
Software and Communications
Joint Content Valuations and Proactive Caching for Content Distribution Networks
Due to the advances in machine learning techniques, recommender systems nowadays are capable of learning and influencing the users' decisions. Hence, recommendations became an important facility to reduce the cost (or increase the profit) of the operators of the demand networks. In this paper we formulate and study the problem of dynamically optimizing the demand shaping, through content recommendation, and proactive caching. The formulated problem suffers from the curse of dimensionality, so we devise an approximate algorithm optimizing only over a short look-ahead window. The approximate
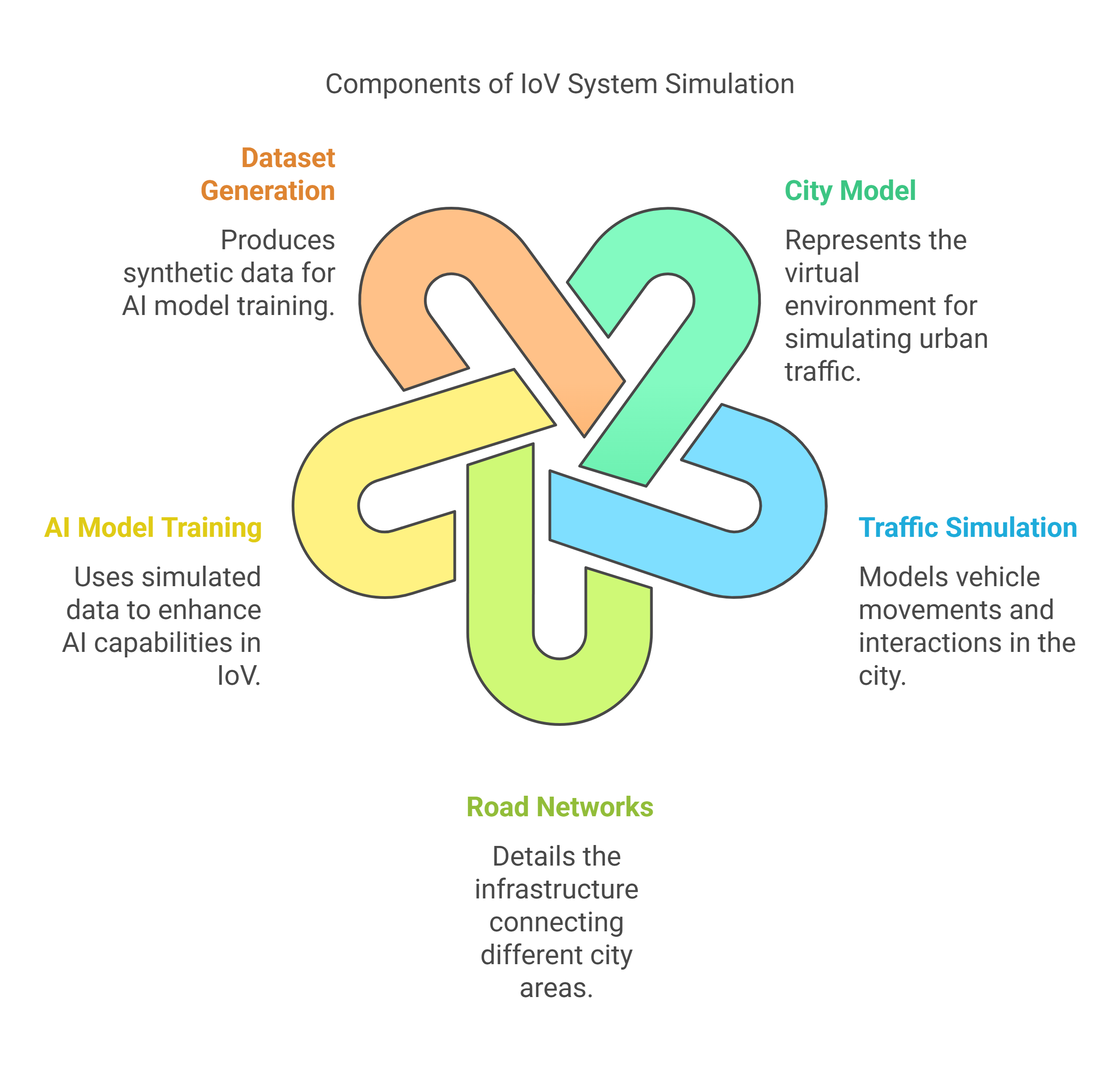
A Probabilistic City Model Generation for Application in Internet of Vehicles Technology
As the main pillar of the Smart City, Smart Highway manifests the centralized connectivity concept between the self-driving vehicles. Internet of Vehicle or IoV is the solution for improved connectivity between driverless vehicles. One of the major challenges in IoV research is the lack of datasets available. That is why the Internet of vehicles is one of the hot topics in research nowadays. IoV field is still a new topic in research, which leaves a huge shortage in the datasets available to train any Artificial Intelligent (AI) model for IoV systems. IoV systems have many research points such
Deep Learning-Based Context-Aware Video Content Analysis on IoT Devices
Integrating machine learning with the Internet of Things (IoT) enables many useful applica-tions. For IoT applications that incorporate video content analysis (VCA), deep learning models are usually used due to their capacity to encode the high-dimensional spatial and temporal representations of videos. However, limited energy and computation resources present a major challenge. Video captioning is one type of VCA that describes a video with a sentence or a set of sentences. This work proposes an IoT-based deep learning-based framework for video captioning that can (1) Mine large open-domain
A Generic AI-Based Technique for Assessing Student Performance in Conducting Online Virtual and Remote Controlled Laboratories
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic and the development of educational technology, e-learning has become essential in the educational process. However, the adoption of e-learning in sectors such as engineering, science, and technology faces a particular challenge as it needs a special Laboratory Learning Management System (LLMS) capable of supporting online lab activities through virtual and controlled remote labs. One of the most challenging tasks in designing such LLMS is how to assess a student's performance while an experiment is being conducted and how stuttering students can be automatically
Correction to: Optimization of energy-constrained wireless powered communication networks with heterogeneous nodes (Wireless Networks, (2019), 10.1007/s11276-017-1587-x)
The original version of this article contained error in author affiliation. Also, the article note and acknowledgement sections are missing. © 2018, Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Smart cloud platform for data management in the age of the internet of vehicles
Smart cars, with the emergence of the Internet of Vehicles (IoV), are expected to generate huge volumes of data at rates that typical data management systems will not be able to handle. Such data can be extremely useful to both analytics and machine learning applications. This paper discusses and demonstrates the process of architecting and building a scalable data management system for the IoV in a smart city environment, using Apache Spark, Apache Kafka and Apache Cassandra, which results in a scalable, resilient and fault-Tolerant data management system that facilitates performing big data

Design for Ergonomics: Application of Single- Passenger Electric Car via Design of Experiments
Design for Ergonomics is still an important concept in new product development. Although some assessment tools could predict if a certain posture is convenient, determining the ergonomics for a new product is still challenging. In this paper, a full factorial L32 Orthogonal Array design is used in the conceptual design phase for a single- passenger electric car. Design of experiments is used to find the significant variables affecting the comfort of the driver at different confidence levels. The significant variables are identified through Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) and response graph/

Integration of simulation modelling and lean management to improve patient flow at outpatient clinics
The outpatient clinics suffer from various inefficiencies such as long queues, long waiting times and low utilisation of medical resources. Simulation modelling and process improvement techniques have been applied separately to tackle such inefficiencies. This paper demonstrates how simulation modelling and lean management can be integrated to improve the patient flow and performance of outpatient clinics. The proposed framework for integrating lean and simulation consists of three main phases where the first phase includes the system description, data collection and analysis, and simulation
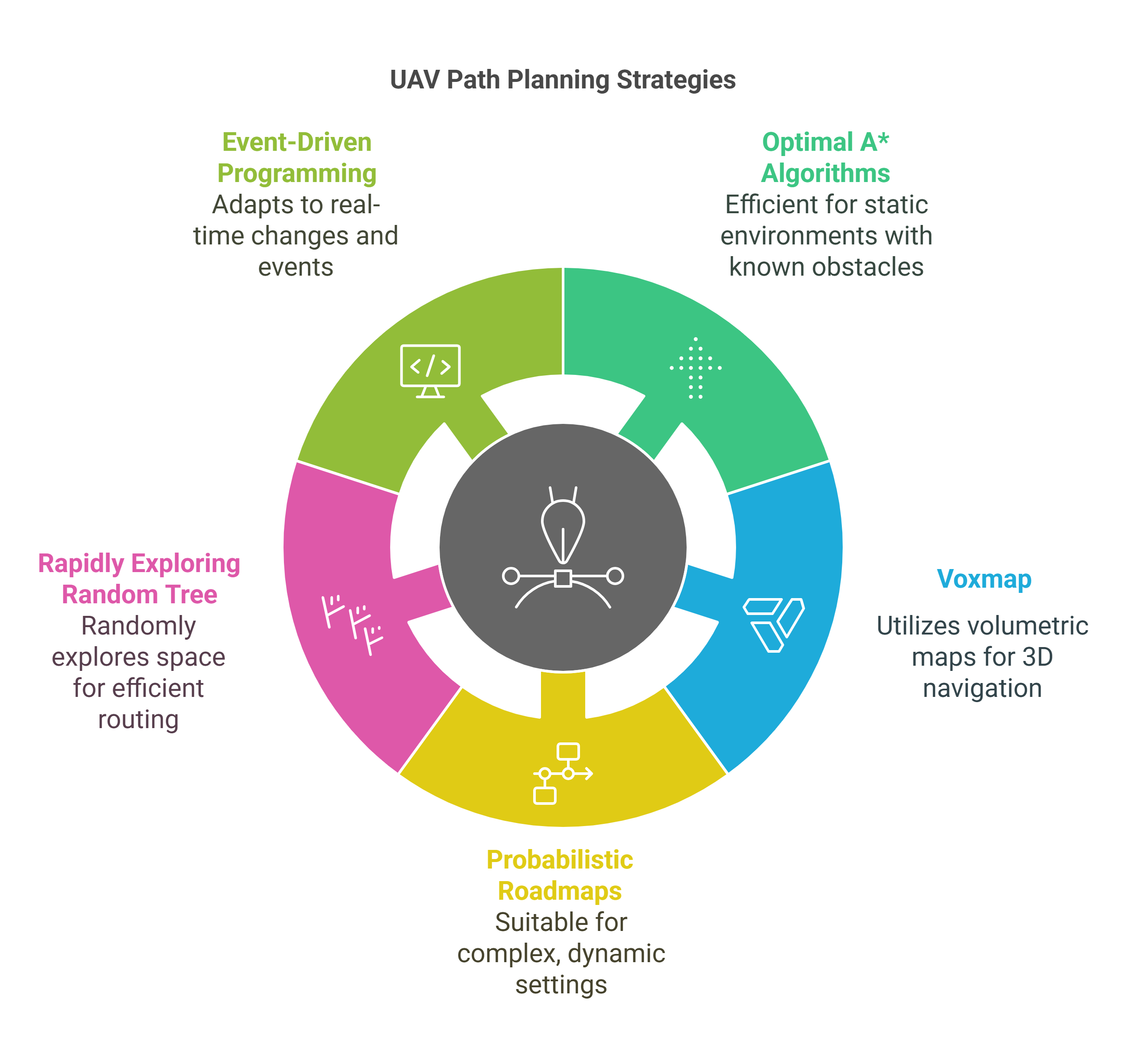
Event-driven programming-based path planning and navigation of UAVs around a complex urban environment
This chapter focuses on path planning techniques for autonomous navigation of small unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) in complex urban environments. It is difficult for UAVs to navigate at low altitudes in dynamic or complex urban environments because they encounter large structures, unpredictable or unrecognized environments, or other UAVs or obstacles flying in their path. Path planning is the core capability of an autonomous UAV to adapt dynamically in changing environments. This chapter will study and implement different path planning algorithms, slowly increasing complexity from optimal A
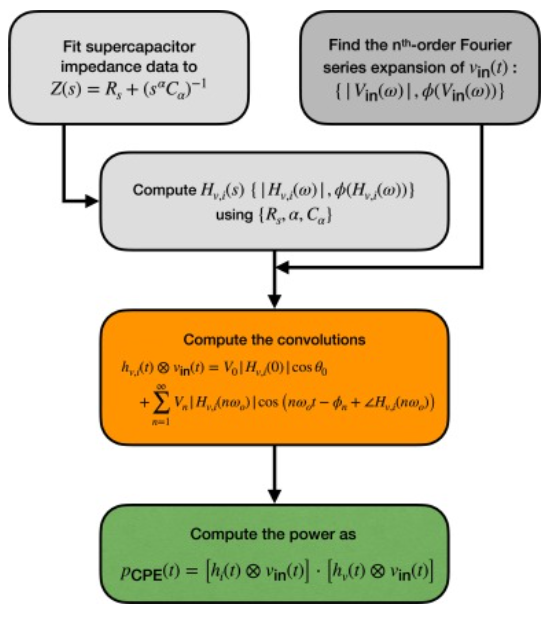
Time-domain response of supercapacitors using their impedance parameters and Fourier series decomposition of the excitation signal
Supercapacitors are mostly recognized for their high power density capabilities and fast response time when compared to secondary batteries. However, computing their power in response to a given excitation using the standard formulæof capacitors is misleading and erroneous because supercapacitors are actually non-ideal capacitive devices that cannot be characterized with a single constant capacitance. In this study we show how to estimate accurately the time-domain power and energy of supercapacitors in response to any excitation signal represented in terms of its Fourier series coefficients