
Circuit Theory and Applications
Thermal Air Braking
This paper introduces the concept of thermal air braking, which involves heating a portion of the airfoil's upper surface to achieve the braking effect. A 2D Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) analysis is conducted using ANSYS Fluent software to study the impact of heating the upper back portion of the top surface of an airfoil. The study compares the results of the heated and non-heated cases for NACA 4415. Different aerodynamic efficiencies are investigated, such as lift coefficient (CL), drag coefficient (CD), lift-to-drag coefficient (CL/CD), and pressure coefficient (CP). The results are

Modeling and Control of a Novel Design of Series Elastic Actuator for Upper Limb Rehabilitation
The field of rehabilitation robotics for upper limb assistance has grown rapidly in the past few years. Rehabilitation robots have direct contact with human joints, which presents a serious safety concern. In this paper, a novel design for a series elastic actuator (SEA) is presented for upper limb rehabilitation of sensorimotor dysfunctions. The proposed SEA ensures safety and robust torque control under various disturbances. The proposed SEA is modeled and simulated using MATLAB Simulink to obtain Input/Output driven data. For the proposed system, two modeling approaches, ARMAX and NN, are
A review of upper limb robot assisted therapy techniques and virtual reality applications
Impairments in the sensorimotor system negatively impact the ability of individuals to perform daily activities autonomously. Upper limb rehabilitation for stroke survivors and cerebral palsy (CP) children is essential to enhance independence and quality of life. Robot assisted therapy has been a bright solution in the last two decades to promote the recovery process for neurological disorders patients. Nevertheless, defining the optimum intervention of robot assisted therapy (RAT) in different cases is not clear yet. With this aim, the presented study reviewed the current literature on RAT
Deep Learning Based Kinematic Modeling of 3-RRR Parallel Manipulator
This paper presents a novel low cost design for a 3-RRR Planar Parallel Manipulator (PPM). These manipulators proved their superiority over serial manipulators due to their speed, precision and smaller work space where the work space area is accounted for in the design to ensure that the robot is performing its task in a smooth and simple way without getting into any singularity points. The challenge with PPM is to obtain the kinematic constraint equations of the manipulator due to their complex non-linear behavior. Screw theory is a new approach that is used to compute the direct and inverse
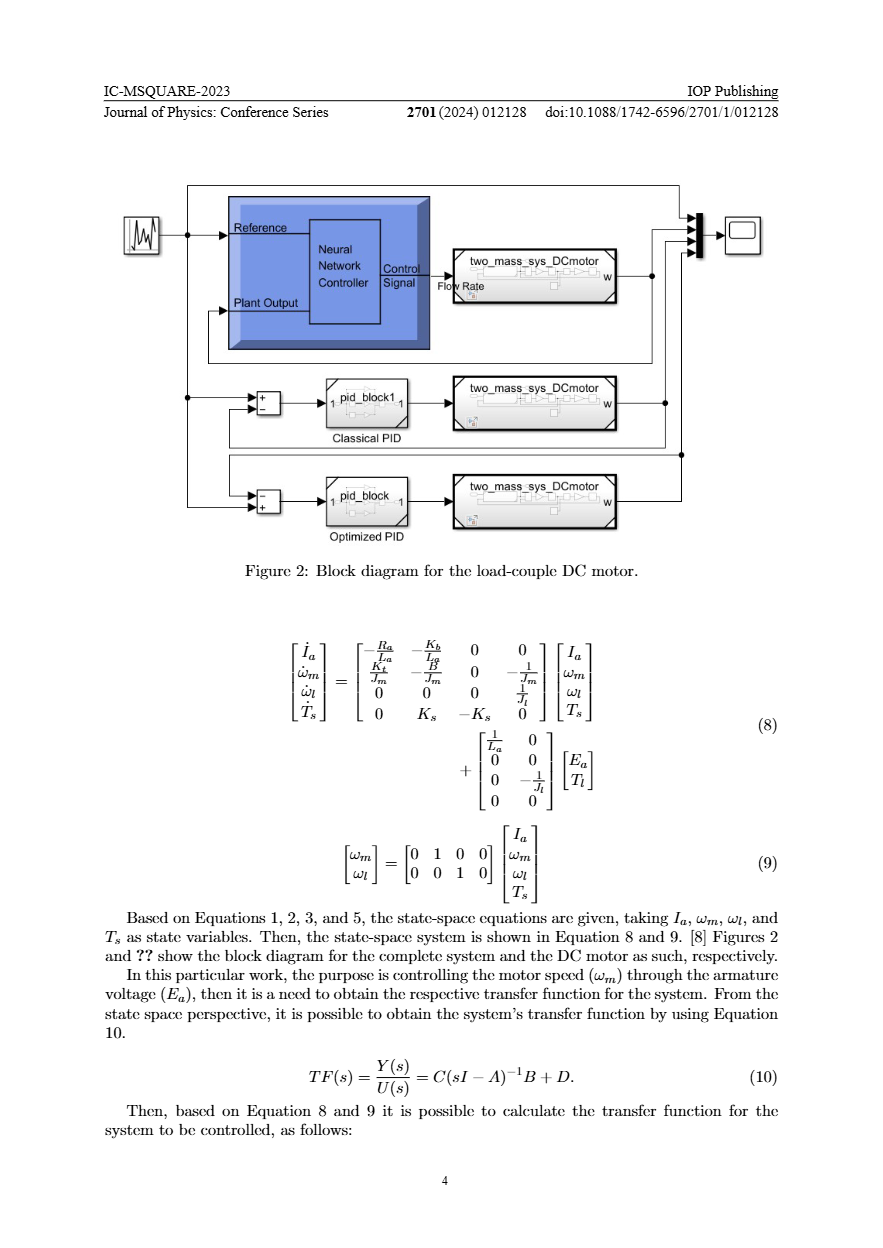
Optimized PID and NN-based Speed Control of a Load-coupled DC Motor
In this work, three control strategies are presented, compared, and discussed, applied on a load-coupled DC motor. The purpose is to control in an optimal way the motor speed in terms of the armature voltage. Two strategies are based on PID control, working on the classical PID controller and the optimized one by using particle swarm optimization (PSO) to tune the PID controller parameters. The other strategy is based on neural networks (NNs) where two NNs are built to model and control the system. Based on the results, all the strategies reach excellent performances, however, in terms of
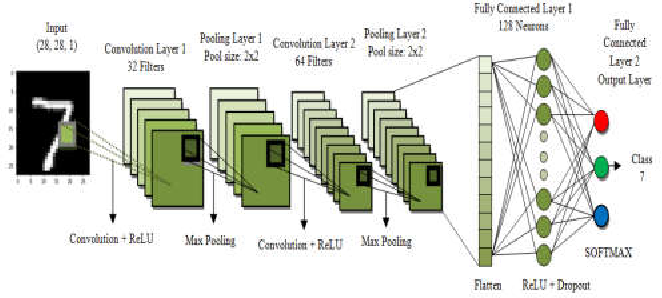
KNN and the CNN for Handwritten Digit Recognition: A comparative study
The automatic identification of handwritten digits by computers or other devices is referred to as "handwritten digit recognition technology,"and it has a wider range of potential applications in the processing of bank bills, financial statements, and postage stamps. This study examines the methods KNN, and CNN, and their use in handwritten digit recognition using samples from the MNIST handwritten digit database. In order to achieve the best results for each method, this work rewrites KNN with Python and CNN with Tensorflow throughout the training phase. The benefits and drawbacks of the two
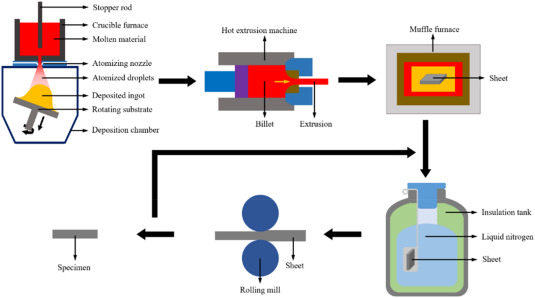
Effect of cryogenic and room-temperature rolling on the microstructural evolution and mechanical behavior of spray-formed 7055 Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy
This study investigates the effects of room-temperature rolling (RTR) and cryogenic rolling (CR) on the microstructure, mechanical properties, and fracture morphology of spray-formed (SF) 7055 Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy, with a focus on the deformation across reductions ranging from 20 % to 80 %. Utilizing SF as the base processing technique, the study aims to overcome challenges associated with the alloy's high content during conventional casting, such as segregation, grain coarsening, and the formation of internal defects. The findings indicate that CR significantly enhances the ductility and refines
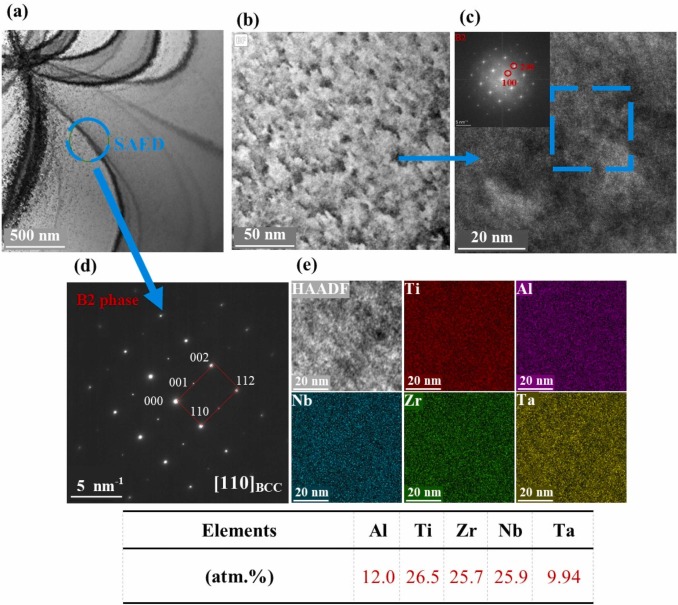
Development of low-density AlNbTaTiZr refractory high-entropy-intermetallic-alloy: Microstructural evolution, mechanical properties, and high-temperature deformation
This study investigates the structural evolution, mechanical properties and high-temperature performance of a novel low-density refractory high entropy intermetallic alloy (RHEIA); Al12Nb25.5Ta8.5Ti27.5Zr26.5. The alloy was prepared by vacuum arc melting, homogenized and subjected to various heat treatments at 600°C, 800°C and 1000°C. The resulting microstructure was revealed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) with attached electron back-scattered diffraction (EBSD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD). The as-received RHEIA showed an initial yield strength of
Analytical solution of thermal effect on unsteady visco-elastic dusty fluid between two parallel plates in the presence of different pressure gradients
Background: Thermal diffusion of dusty fluids has valuable interference in various fields, including waste-water treatment, oil transportation, and power plant pipes. Dusty fluids are used in lots of industrial fields as a result of their improved heat transfer and heat management capabilities. These industries range from renewable energy systems to aerobic plastic sheet extrusion, manufacturing, and rolling and reaching metal sheet cooling. Results: The work embodied in this paper presents the analytical solution performed to predict the effects of thermal diffusion on dusty, viscous
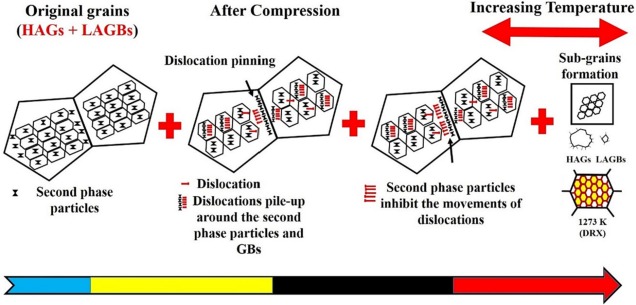
Development and characterization of a low-density TiNbZrAlTa refractory high entropy alloy with enhanced compressive strength and plasticity
A new refractory high entropy alloy (RHEA) is designed by combining refractory elements Nb and Ta with Ti, Zr, and Al, resulting in a (TiNbZr)89(AlTa)11 alloy composition with a low-density of 6.0 g/cm3. The novel RHEA features a BCC matrix with B2 and Zr5Al3 nano precipitates, exhibiting a compressive yield strength of ∼890 MPa and specific yield strength of ∼148.3 MPa g−1 cm3. Remarkably, the alloy demonstrates excellent compressive plasticity of ∼70% at 298 K. As the temperature increases to 873 K, 1073 K, and 1273 K, the yield strength of the RHEA gradually decreases to ∼610 MPa, ∼ 210 MPa