

Type 2 Diabetes (T2D) is a complex chronic illness that affects around 90% of diabetic patients worldwide. Prediabetes is an elementary phase for T2D that is recommended to be early diagnosed to prevent its progression. In this study, we used 16S rRNA data from the gut and nasal cavity of prediabetic and control patients to identify common and exclusive diabetic pathways for each body site. Furthermore, using the Phylogenetic Investigation of Communities by Reconstruction of Unobserved States (PICRUSt) as well as MicobiomeExplorer in the pathway enrichment analysis, we also identified the

The Immune Checkpoint Blockade has transformed cancer treatment. Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte Associated Protein 4 (CTLA4), Programmed death-1 (PD-1) are antibodies that block immune checkpoint proteins that have been FDA approved for treating a variety of cancers including melanoma, renal carcinoma, and non-small cell lung cancer. Immunotherapy tend to stimulate the immune system of patients to detect and kill cancer cells while sparing normal cells by using checkpoints such as CTLA-4 and PD-1, which are molecules on immune cells that are turned on or off to allow the immune response to begin
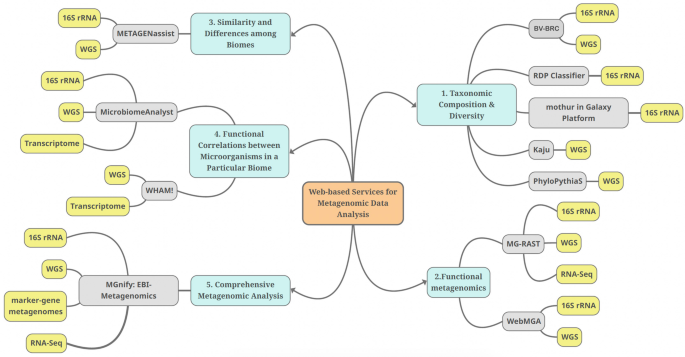
Recently, sequencing technologies have become readily available, and scientists are more motivated to conduct metagenomic research to unveil the potential of a myriad of ecosystems and biomes. Metagenomics studies the composition and functions of microbial communities and paves the way to multiple applications in medicine, industry, and ecology. Nonetheless, the immense amount of sequencing data of metagenomics research and the few user-friendly analysis tools and pipelines carry a new challenge to the data analysis. Web-based bioinformatics tools are now being developed to facilitate the

Fall prediction is a critical process in ensuring the safety and well-being of individuals, particularly the elderly population. This paper focuses on the development of a fall detection and prediction system using wearable sensors and machine learning algorithms. The system issues an alarm upon predicting the occurrence of falling and sends alerts to a monitoring centre for timely assistance. Wearable sensor devices, including Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs) equipped with accelerometers, gyroscopes, and magnetometers are utilized for data collection. UPFALL, a comprehensive online freely

This paper tackles the problem of generating pho-torealstic images of synthetically rendered human avatar faces from computer graphics engines, our approach leverages the high capabilities of generative models as StyleGAN that can generate high quality human faces that are hard to distinguish from real human faces images. We present a framework that effectively bridges the gap between synthetic and real domain through Single shot GAN inversion that maps the synthetic image into the real latent space of StyleGAN. Benchmarks and Quantitative results show that our method demonstrate significant
Omnidirectional mobile robots are considered for many research applications due to their maneuverability in tight spaces and smoothness of motion. This paper presents a novel design of a T-model mecanum wheeled mobile robot (3-MWMR), the derivation of the inverse and forward kinematics model of the proposed robot, the physical body design of the proposed T-model shape, the simulation of the system dynamics and omnidirectional capabilities of the robot on CoppeliaSim V-rep and MATLAB. The experimental results obtained validates the proof of concept of the proposed model for reduced power losses
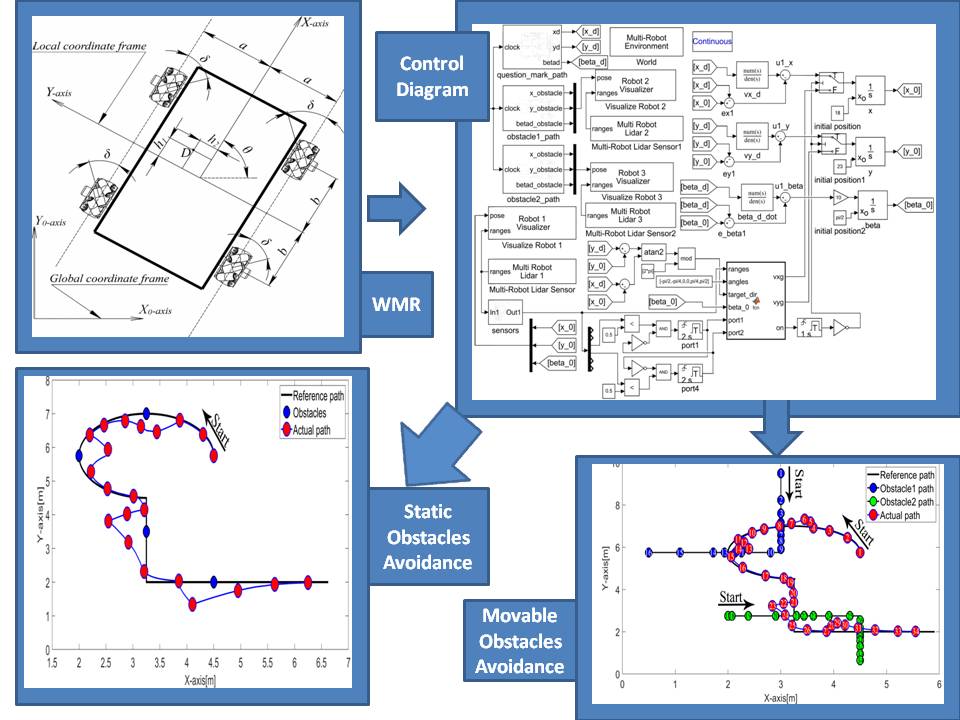
mobile robots play an enormous role in different fields of daily life applications including military, safety, and logistic multi-tasking capabilities. A new approach is introduced to the market which is the 3 Mecanum wheeled mobile robot (3-MWMR) is being tested and validated. The main goal of the proposed design is to achieve all the desired directions of motion and to improve the performance of the mobile robot in avoiding obstacles using the fuzzy logic controller. © 2022 IEEE.
The Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) system is one of the essential human-computer interface applications. Despite the rapid advancement of technology, there is still a gap in SER research in the Arabic language corpus. The goal of this research is to build an Arabic-based SER based on a feature set that has both high performance and low computational cost. Two novel feature sets were implemented using a mix of spectral and prosodic features. An Arabic semi-natural corpus 'EYASE' was adopted for testing the proposed system. Five machine learning classifiers using the different feature sets
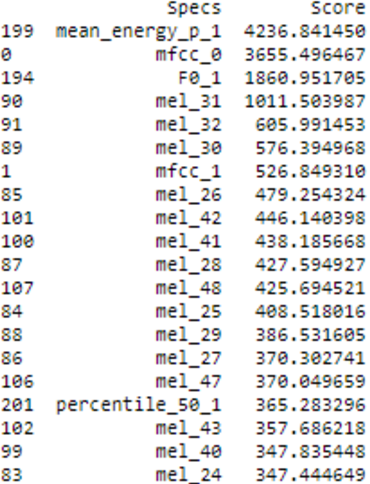
The Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) system is an approach to identify individuals' emotions. This is important for human-machine interface applications and for the emerging Metaverse. This work presents a bilingual Arabic-English speech emotion recognition system based on EYASE and RAVDESS datasets. A novel feature set was composed by using spectral and prosodic parameters to obtain high performance at a low computational cost. Different classification models were applied. These machine learning classifiers are Random Forest, Support Vector Machine, Logistic Regression, Multi-Layer Perceptron
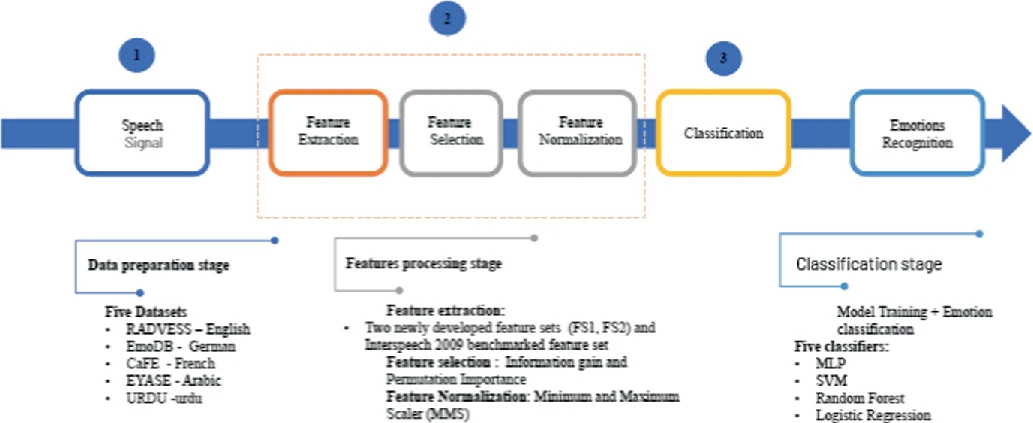
Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) systems are widely regarded as essential human-computer interface applications. Extracting emotional content from voice signals enhances the communication between humans and machines. Despite the rapid advancement of Speech Emotion Recognition systems for several languages, there is still a gap in SER research for the Arabic language. The goal of this research is to build an Arabic-based SER system using a feature set that has both high performance and low computational cost. Two novel feature sets were created using a mix of spectral and prosodic features