
Energy and Water
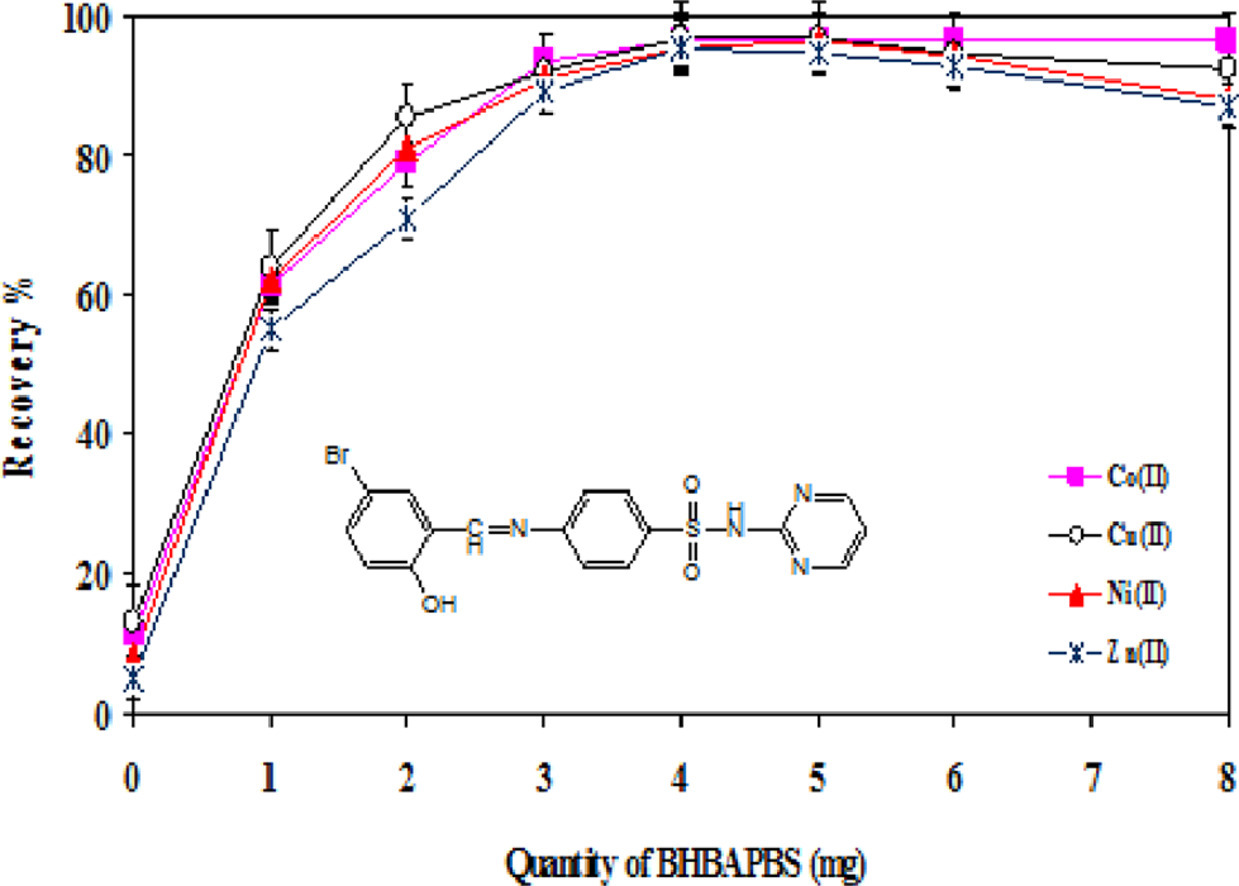
Utilizing a newly developed carrier element free coprecipitation method for preconcentration and quantification of Co(II), Cu(II), Ni(II), and Zn(II) in environmental samples
Co(II), Cu(II), Ni(II), and Zn(II) ions from food and water sample have been separated and preconcentrated using a novel, straightforward, and precise carrier element-free coprecipitation approach. The suggested procedure relied on the utilization of 4-(5‑bromo-2-hydroxybenzylideneamino)-N-(pyrimidin-2-yl)-benzenesulfonamide (BHBAPBS) as a novel co-precipitant at neutral medium and the flame atomic absorption spectrometry identification of the studied metal ions under investigation. To obtain the metal ions for analysis, Several variables, like pH, volume of the sample, co-precipitant amount
Joint Content Valuations and Proactive Caching for Content Distribution Networks
Due to the advances in machine learning techniques, recommender systems nowadays are capable of learning and influencing the users' decisions. Hence, recommendations became an important facility to reduce the cost (or increase the profit) of the operators of the demand networks. In this paper we formulate and study the problem of dynamically optimizing the demand shaping, through content recommendation, and proactive caching. The formulated problem suffers from the curse of dimensionality, so we devise an approximate algorithm optimizing only over a short look-ahead window. The approximate
Deep Learning-Based Context-Aware Video Content Analysis on IoT Devices
Integrating machine learning with the Internet of Things (IoT) enables many useful applica-tions. For IoT applications that incorporate video content analysis (VCA), deep learning models are usually used due to their capacity to encode the high-dimensional spatial and temporal representations of videos. However, limited energy and computation resources present a major challenge. Video captioning is one type of VCA that describes a video with a sentence or a set of sentences. This work proposes an IoT-based deep learning-based framework for video captioning that can (1) Mine large open-domain
Correction to: Optimization of energy-constrained wireless powered communication networks with heterogeneous nodes (Wireless Networks, (2019), 10.1007/s11276-017-1587-x)
The original version of this article contained error in author affiliation. Also, the article note and acknowledgement sections are missing. © 2018, Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Robust adaptive supervisory fractional order controller for optimal energy management in wind turbine with battery storage
To address the challenges of poor grid stability, intermittency of wind speed, lack of decision-making, and low economic benefits, many countries have set strict grid codes that wind power generators must accomplish. One of the major factors that can increase the efficiency of wind turbines (WTs) is the simultaneous control of the different parts in several operating area. A high performance controller can significantly increase the amount and quality of energy that can be captured from wind. The main problem associated with control design in wind generator is the presence of asymmetric in the
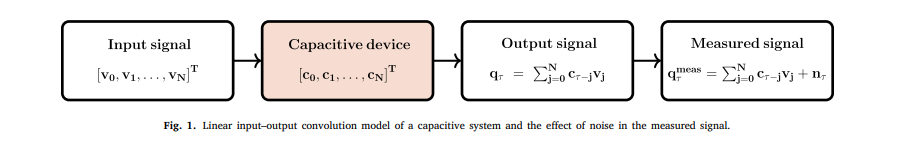
Tikhonov regularization for the deconvolution of capacitance from the voltage–charge response of electrochemical capacitors
The capacitance of capacitive energy storage devices cannot be directly measured, but can be estimated from the applied input and measured output signals expressed in the time or frequency domains. Here the time-domain voltage–charge relationship of non-ideal electrochemical capacitors is treated as an ill-conditioned convolution integral equation where the unknown capacitance kernel function is to be found. This comes from assuming a priori that in the frequency domain the charge is equal to the product of capacitance by voltage, which is in line with the definition of electrical impedance

Approximation and realization of power-law all-pass filters
Non-integer power-law all-pass transfer functions, are approximated by suitable integer-order transfer functions in this work. The derivation of the integer-order transfer functions is based on the analytic expansion of the (non-integer) power-law transfer functions through the utilization of the binomial theorem. The offered benefit is the derivation of stable integer-order transfer functions. This study is supported by experimental results, obtained using a Field Programmable Analog Array device, after the employment of curve fitting based approximation techniques. © 2022 Elsevier GmbH
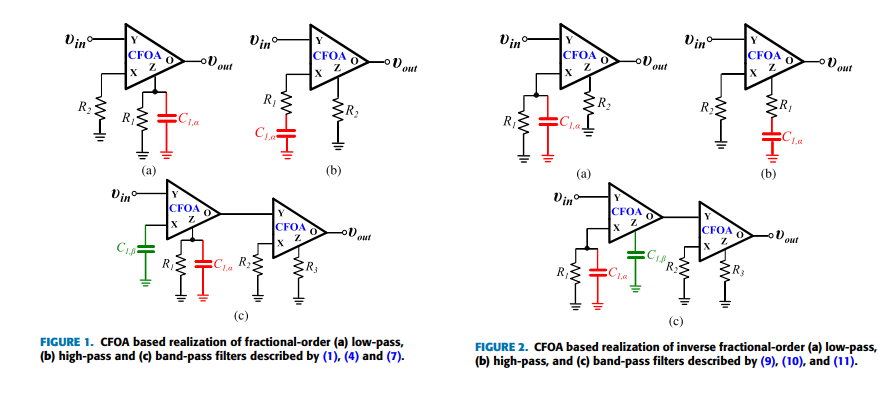
Non-Integer Order Generalized Filters Designs
Non-integer order filters can be derived from a generalized structure presented in this work. More specifically, fractional-order and power-law filters of single- or double-order are special cases of non-integer order filters with three degrees of freedom and can be implemented using a Current Feedback Operational Amplifier as the active element. The transfer function is formed as a ratio of two impedances which can be synthesized using Foster or Cauer RC networks. A curve-fitting based technique is employed for approximating the magnitude and phase of each impedance. The behavior of the

In-Memory Associative Processors: Tutorial, Potential, and Challenges
In-memory computing is an emerging computing paradigm that overcomes the limitations of exiting Von-Neumann computing architectures such as the memory-wall bottleneck. In such paradigm, the computations are performed directly on the data stored in the memory, which highly reduces the memory-processor communications during computation. Hence, significant speedup and energy savings could be achieved especially with data-intensive applications. Associative processors (APs) were proposed in the seventies and recently were revived thanks to the high-density memories. In this tutorial brief, we
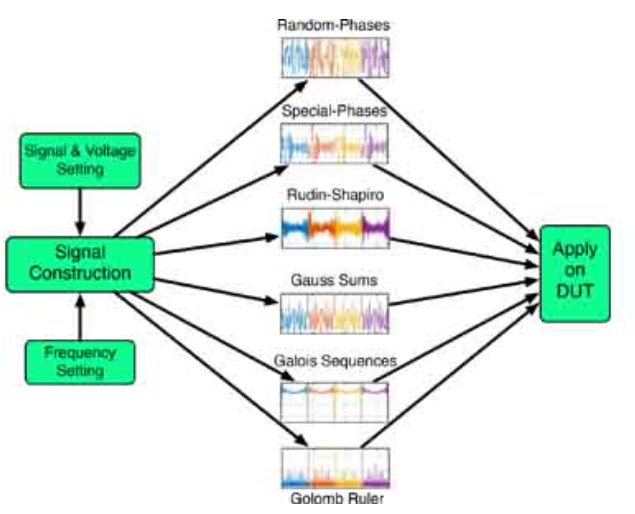
Wide Bandwidth Signals for Joint Time-Frequency Characterization of Nonlinear and Time-Varying Circuits
In this work, we generate and use a total of six different wideband signals for joint time-frequency characterization of nonlinear time-invariant [N-shaped differential resistor (NDR)] and linear time-varying (thermistor) circuits. A data acquisition board is used for applying the signals in the form of a voltage excitation and reading the induced current. The input signals have flat power spectra, thus avoiding the need for iterative calibration loops required to obtain signals with low crest factor. Such iterative loops are unavoidable when using random, pseudorandom, or chaotic signals all