
Circuit Theory and Applications

OMICS and bioinformatics in Parkinson disease and related movements disorders
This chapter explores the integration of omics and bioinformatics for Parkinson's disease (PD) diagnosis and potential cure discovery. It begins with an overview of PD and its prevalence, followed by an examination of key mutations in genes linked to the disease. These mutations lead to dysfunctional proteins, triggering PD progression. The chapter delves into techniques like whole-exome sequencing (WES), genome-wide association sequencing (GWAS), and whole-genome sequencing (WGS). These methods enable the exploration of omics levels such as lipidomics, metabolomics, genomics, and proteomics

Stem cell for PD: Technical considerations
The emergence of very sophisticated stem therapy or regenerative medicine can be attributed to the identification and extraction of pluripotent ESCs. This breakthrough resolved the ethical dilemma linked to embryonic stem cells and facilitated the initiation of clinical trials and subsequent rapid progress in the subsequent years. This chapter explores the prospect of stem cell therapy as a treatment for Parkinson's disease (PD), a degenerative neurological condition. The text commences by providing an overview of stem cells, clarifying their distinct regenerative characteristics and their
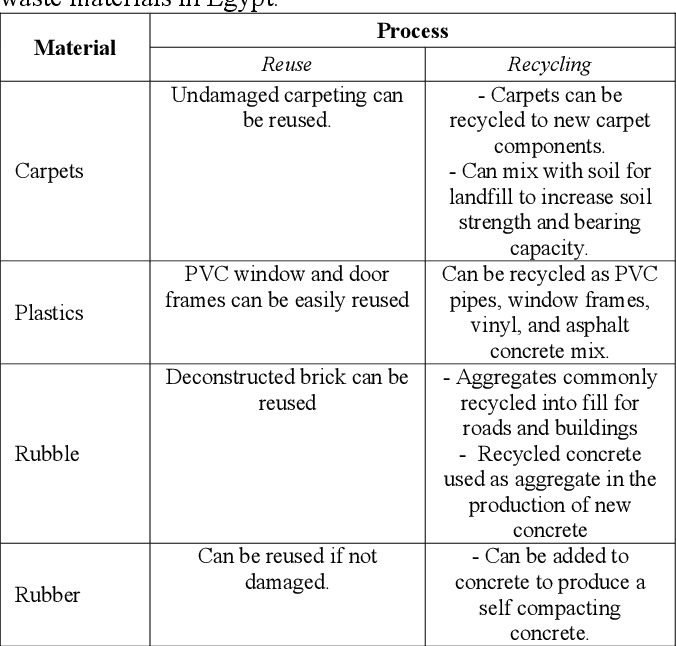
Utilization of Construction and Demolition Waste Materials in landscaping
Construction wastes have become the largest source of different solid wastes in Egypt as construction and demolition processes generates millions of tons of construction and demolishing wastes every year. The increasing generation of construction and demolishing wastes has caused huge impacts to the environment and agitated growing public concern in the local community. Therefore, the minimization of construction and demolishing wastes has turned into an imperative factor. The main purpose of this research is to provide a comprehensive overview of reusing and recycling construction and
Humanizing Smart Cities: A Preconception to a Better Life for All
As cities face the challenge of conceiving new and more competitive and sustainable development models, there has been an emergence of introducing technology to cities to enhance the quality of life it provides to the citizens. The 'Smart City' was proposed as a new prototype of technology-based urban development. These smart cities witness the emergence of the metaverse and platform societies, machine learning and artificial intelligence (ML/AI), big data, the Internet of Things (IoT) systems, and many other innovative and advanced technologies. However, the idea of the Smart City has
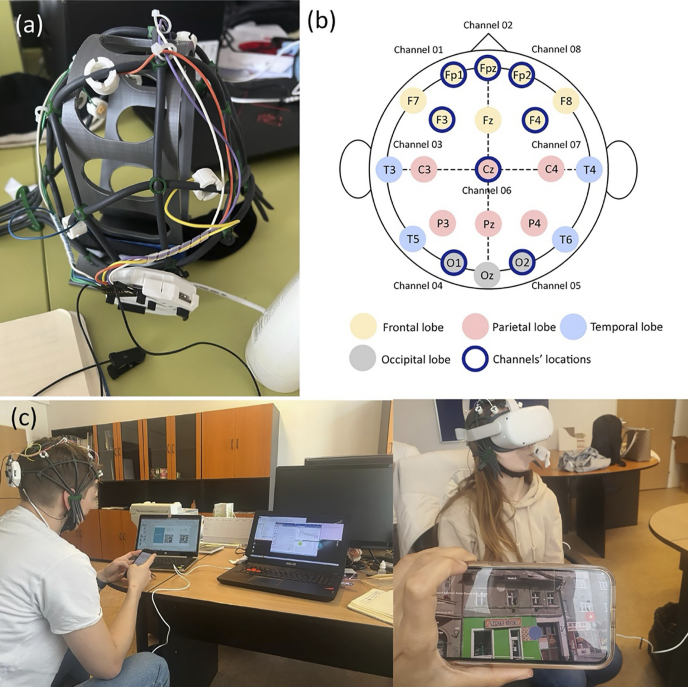
Exploring the restorative environments in Bratislava using EEG and VR: a neuro-urbanism approach
Purpose: Residing in a densely populated urban area possesses its allure; nonetheless, it can significantly impact physical and mental well-being owing to the persistent stress and information overload inherent in urban settings. This study aims to introduce a neuro-urbanism framework that can guide urban planners and designers in quantitatively evaluating individuals' responses to virtual simulated environments. Design/methodology/approach: Our study consisted of two phases after randomly selecting six locations representing three types of urban areas in Bratislava, Slovakia: urban spaces
The architectural features of socio-spatial transformation in Hassan Al-Imam’s Cairo Trilogy
The urban scenery that dominated Cairo since the nineteenth century was a spatial superimposition of tradition and modernity, represented in the social and architectural composition of the city. The cinematic medium in Egypt attempted to visualize such overlap through a vivid depiction of spatial transformations occur-ring within the micro and macro urban levels revealing hidden aspects of social order and organizational behaviour. This article sheds light on Egyptian filmmaker Hassan Al-Imam’s Cairo Trilogy films, based on the critically acclaimed novels by Nobel Prize laureate Naguib Mahfouz
Young people’s preferences in public spaces
Purpose: Few public places are designed with due consideration to the needs and preferences of teens. Teens in public spaces are often viewed with apprehension from other user groups. Teens hanging out in public spaces are always observed with caution and are sometimes associated with negative behaviour by other community members. In designing public spaces that are suitable for the teens and not alienating them to other members of the community, it is necessary to understand how teens perceive their environment and what they expect from it. The psychological, social and emotional development
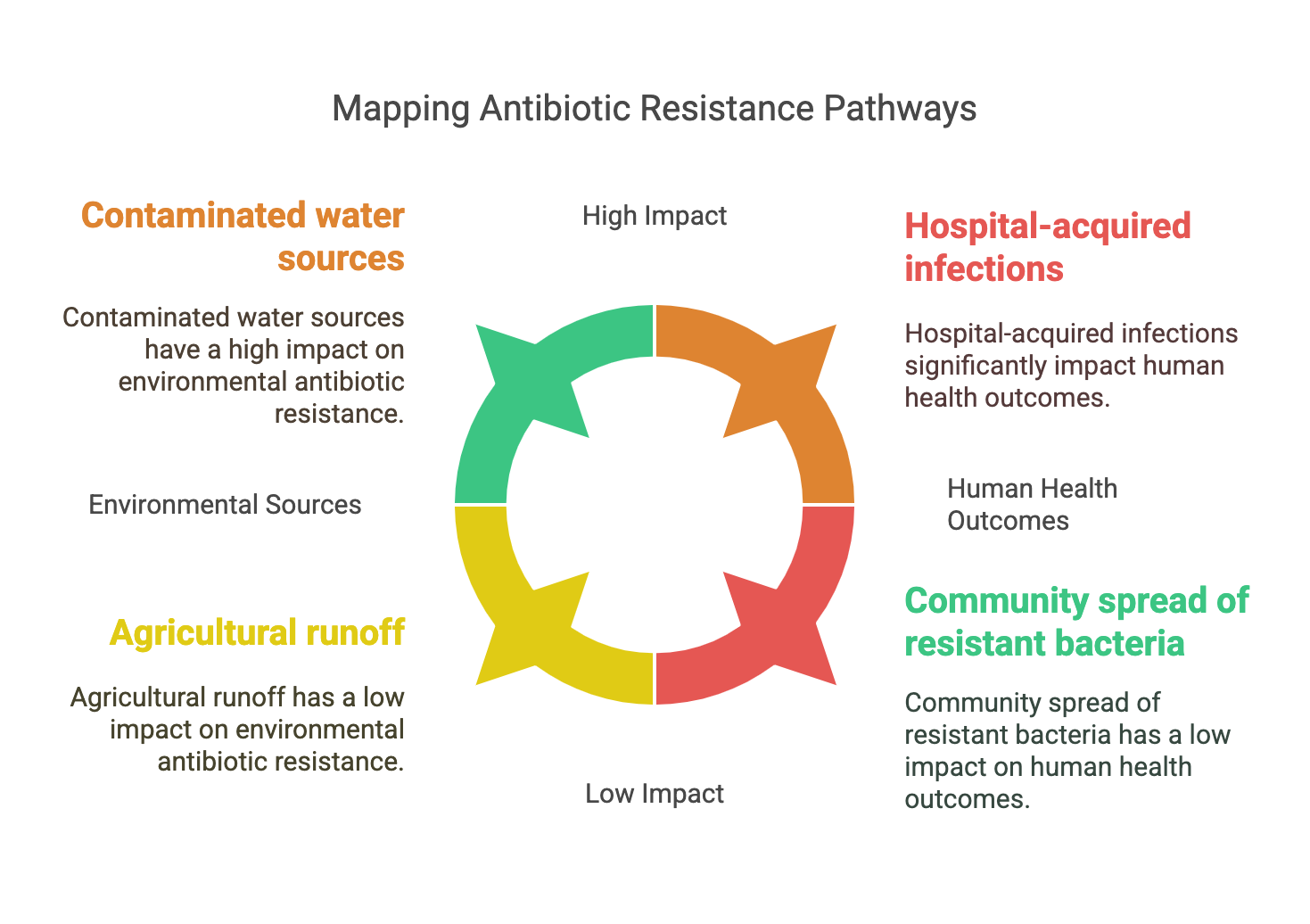
Tracking Antibiotic Resistance from the Environment to Human Health
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is one of the threats to our world according to the World Health Organization (WHO). Resistance is an evolutionary dynamic process where host-associated microbes have to adapt to their stressful environments. AMR could be classified according to the mechanism of resistance or the biome where resistance takes place. Antibiotics are one of the stresses that lead to resistance through antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs). The resistome could be defined as the collection of all ARGs in an organism’s genome or metagenome. Currently, there is a growing body of evidence
In-Silico targeting of SARS-CoV-2 NSP6 for drug and natural products repurposing
Non-Structural Protein 6 (NSP6) has a protecting role for SARS-CoV-2 replication by inhibiting the expansion of autophagosomes inside the cell. NSP6 is involved in the endoplasmic reticulum stress response by binding to Sigma receptor 1 (SR1). Nevertheless, NSP6 crystal structure is not solved yet. Therefore, NSP6 is considered a challenging target in Structure-Based Drug Discovery. Herein, we utilized the high quality NSP6 model built by AlphaFold in our study. Targeting a putative NSP6 binding site is believed to inhibit the SR1-NSP6 protein-protein interactions. Three databases were
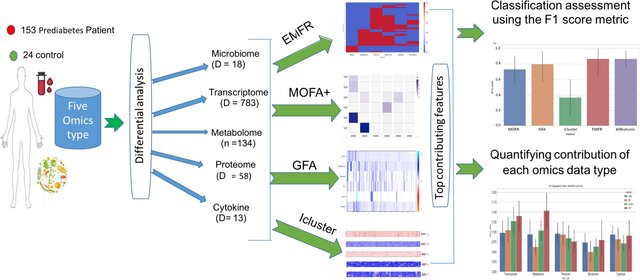
Comparative evaluation of multiomics integration tools for the study of prediabetes: insights into the earliest stages of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D) remains a critical health concern, particularly in its early disease stages such as prediabetes. Understanding these early stages is paramount for improving patient outcomes. Multiomics data integration tools offer promise in unraveling the underlying mechanisms of T2D. The advent of high-throughput technology and the increasing availability of multiomics data has led to the development of several statistical and network-based integration methods. However, the performance of such methods varies, requiring their output evaluation in an unbiased manner. Here, we