Faculty Building
UB2
Office Number
S17
Ahmed Soltan received the B.Sc. and M.Sc. degrees from the University of Cairo, Cairo, Egypt, in 2004 and 2008, respectively. He received the Ph.D. degree in electronics and communication from Cairo University in 2014. He received the 2014–2016 best thesis award from Cairo for his Ph.D. thesis. He worked on circuit and system design and modelling in the fractional order domain during his Ph.D. research. He is currently an associate professor at Nile University, Egypt. He was a Research Associate and EDA/CAD Specialist with the School of Engineering, Newcastle University, Newcastle upon Tyne, U.K. He was a Teacher Assistant with the faculty of Engineering, Fayoum University, Fayoum, Egypt, for nine years and was an R&D Firmware Engineer for eight years. He also was an R&D Manager for an LED company at Qatar for one year and a half. His current research interests include smart energy harvesting systems and power management for biomedical implantable devices and lab-on-chip systems.
He is interested in the thermal impact of the implantable devices on human tissues, embedded system design for lab-on-chip system, the investigation of fractional circuits and systems, specifically in fractional order analog filters for signal processing, and fractional order modelling for biomedical applications. Dr. Soltan’s research aims to establish a new healthcare monitoring system and diagnosis on the fly by the development of autonomous devices. Dr. Soltan published more than 60 papers in a prestige journals. He got the award the best thesis award from Cairo University for 2014 and he got the State Encouragement Award in Egypt 2019 for his contribution in the field of biomedical research in Egypt and worldwide. He is won a Fellowship from Royal Academy of Engineering in Leaders in Innovations (LIF) and he is a fellow from the higher Academy of Education in the UK.
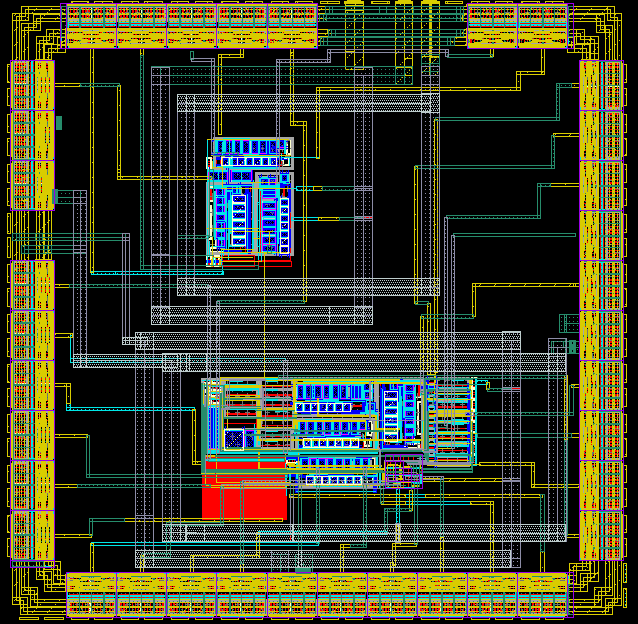
Cheap and Effective Device for Diagnosis on the Fly for Glucose Level in Human Body
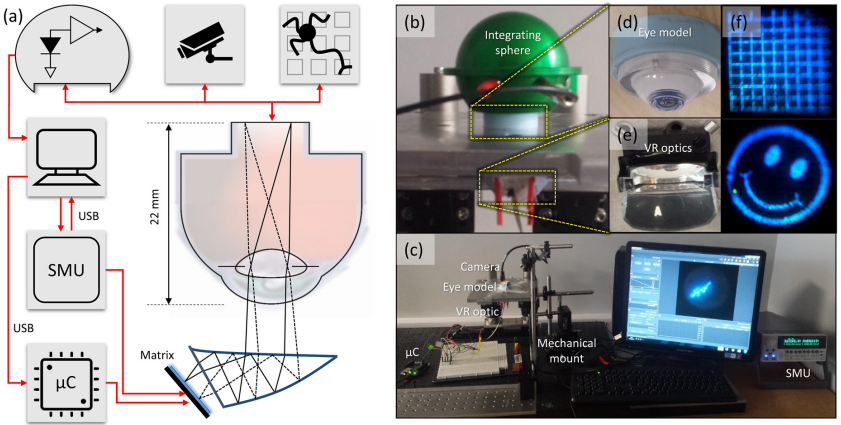
Fractional order Image Processing Platform for Retinal Pigmontosa Patients

IoT-based Platform for Wearable Devices for Continuous Healthcare Monitoring
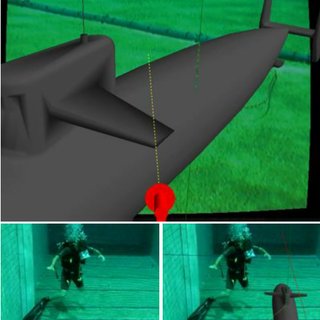
An Underwater AR based System for Marine Life Detection and Classification for Divers and Tourists
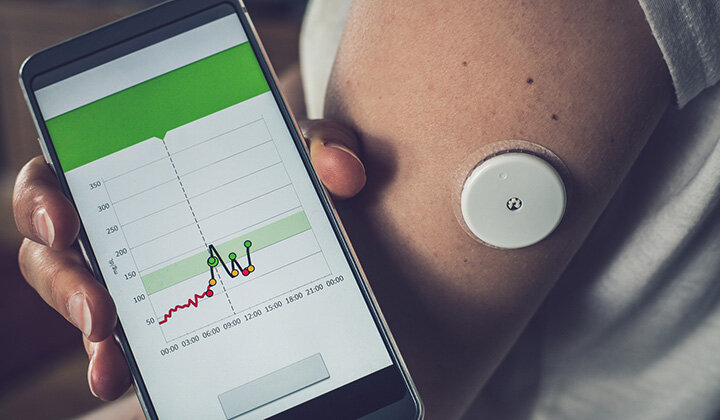
Pre-emergency Alert IoT System-based on Wearable Devices for Diabetic Patient
Low-Power Artificial Intelligence Framework for Internet of Things Applications