
Healthcare
Transcriptomic marker screening for evaluating the mortality rate of pediatric sepsis based on Henry gas solubility optimization
Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening medical condition that increases mortality in pediatric populations admitted in the intensive care unit (ICU). Due to the unpredictable nature of the disease course, it was challenging to find the informative genetic biomarkers at the earliest stages. Consequently, a considerable attention has been paid for the early prediction of pediatric sepsis based on genetic biomarkers analysis that would promote the early medical intervention. Therefore, the proposed study attempted to demonstrate the feasibility of Henry Gas Solubility Optimization (HGSO) in
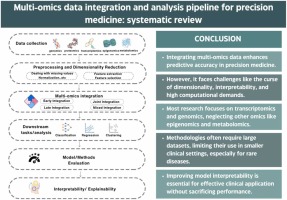
Multi-omics data integration and analysis pipeline for precision medicine: Systematic review
Precision medicine has gained considerable popularity since the “one-size-fits-all” approach did not seem very effective or reflective of the complexity of the human body. Subsequently, since single-omics does not reflect the complexity of the human body's inner workings, it did not result in the expected advancement in the medical field. Therefore, the multi-omics approach has emerged. The multi-omics approach involves integrating data from different omics technologies, such as DNA sequencing, RNA sequencing, mass spectrometry, and others, using computational methods and then analyzing the
New antileishmanial quinoline linked isatin derivatives targeting DHFR-TS and PTR1: Design, synthesis, and molecular modeling studies
In a search for new drug candidates for one of the neglected tropical diseases, leishmaniasis, twenty quinoline-isatin hybrids were synthesized and tested for their in vitro antileishmanial activity against Leishmania major strain. All the synthesized compounds showed promising in vitro activity against the promastigote form in a low micromolar range (IC50 = 0.5084–5.9486 μM) superior to the reference miltefosine (IC50 = 7.8976 μM). All the target compounds were then tested against the intracellular amastigote form and showed promising inhibition effects (IC50 = 0.60442–8.2948 μM versus 8.08
Genomic image representation of human coronavirus sequences for COVID-19 detection
Coronavirus (CoV) disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a severe pandemic affecting millions worldwide. Due to its rapid evolution, researchers have been working on developing diagnostic approaches to suppress its spread. This study presents an effective automated approach based on genomic image processing (GIP) techniques to rapidly detect COVID-19, among other human CoV diseases, with high acceptable accuracy. The GIP technique was applied as follows: first, genomic graphical mapping techniques were used to convert the genome sequences into genomic grayscale images. The frequency chaos game
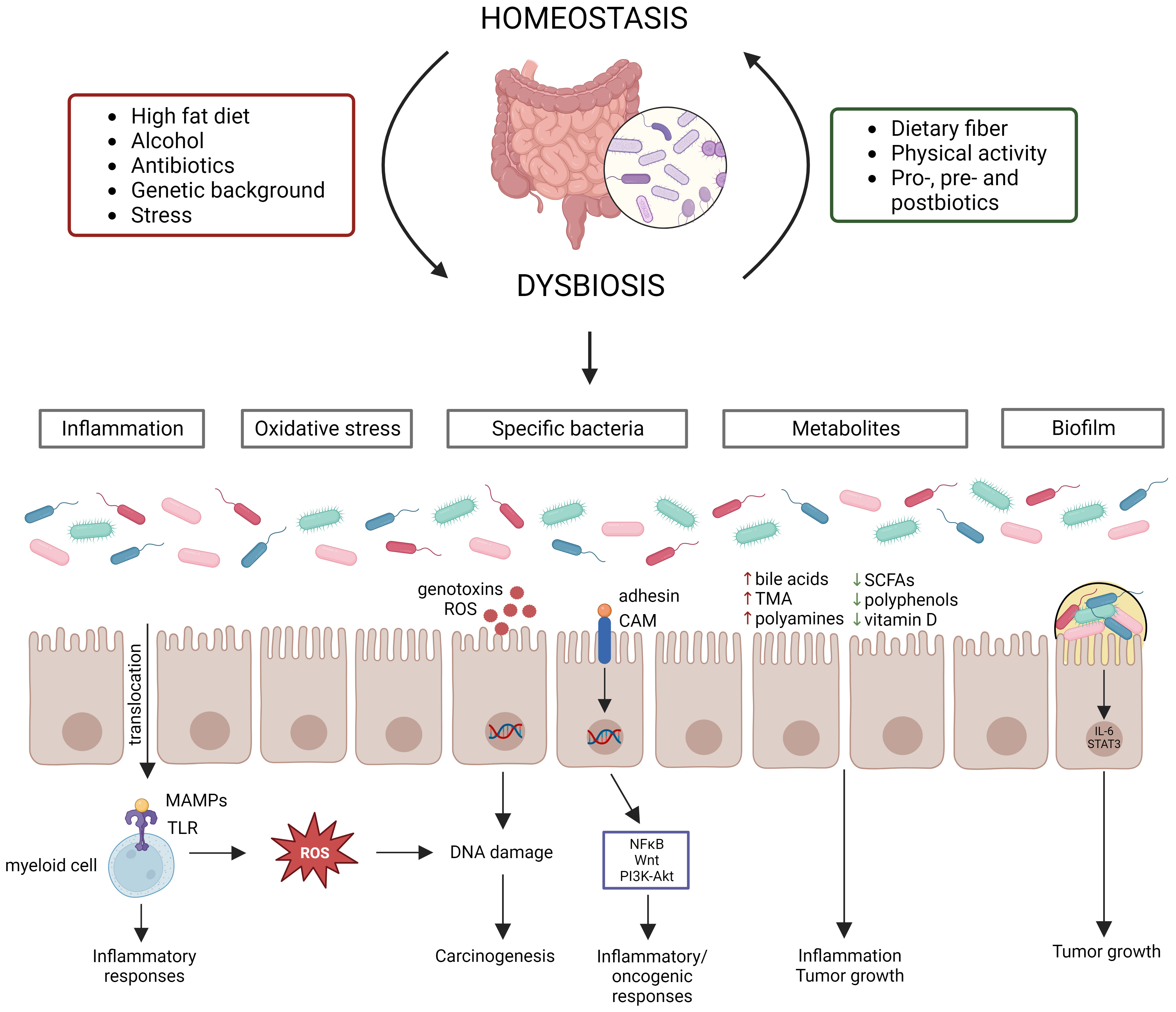
Dissecting the role of the gut microbiome and fecal microbiota transplantation in radio- and immunotherapy treatment of colorectal cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most commonly diagnosed cancers and poses a major burden on the human health worldwide. At the moment, treatment of CRC consists of surgery in combination with (neo)adjuvant chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy. More recently, immune checkpoint blockers (ICBs) have also been approved for CRC treatment. In addition, recent studies have shown that radiotherapy and ICBs act synergistically, with radiotherapy stimulating the immune system that is activated by ICBs. However, both treatments are also associated with severe toxicity and efficacy issues, which can
Clay chips and beads capture in situ barley root microbiota and facilitate in vitro long-term preservation of microbial strains
Capturing the diverse microbiota from healthy and/or stress resilient plants for further preservation and transfer to unproductive and pathogen overloaded soils, might be a tool to restore disturbed plant-microbe interactions. Here, we introduce Aswan Pink Clay as a low-cost technology for capturing and storing the living root microbiota. Clay chips were incorporated into the growth milieu of barley plants and developed under gnotobiotic conditions, to capture and host the rhizospheric microbiota. Afterward, it was tested by both a culture-independent (16S rRNA gene metabarcoding) and
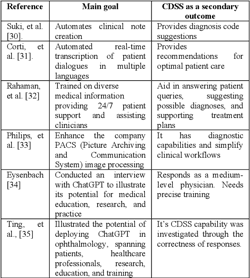
A Review of the Role of ChatGPT for Clinical Decision Support Systems
The development of artificial intelligence (AI) provided powerful assistant tools for humans in various aspects. Healthcare is rapidly evolving, with AI playing a crucial role in improving patient care. The extensive use of AI in Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS) enables providing real-time evidence-based recommendations to healthcare professionals at the point of Care. The AI chatbot ChatGPT proved its ability to solve several natural language processing tasks. One notable advancement is the integration of ChatGPT into Clinical Decision Support Systems. ChatGPT, despite not being

Harris Hawks Feature Optimization for Identifying the Informative Pathogens of Pediatric Sepsis
One of the most fatal potentially life-threatening medical condition that increases the mortality in pediatric populations is pediatric sepsis. Unfortunately, the improper control of such disease can lead to tissue damage and organ dysfunction because of the overwhelming the human body's response to an infection. Therefore, early recognition and intervention can clearly improve outcome for infants and children with conditions that lead to sepsis before the admission to the intensive care unit (ICU). Accordingly, 17 informative differential expressed genes have been selected using a nature
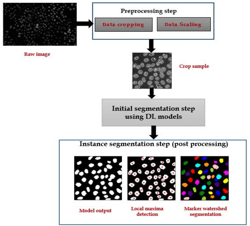
A comparative study for nuclei segmentation using latest deep learning optimizers
Nuclei segmentation is a critical task in biological image analysis, with numerous applications in cancer diagnosis, grading, staging, and treatment planning. However, this task is challenging, particularly when dealing with low-resolution and low signal-to-noise ratio microscopy images. Segmentation problems arise, such as touching and missing cells, which make the process even more challenging. Deep learning models, including Attention U-Net and TransUNet, have demonstrated exceptional performance in medical image segmentation. Nonetheless, the choice of optimizer can significantly impact
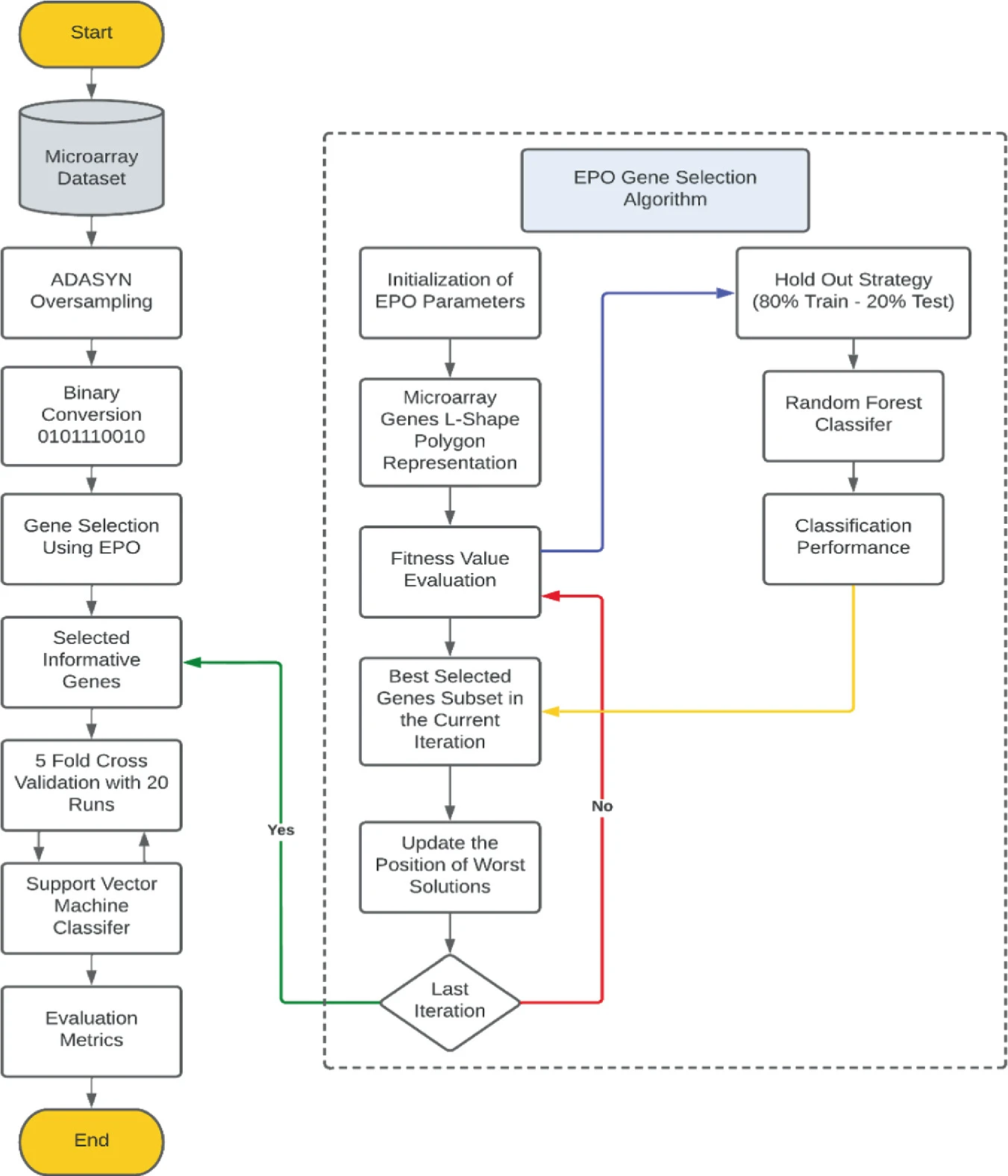
Computational Microarray Gene Selection Model Using Metaheuristic Optimization Algorithm for Imbalanced Microarrays Based on Bagging and Boosting Techniques
Genomic microarray databases encompass complex high dimensional gene expression samples. Imbalanced microarray datasets refer to uneven distribution of genomic samples among different contributed classes which can negatively affect the classification performance. Therefore, gene selection from imbalanced microarray dataset can give rise to misleading, and inconsistent nominated genes that would alter the classification performance. Such unsatisfactory classification performance is due to the skewed distribution of the samples across the microarrays toward the majority class. In this paper, we