preserves the chaotic dynamics and exhibits continuous chaotic behavior for all values of the rotation angle. The
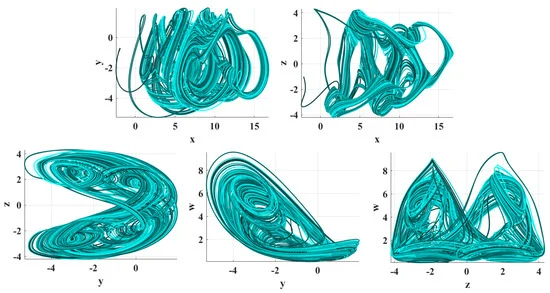
An Encryption Application and FPGA Realization of a Fractional Memristive Chaotic System
The work in this paper extends a memristive chaotic system with transcendental nonlinearities to the fractional-order domain. The extended system’s chaotic properties were validated through bifurcation analysis and spectral entropy. The presented system was employed in the substitution stage of an image encryption algorithm, including a generalized Arnold map for the permutation. The encryption scheme demonstrated its efficiency through statistical tests, key sensitivity analysis and resistance to brute force and differential attacks. The fractional-order memristive system includes a
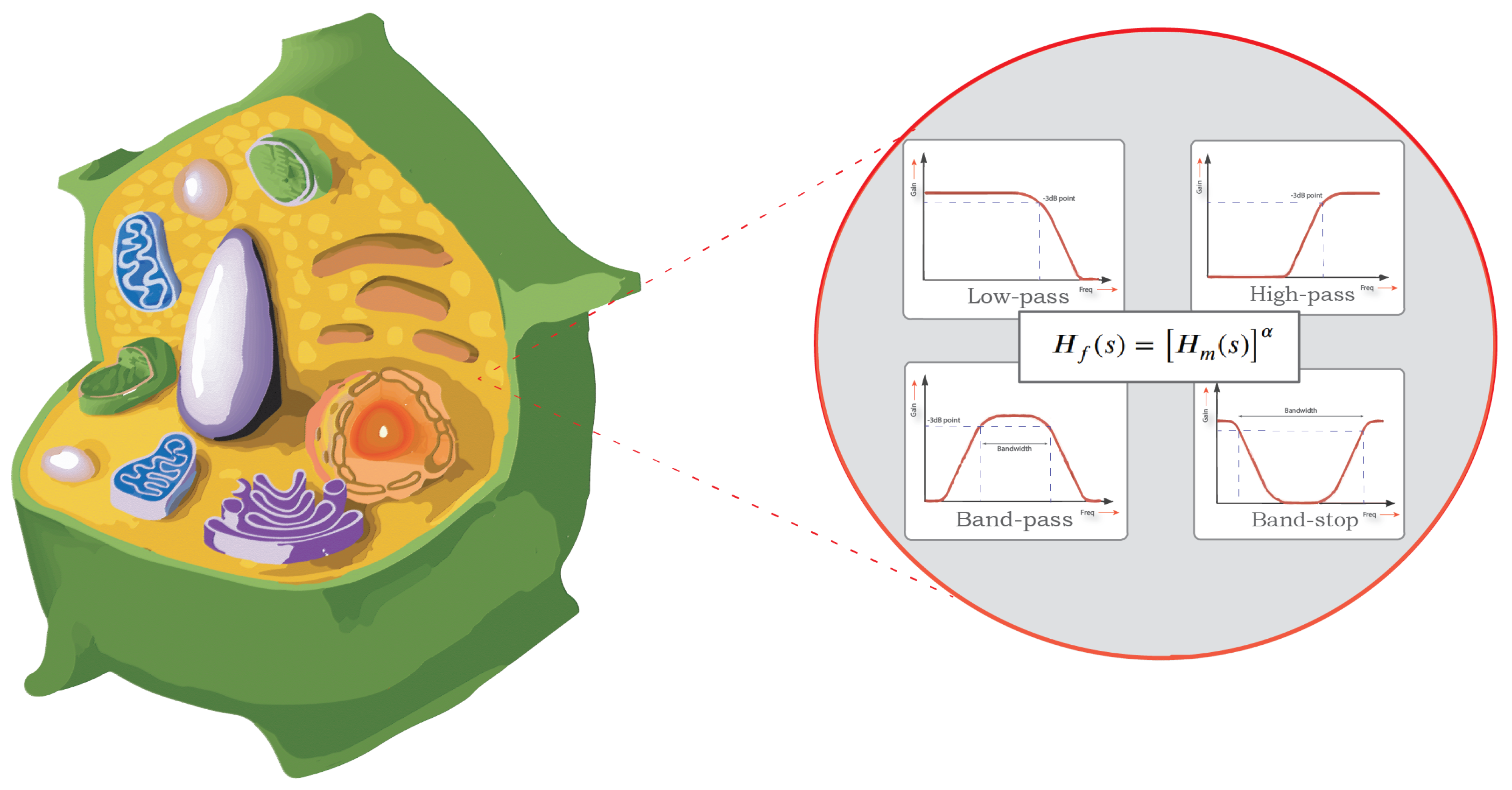
Plant Tissue Modelling Using Power-Law Filters
Impedance spectroscopy has became an essential non-invasive tool for quality assessment measurements of the biochemical and biophysical changes in plant tissues. The electrical behaviour of biological tissues can be captured by fitting its bio-impedance data to a suitable circuit model. This paper investigates the use of power-law filters in circuit modelling of bio-impedance. The proposed models are fitted to experimental data obtained from eight different fruit types using a meta-heuristic optimization method (the Water Cycle Algorithm (WCA)). Impedance measurements are obtained using a
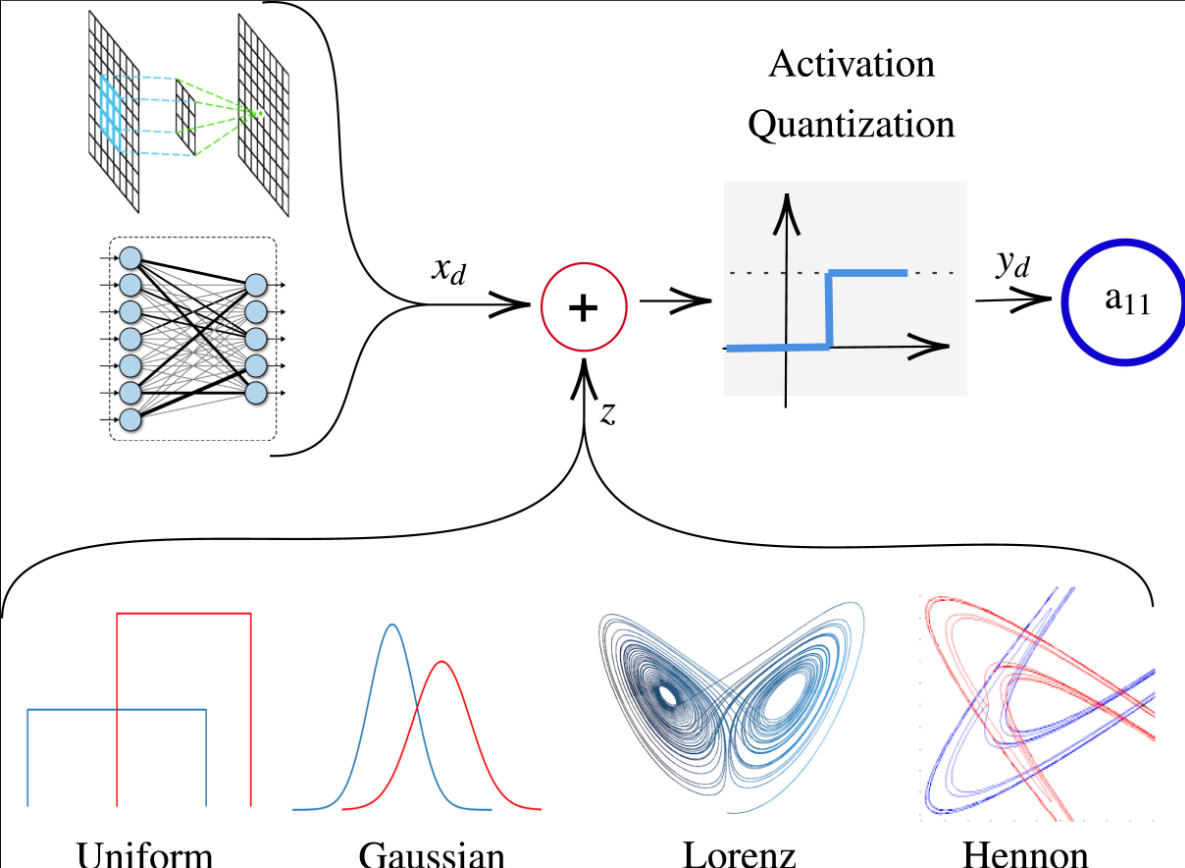
Chaotic neural network quantization and its robustness against adversarial attacks
Achieving robustness against adversarial attacks while maintaining high accuracy remains a critical challenge in neural networks. Parameter quantization is one of the main approaches used to compress deep neural networks to have less inference time and less storage memory size. However, quantization causes severe degradation in accuracy and consequently in model robustness. This work investigates the efficacy of stochastic quantization to enhance robustness and accuracy. Noise injection during quantization is explored to understand the impact of noise types and magnitudes on model performance
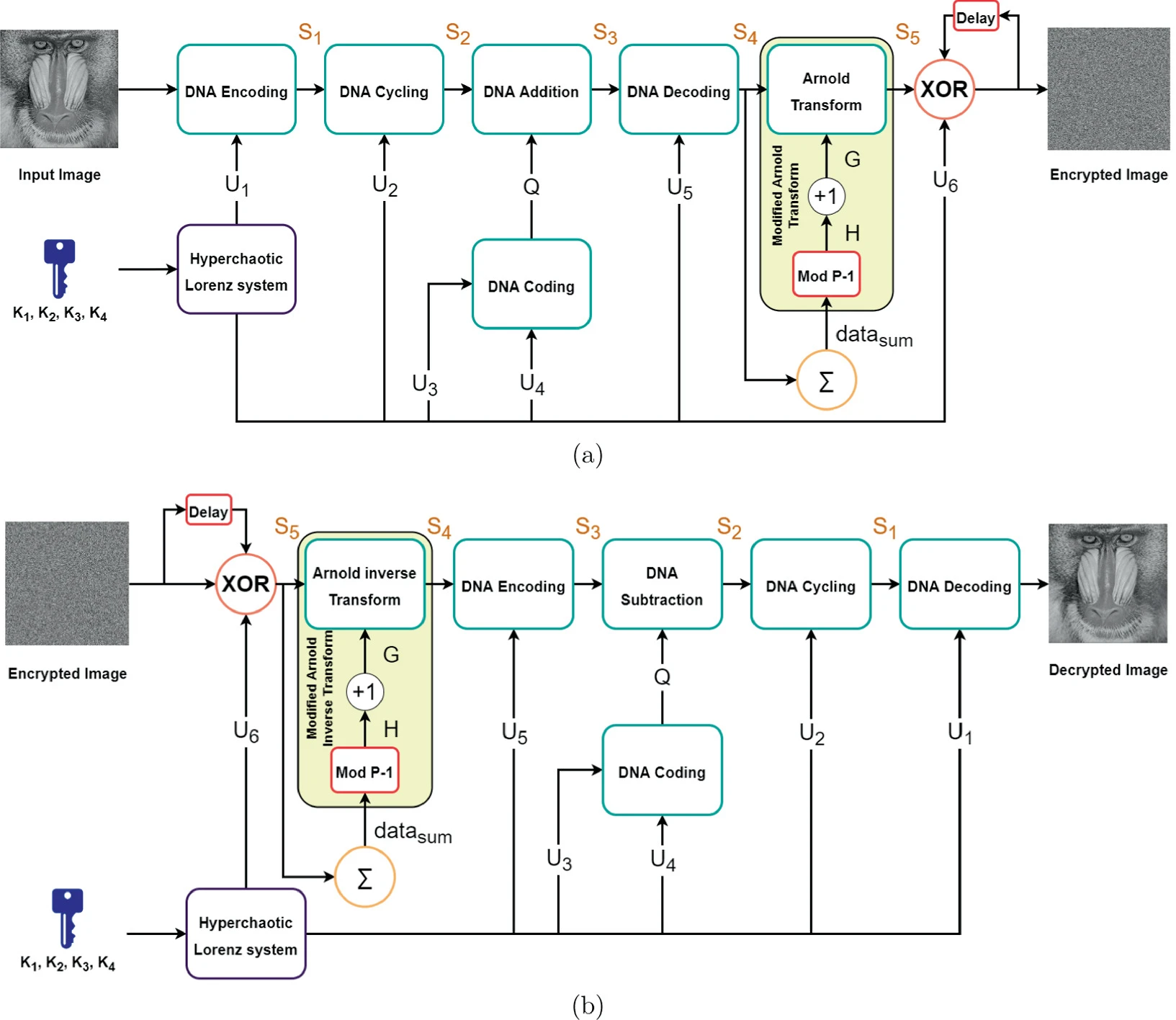
Chaos-Based Image Encryption Using DNA Manipulation and a Modified Arnold Transform
Digital images, which we store and communicate everyday, may contain confidential information that must not be exposed to others. Numerous researches are interested in encryption, which protects the images from ending up in the hands of unauthorized third parties. This paper proposes an image encryption scheme using chaotic systems, DNA manipulation, and a modified Arnold transform. Both DNA manipulation and hyperchaotic Lorenz system are utilized in the substitution of the images’ pixel values. An additional role of hyperchaotic Lorenz system is that it generates the random numbers required